Question: The C/C++ program below demonstrates how to create new child processes in a UNIX operating system. Base the answers of the next three questions
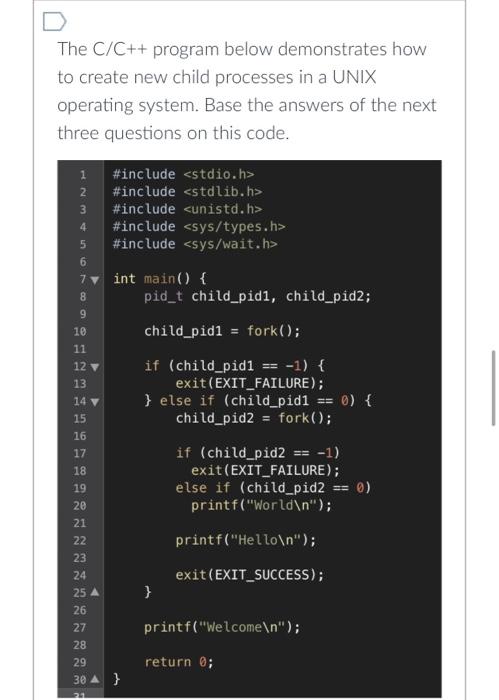
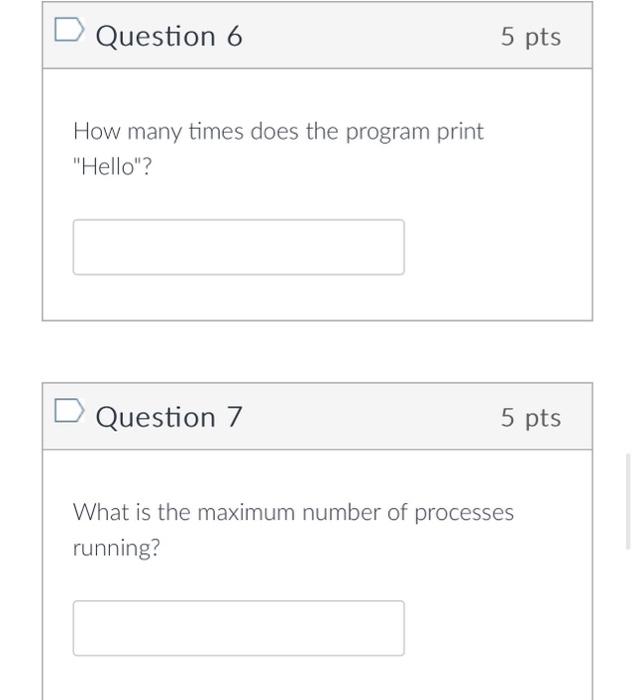

The C/C++ program below demonstrates how to create new child processes in a UNIX operating system. Base the answers of the next three questions on this code. 1 #include 2 #include #include 4 #include #include 3 56 7 int main() { 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 V 15 16 17 18 19 20 Z2224127828 23 25 A 26 29 30 } 21 pid_t child_pidl, child_pid2; child_pid1= fork(); if (child_pidl == -1) { exit(EXIT_FAILURE); else if (child_pidl == 0) { child_pid2 = fork(); } if (child_pid2 == -1) exit (EXIT_FAILURE); else if (child_pid2 == 0) printf("World "); printf("Hello "); exit (EXIT_SUCCESS); printf("Welcome "); return 0; Question 6 How many times does the program print "Hello"? Question 7 5 pts 5 pts What is the maximum number of processes running? What statement about signals is correct? A signal generated by the occurrence of a particular event is delivered to and handled by the kernel. Threads can be cancelled immediately with asynchronous cancellation if thread has cancellation enabled. The default handler can never be overridden by a user-defined signal handler. kill(pid t pid, int signal) is a UNIX function that tells the kernel how to handle a signal generated by a specific process.
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (143 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Lets analyze the provided CC code to answer the questions include include include include include int main pidt childpid1 childpid2 childpid1 fork if ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


