Question: the attached table are the format for the problem root letc/passwd: r,w,x; /usr/bin: r,w,x; /u/roberto: r,w,x; /admin/: r,w,x mike /usr/passwd: r; /usr/bin: r,x roberto /usr/passwd:
 the attached table are the format for the problem
the attached table are the format for the problem
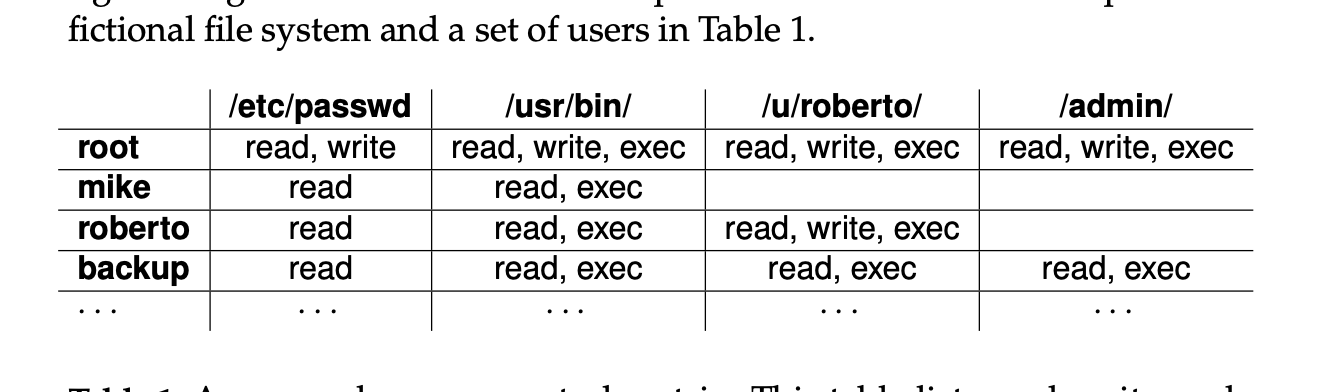
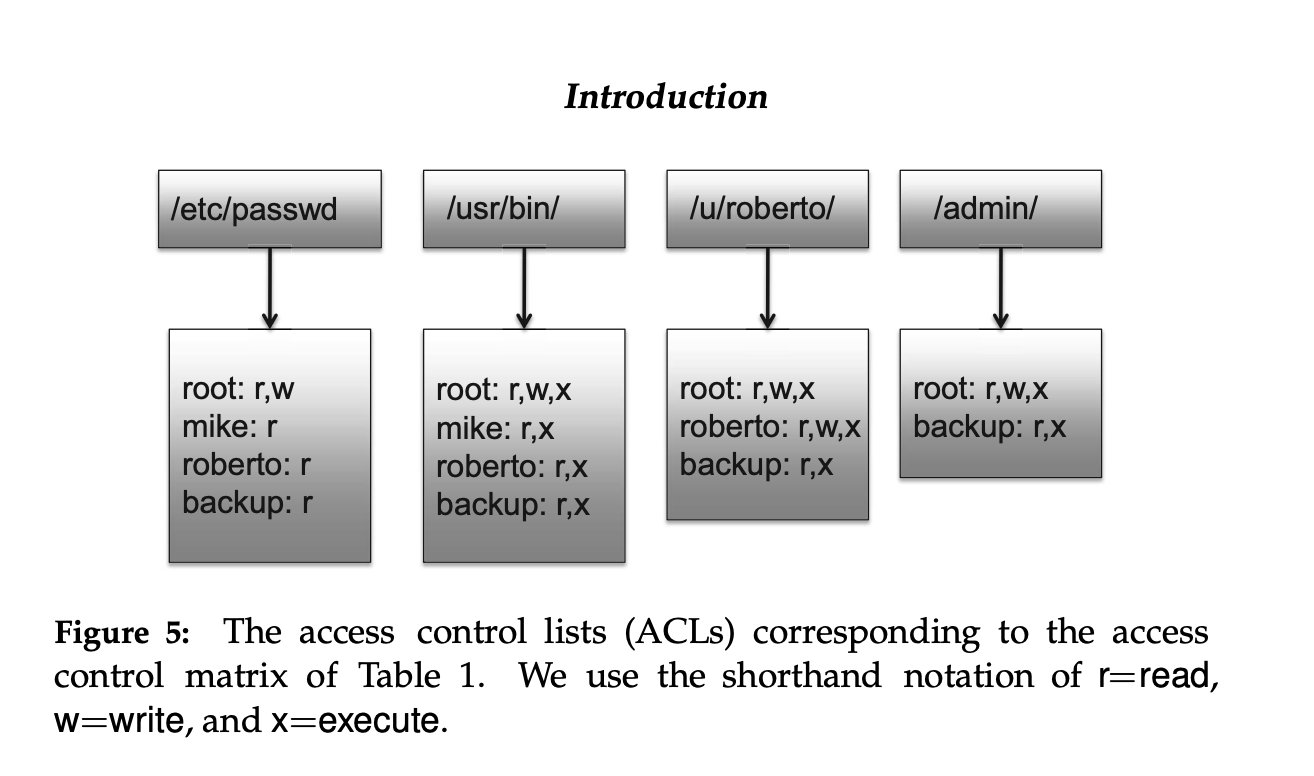
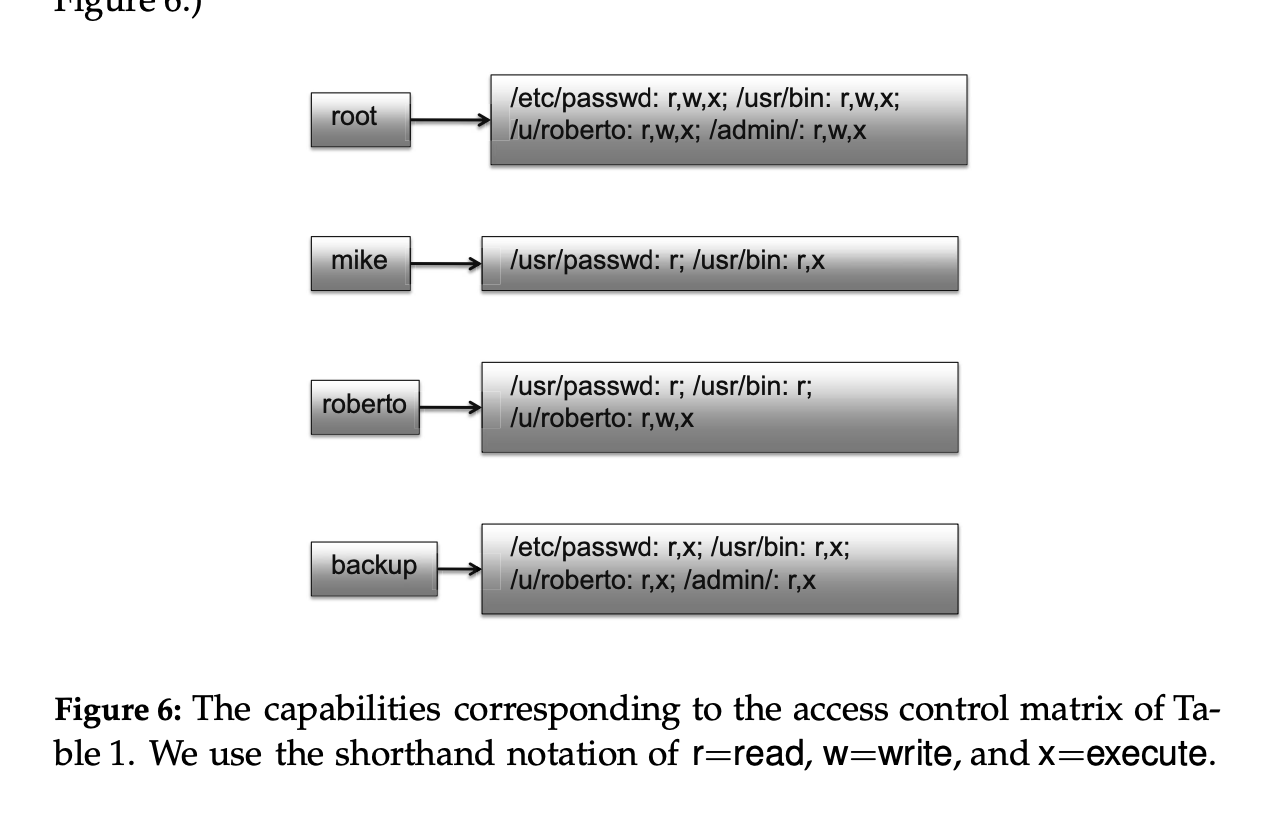
root letc/passwd: r,w,x; /usr/bin: r,w,x; /u/roberto: r,w,x; /admin/: r,w,x mike /usr/passwd: r; /usr/bin: r,x roberto /usr/passwd: r; /usr/bin: r; /u/roberto: r,w,X backup letc/passwd: r,x; /usr/bin: r,x; /u/roberto: r,x; ladmin/: r,x Figure 6: The capabilities corresponding to the access control matrix of Ta- ble 1. We use the shorthand notation of r=read, w=write, and x=execute. Problem 1. Access Control (30 pt., 10 pt. each) Assumption: Privileges: read ("R"), write ("W"), execute ("X") Resources: Image files: tamuc.jpg, jkim.png, csci351.gif Document files: syllabus.doc, lecture.ppt Binary files: a.exe, b.exe, c.exe Access permissions: A has privilege to read all the image files. B has privilege to read and write all the document files. A and C have privilege to read syllabus.doc" A and B have privilege to read and execute a.exe, b.exe". B and C have privilege to read tamuc.jpg. a. Construct the corresponding access control matrix. To answer, use the format in Table 