Question: Thank you so much for your help :-) High-Low Method for a Service Company Boston Railroad decided to use the high-low method and operating data


Thank you so much for your help :-)
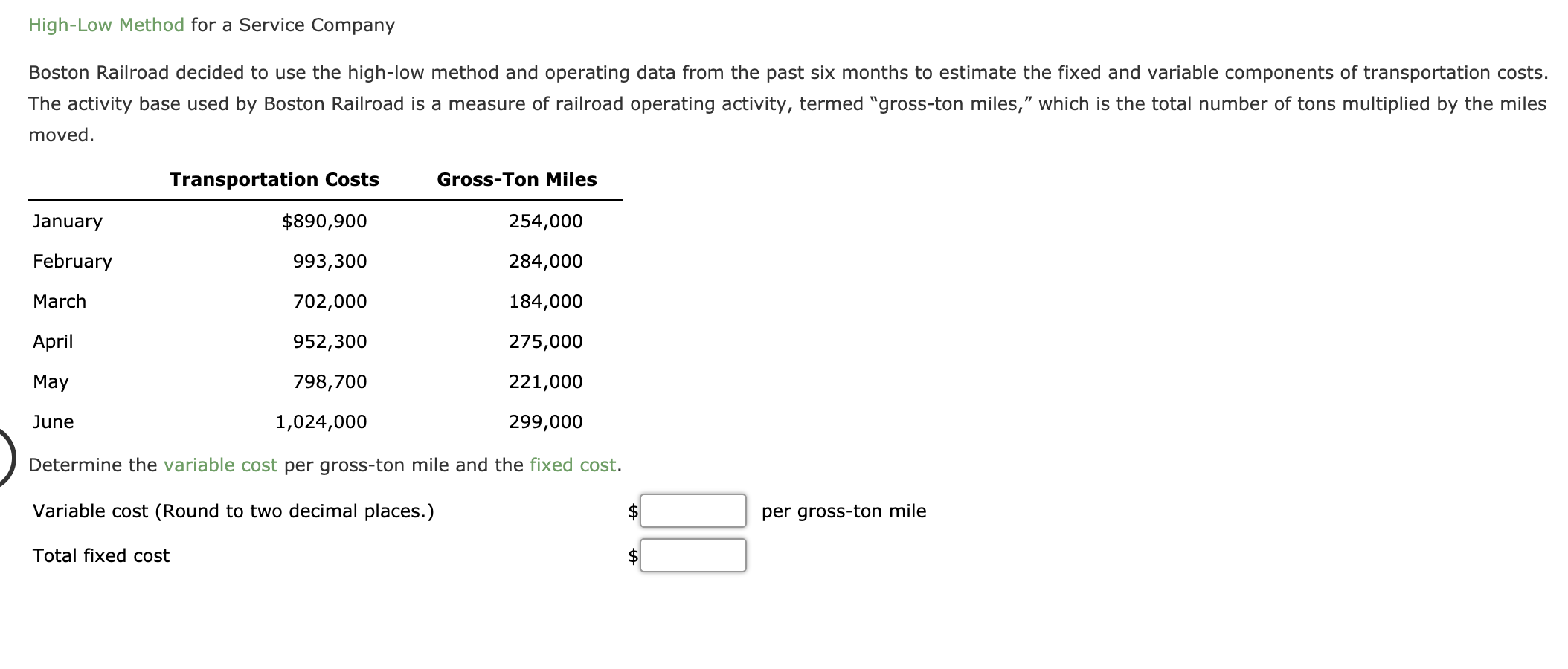
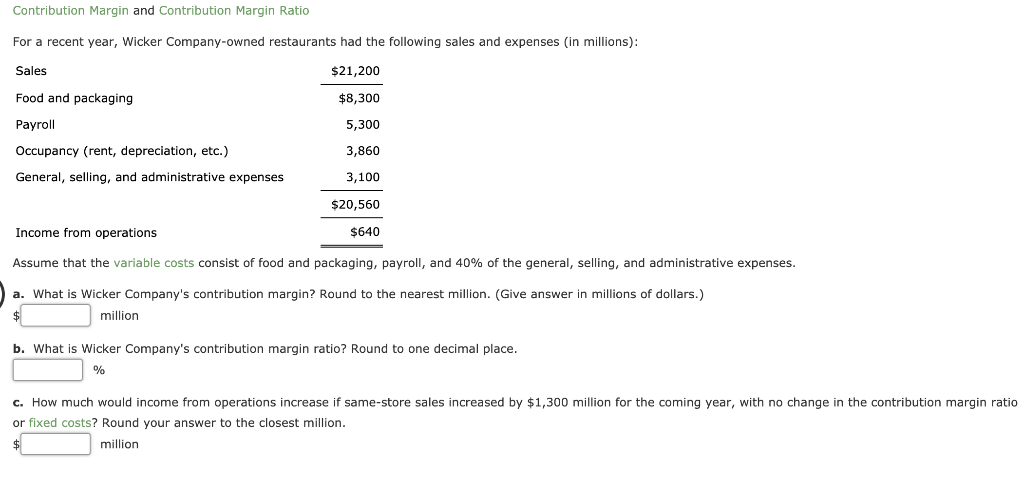
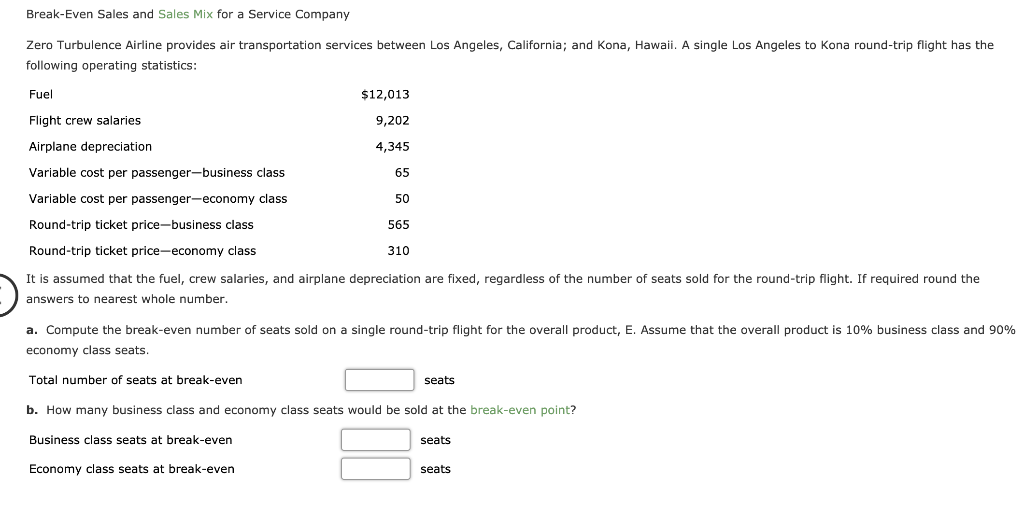
High-Low Method for a Service Company Boston Railroad decided to use the high-low method and operating data from the past six months to estimate the fixed and variable components of transportation costs. The activity base used by Boston Railroad is a measure of railroad operating activity, termed "gross-ton miles," which is the total number of tons multiplied by the miles moved. Transportation Costs Gross-Ton Miles January $890,900 254,000 February 993,300 284,000 March 702,000 184,000 April 952,300 275,000 May 798,700 221,000 June 1,024,000 299,000 Determine the variable cost per gross-ton mile and the fixed cost. Variable cost (Round to two decimal places.) $ per gross-ton mile Total fixed cost Contribution Margin and Contribution Margin Ratio For a recent year, Wicker Company-owned restaurants had the following sales and expenses (in millions): Sales $21,200 $8,300 Food and packaging Payroll 5,300 3,860 Occupancy (rent, depreciation, etc.) General, selling, and administrative expenses 3,100 $20,560 Income from operations $640 Assume that the variable costs consist of food and packaging, payroll, and 40% of the general, selling, and administrative expenses. a. What is Wicker Company's contribution margin? Round to the nearest million. (Give answer in millions of dollars.) million b. What is Wicker Company's contribution margin ratio? Round to one decimal place. % C. How much would income from operations increase if same-store sales increased by $1,300 million for the coming year, with no change in the contribution margin ratio or fixed costs? Round your answer to the closest million. million Break-Even Sales Currently, the unit selling price of a product is $410, the unit variable cost is $340, and the total