Question: The basic laws of Boolean algebra are listed below. Note that inverse can be expressed any of three ways: with a bar on top, with
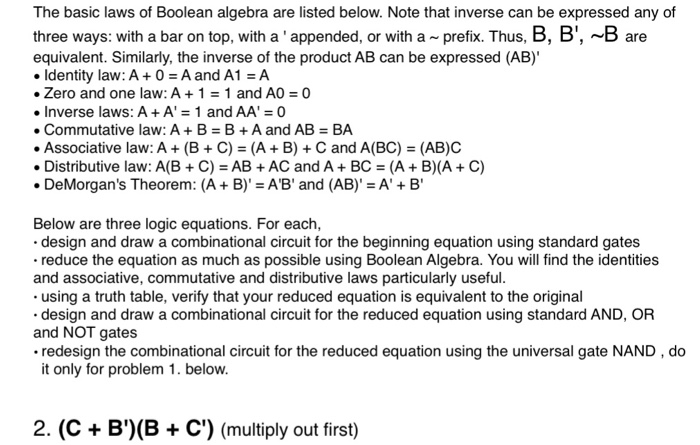
The basic laws of Boolean algebra are listed below. Note that inverse can be expressed any of three ways: with a bar on top, with a 'appended, or with a ~ prefix. Thus, B, B', ~B are equivalent. Similarly, the inverse of the product AB can be expressed (AB) . Identity law: A + 0 = A and A1 = A Zero and one law: A + 1 1 and A0 = 0 . Inverse laws: A + A' = 1 and AA' = 0 Commutative law: A + B = B + A and AB = BA Associative law: A + (B + C) = (A + B) + C and A(BC) = (AB)C Distributive law: A(B + C) = AB + AC and A + BC = (A + B)(A + C) . DeMorgan's Theorem: (A + B-AB' and (AB)' = A' + B' Below are three logic equations. For each, design and draw a combinational circuit for the beginning equation using standard gates reduce the equation as much as possible using Boolean Algebra. You will find the identities and associative, commutative and distributive laws particularly useful .using a truth table, verify that your reduced equation is equivalent to the original design and draw a combinational circuit for the reduced equation using standard AND, OR and NOT gates redesign the combinational circuit for the reduced equation using the universal gate NAND , do it only for problem 1. below 2. (CB') (B C') (multiply out first)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