1.1 in the textbook. b. Construct the corresponding access control list. To answer, use the format in Figure 1.5 in the textbook. C. Construct the corresponding capabilities list. To answer, use the format in Figure 1.6 in the textbook. fictional file system and a set of users in Table 1. /u/roberto/ read, write, exec ladmin/ read, write, exec root mike roberto backup letc/passwd read, write read read read /usr/bin/ read, write, exec read, exec read, exec read, exec read, write, exec read, exec read, exec M Introduction letc/passwd /usr/bin/ /u/roberto/ ladmin/ root: r,w mike: r roberto: r backup: r root: r,W,X backup: r,x root: r,w,X mike: r,x roberto: r,x backup: r,x root: r,w,X roberto: r,w,x backup: r,x Figure 5: The access control lists (ACLs) corresponding to the access control matrix of Table 1. We use the shorthand notation of r=read, w=write, and x=execute. root letc/passwd: r,w,x; /usr/bin: r,w,x; /u/roberto: r,w,x; /admin/: r,w,x mike /usr/passwd: r; /usr/bin: r,x roberto /usr/passwd: r; /usr/bin: r; /u/roberto: r,w,X backup letc/passwd: r,x; /usr/bin: r,x; /u/roberto: r,x; ladmin/: r,x Figure 6: The capabilities corresponding to the access control matrix of Ta- ble 1. We use the shorthand notation of r=read, w=write, and x=execute. Problem 1. Access Control (30 pt., 10 pt. each) Assumption: Privileges: read ("R"), write ("W"), execute ("X") Resources: Image files: tamuc.jpg, jkim.png, csci351.gif Document files: syllabus.doc, lecture.ppt Binary files: a.exe, b.exe, c.exe Access permissions: A has privilege to read all the image files. B has privilege to read and write all the document files. A and C have privilege to read syllabus.doc" A and B have privilege to read and execute a.exe, b.exe". B and C have privilege to read tamuc.jpg. a. Construct the corresponding access control matrix. To answer, use the format in Table 1.1 in the textbook. b. Construct the corresponding access control list. To answer, use the format in Figure 1.5 in the textbook. C. Construct the corresponding capabilities list. To answer, use the format in Figure 1.6 in the textbook. fictional file system and a set of users in Table 1. /u/roberto/ read, write, exec ladmin/ read, write, exec root mike roberto backup letc/passwd read, write read read read /usr/bin/ read, write, exec read, exec read, exec read, exec read, write, exec read, exec read, exec M Introduction letc/passwd /usr/bin/ /u/roberto/ ladmin/ root: r,w mike: r roberto: r backup: r root: r,W,X backup: r,x root: r,w,X mike: r,x roberto: r,x backup: r,x root: r,w,X roberto: r,w,x backup: r,x Figure 5: The access control lists (ACLs) corresponding to the access control matrix of Table 1. We use the shorthand notation of r=read, w=write, and x=execute
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