fixed costs are $1,344,000. A proposal is being evaluated to increase the unit selling price to $460. a. Compute the current break-even sales (units). units b. Compute the anticipated break-even sales (units), assuming that the unit selling price is increased to the proposed $460, and all costs remain constant. units Break-Even Sales and Sales Mix for a Service Company Zero Turbulence Airline provides air transportation services between Los Angeles, California; and Kona, Hawaii. A single Los Angeles to Kona round-trip flight has the following operating statistics: Fuel $12,013 Flight crew salaries 9,202 Airplane depreciation 4,345 65 Variable cost per passenger-business class Variable cost per passenger-economy class Round-trip ticket price-business class 50 565 Round-trip ticket price--economy class 310 It is assumed that the fuel, crew salaries, and airplane depreciation are fixed, regardless of the number of seats sold for the round-trip flight. If required round the answers to nearest whole number. a. Compute the break-even number of seats sold on a single round-trip flight for the overall product, E. Assume that the overall product is 10% business class and 90% economy class seats. Total number of seats at break-even seats b. How many business class and economy class seats would be sold at the break-even point? Business class seats at break-even seats Economy class seats at break-even seats Sales Mix and Break-Even Sales Dragon Sports Inc. manufactures and sells two products, baseball bats and baseball gloves. The fixed costs are $252,800, and the sales mix is 80% bats and 20% gloves. The unit selling price and the unit variable cost for each product are as follows: Products Unit Selling Price Unit Variable Cost Bats $80 $60 Gloves 200 120 a. Compute the break-even sales (units) for both products combined. units b. How many units of each product, baseball bats and baseball gloves, would be sold at break-even point? Baseball bats units Baseball gloves units
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


