Question: The answer to the question is the two equations in the second photo. I am unsure how to get there. The constants are not given

The answer to the question is the two equations in the second photo. I am unsure how to get there.

The constants are not given
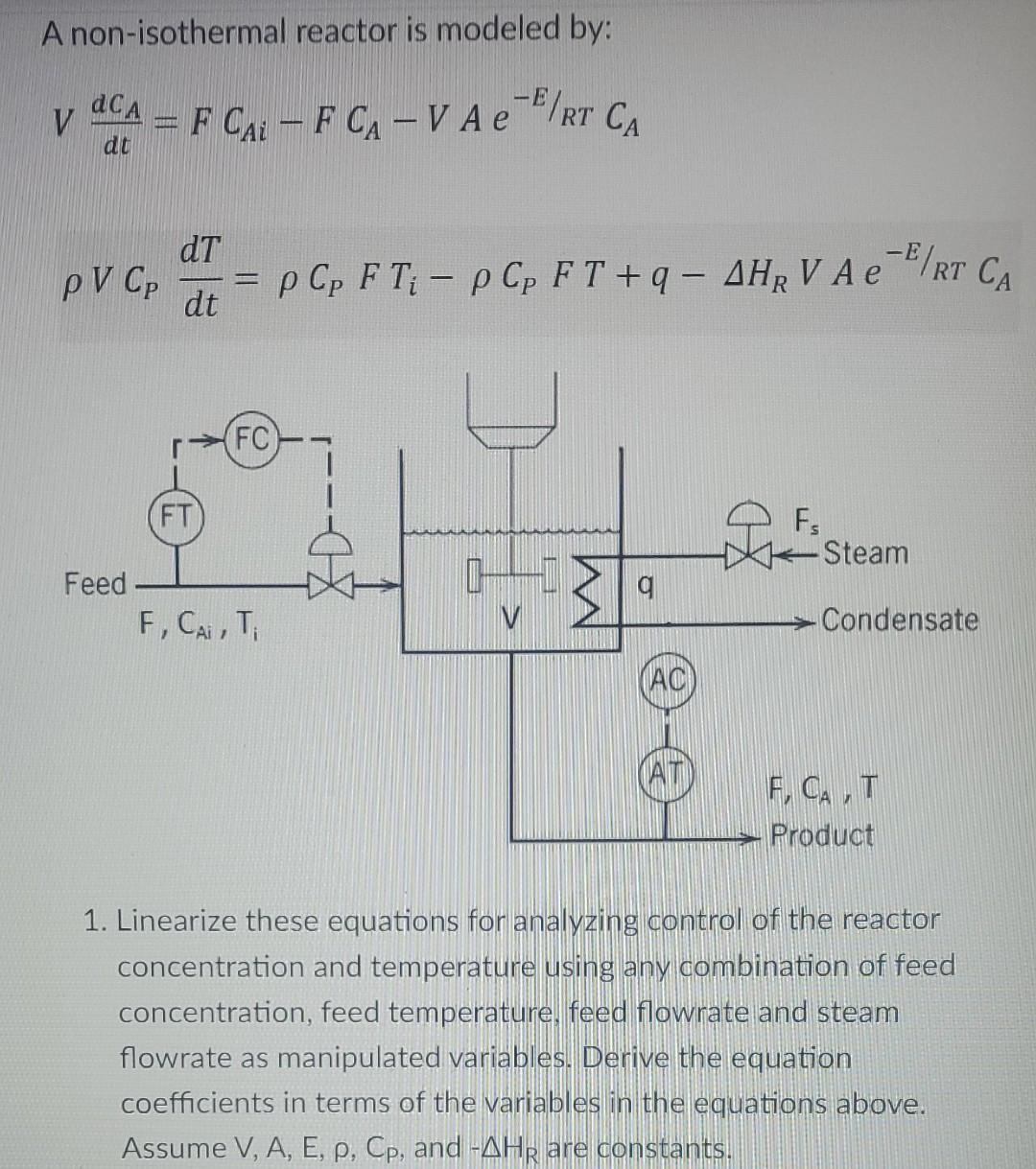
A non-isothermal reactor is modeled by: -E dcA V dt - F Cai - F CA-V Ae RT CA - dT PV Cp dt - p Cp FT; - p Cp FT +9 - AHR V A e-P/RT CA (FC) (FT Fs -Steam Feed F CAT 3 q Condensate (AO F, CAT Product 1. Linearize these equations for analyzing control of the reactor concentration and temperature using any combination of feed concentration, feed temperature, feed flowrate and steam flowrate as manipulated variables. Derive the equation coefficients in terms of the variables in the equations above. Assume V, A, E, p, Cp, and -AHR are constants. dCA 100 = -50CA 0.967 T +4 F + 10 Cai dt dt 830 dt. = -40,000 CA + 1050.25 1 1,245 F +83 T: + 9 2. After substituting in the values of constants and steady state values, the linearized equations are: dCA 100 dt = -50CA - 0.967 T + 4 F + 10 Cai - dT 830 = -40,000 CA + 1050.25 T - 1,245 F +83 T; +9 - dt A non-isothermal reactor is modeled by: -E dcA V dt - F Cai - F CA-V Ae RT CA - dT PV Cp dt - p Cp FT; - p Cp FT +9 - AHR V A e-P/RT CA (FC) (FT Fs -Steam Feed F CAT 3 q Condensate (AO F, CAT Product 1. Linearize these equations for analyzing control of the reactor concentration and temperature using any combination of feed concentration, feed temperature, feed flowrate and steam flowrate as manipulated variables. Derive the equation coefficients in terms of the variables in the equations above. Assume V, A, E, p, Cp, and -AHR are constants. dCA 100 = -50CA 0.967 T +4 F + 10 Cai dt dt 830 dt. = -40,000 CA + 1050.25 1 1,245 F +83 T: + 9 2. After substituting in the values of constants and steady state values, the linearized equations are: dCA 100 dt = -50CA - 0.967 T + 4 F + 10 Cai - dT 830 = -40,000 CA + 1050.25 T - 1,245 F +83 T; +9 - dt
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


