Question: The code for the selection algorithm is written in python. As pointed out the code is incorrect because there may be multiple elements equal to
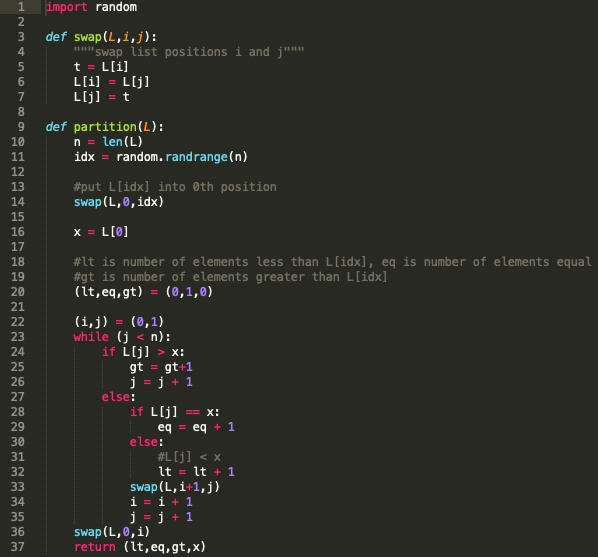
The code for the selection algorithm is written in python. As pointed out the code is incorrect because there may be multiple elements equal to the one we are partitioning around (x) and while the counts lt, eq, gt are computed correctly, the x may not necessarily occur where they should. Give an example where this incorrect code may lead to incorrect result. Also, change the code (dont change the function names etc.) to fix this. Your modified code should also run the partitioning in linear time.
import random
def swap(L,i,j):
"""swap list positions i and j"""
t = L[i]
L[i] = L[j]
L[j] = t
def partition(L):
n = len(L)
idx = random.randrange(n)
#put L[idx] into 0th position
swap(L,0,idx)
x = L[0]
#lt is number of elements less than L[idx], eq is number of elements equal
#gt is number of elements greater than L[idx]
(lt,eq,gt) = (0,1,0)
(i,j) = (0,1)
while (j
if L[j] > x:
gt = gt+1
j = j + 1
else:
if L[j] == x:
eq = eq + 1
else:
#L[j]
lt = lt + 1
swap(L,i+1,j)
i = i + 1
j = j + 1
swap(L,0,i)
return (lt,eq,gt,x)
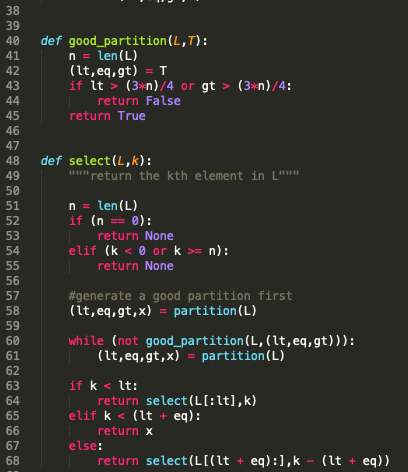
def good_partition(L,T):
n = len(L)
(lt, eq, gt) = T
if lt > (3*n)/4 or gt > (3*n)/4:
return False
return True
def select(L,k):
"""return the kth element in L"""
n = len(L)
if (n == 0):
return None
elif (k = n):
return None
#generate a good partition first
(lt,eq,gt,x) = partition(L)
while (not good_partition(L,(lt,eq,gt))):
(lt,eq,gt,x) = partition(L)
if k
return select(L[:lt],k)
elif k
return x
else:
return select(L[(lt + eq):],k - (lt + eq))
import random def swap(L,i,j): swap list positions i and jo t = L[i] L[i] = L[j] L[j] = t def partition(L): n = len(L) idx = random. randrange(n) #put L[idx] into @th position swap(L, 0, idx) x = L[0] #It is number of elements less than L[idx), eq is number of elements equal #gt is number of elements greater than L[idx] (lt, eq,gt) = (0,1,0) (i,j) = (0,1) while (j
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


