Question: The answer should be in MATLAB For certain applications, there may be an advantage from using either Cartesian coordinates (i.e. expressing position relative to the
The answer should be in MATLAB
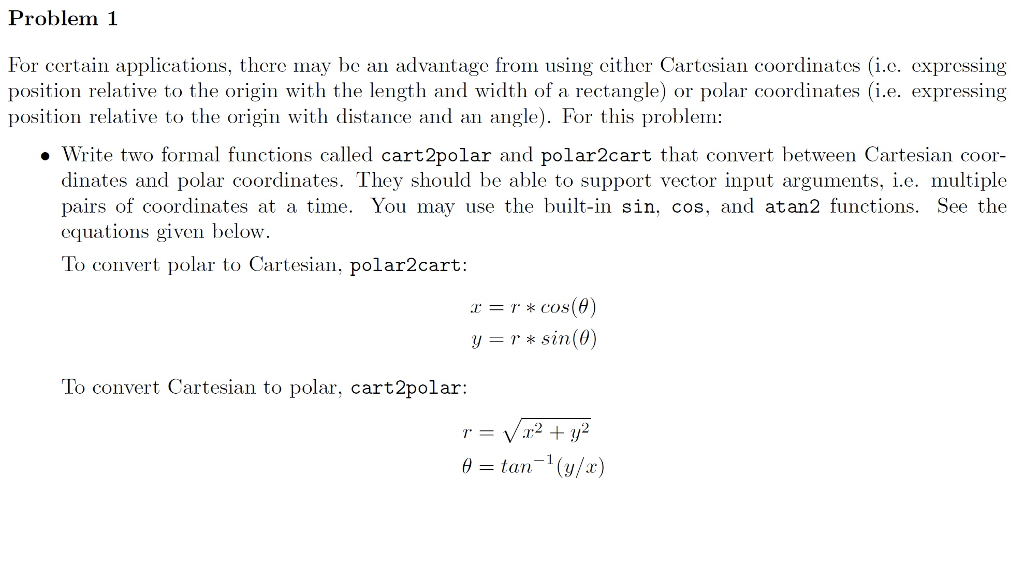
For certain applications, there may be an advantage from using either Cartesian coordinates (i.e. expressing position relative to the origin with the length and width of a rectangle) or polar coordinates (i.e. expressing position relative to the origin with distance and an angle). For this problem: Write two formal functions called cart2polar and polar2cart that convert between Cartesian coordinates and polar coordinates. They should be able to support vector input arguments, i.e. multiple pairs of coordinates at a time. You may use the built-in sin. cos, and atan2 functions. See the equations given below. To convert polar to Cartesian. polar2cart: x = r * cos(theta) y = r * sin(theta) To convert Cartesian to polar, cart2polar: r = Squareroot x^2 + y^2 theta = tan^-1(y/x)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


