Question: (The bold section is the part I'm really stuck on but please complete entire problem) Grenoble Enterprises had sales of $50,000 in March and $60,000
(The bold section is the part I'm really stuck on but please complete entire problem)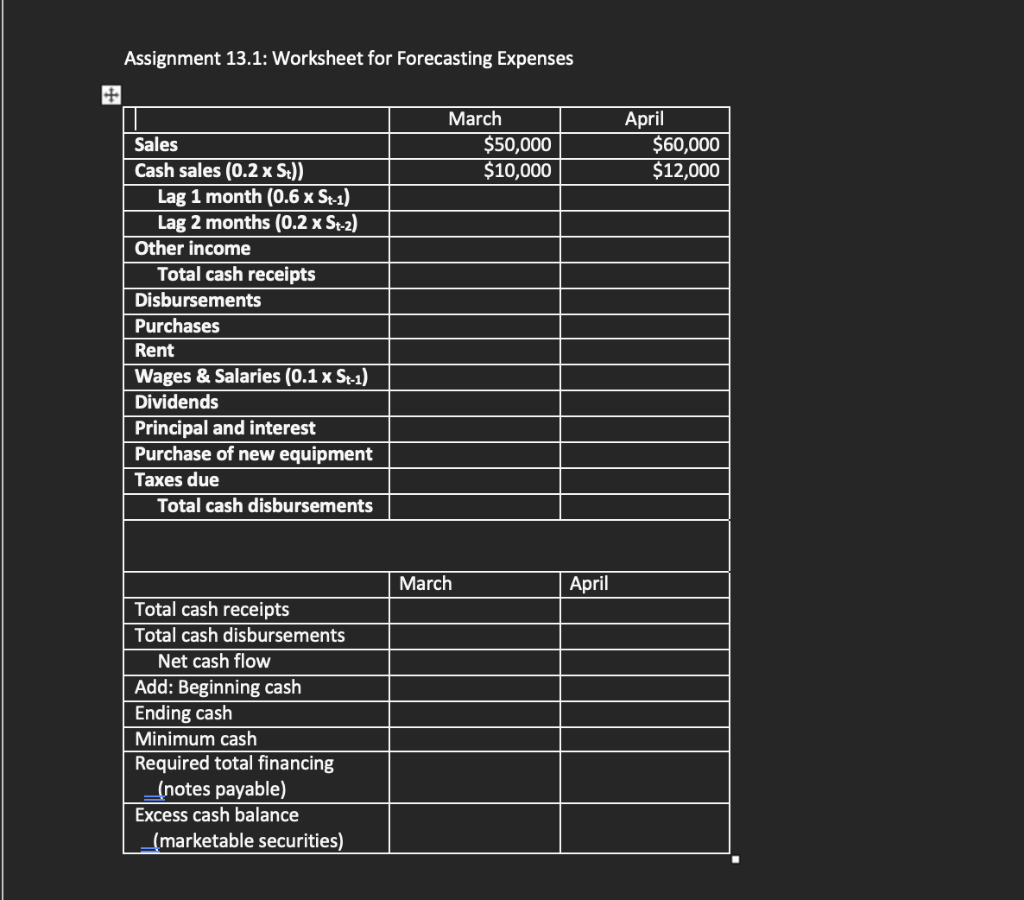
Grenoble Enterprises had sales of $50,000 in March and $60,000 in April. Assume Grenoble used a variety of different revenue and cost forecast approaches and as a result, sales for May, June, and July are forecasted to be $70,000, $80,000, and $100,000, respectively. The firm has a cash balance of $5,000 on May 1 and wishes to maintain a minimum cash balance of$5,000. Given the following data, prepare a schedule showing the forecasted cash receipts(cash revenues) and cash disbursements(cash expenses) for May, June, and July. The firm makes 20% of sales for cash, 60% are collected in the next month, and the remaining 20% are collected in the second month following sale.
- Add the estimated expenses to the exercises to arrive at net cash for each forecasted month.
- Any net cash above the minimum cash requirement will be invested into marketable securities.
- Any net cash less than $5,000 will be borrowed from a bank in the form of a notes payable (promissory note). Ignore interest related to the notes.
- Set up a document/schedule disclosing all cash receipts less cash payments to arrive at net cash for each of the forecasted months.
- The firm receives other income of $2,000 per month.
- The firms actual or expected purchases, all made for cash, are $50,000, $70,000, and $80,000 for the months of May through July, respectively.
- Rent is $3,000 per month.
- Wages and salaries are 10% of the previous months sales.
- Cash dividends of $3,000 will be paid in June.
- Payment of principal and interest of $4,000 is due in June.
- A cash purchase of equipment costing $6,000 is scheduled in July.
- Taxes of $6,000 are due in June.
Assignment 13.1: Worksheet for Forecasting Expenses + March $50,000 $10,000 April $60,000 $12,000 Sales Cash sales (0.2 x St)) Lag 1 month (0.6 x St-1) Lag 2 months (0.2 x St-2) Other income Total cash receipts Disbursements Purchases Rent Wages & Salaries (0.1 x St-1) Dividends Principal and interest Purchase of new equipment Taxes due Total cash disbursements March April Total cash receipts Total cash disbursements Net cash flow Add: Beginning cash Ending cash Minimum cash Required total financing (notes payable) Excess cash balance (marketable securities) Assignment 13.1: Worksheet for Forecasting Expenses + March $50,000 $10,000 April $60,000 $12,000 Sales Cash sales (0.2 x St)) Lag 1 month (0.6 x St-1) Lag 2 months (0.2 x St-2) Other income Total cash receipts Disbursements Purchases Rent Wages & Salaries (0.1 x St-1) Dividends Principal and interest Purchase of new equipment Taxes due Total cash disbursements March April Total cash receipts Total cash disbursements Net cash flow Add: Beginning cash Ending cash Minimum cash Required total financing (notes payable) Excess cash balance (marketable securities)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


