Question: The code which is given is following(java): import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class BTNode{ private int nodeid; private int data; private int levelNum; private BTNode leftChildPtr;


The code which is given is following(java):
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class BTNode{
private int nodeid;
private int data;
private int levelNum;
private BTNode leftChildPtr;
private BTNode rightChildPtr;
public BTNode(){}
public void setNodeId(int id){
nodeid = id;
}
public int getNodeId(){
return nodeid;
}
public void setData(int d){
data = d;
}
public int getData(){
return data;
}
public void setLevelNum(int level){
levelNum = level;
}
public int getLevelNum(){
return levelNum;
}
public void setLeftChildPtr(BTNode ptr){
leftChildPtr = ptr;
}
public void setRightChildPtr(BTNode ptr){
rightChildPtr = ptr;
}
public BTNode getLeftChildPtr(){
return leftChildPtr;
}
public BTNode getRightChildPtr(){
return rightChildPtr;
}
public int getLeftChildID(){
if (leftChildPtr == null)
return -1;
return leftChildPtr.getNodeId();
}
public int getRightChildID(){
if (rightChildPtr == null)
return -1;
return rightChildPtr.getNodeId();
}
}
class BinaryTree{
private int numNodes;
private BTNode arrayOfBTNodes[];
public BinaryTree(int n){
numNodes = n;
arrayOfBTNodes = new BTNode[numNodes];
for (int id = 0; id
arrayOfBTNodes[id] = new BTNode();
arrayOfBTNodes[id].setNodeId(id);
arrayOfBTNodes[id].setLevelNum(-1);
arrayOfBTNodes[id].setLeftChildPtr(null);
arrayOfBTNodes[id].setRightChildPtr(null);
}
}
public void setLeftLink(int upstreamNodeID, int downstreamNodeID){
arrayOfBTNodes[upstreamNodeID].setLeftChildPtr(arrayOfBTNodes[downstreamNodeID]);
}
public void setRightLink(int upstreamNodeID, int downstreamNodeID){
arrayOfBTNodes[upstreamNodeID].setRightChildPtr(arrayOfBTNodes[downstreamNodeID]);
}
public void printLeafNodes(){
for (int id = 0; id
if (arrayOfBTNodes[id].getLeftChildPtr() == null && arrayOfBTNodes[id].getRightChildPtr() == null)
System.out.print(id + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public boolean isLeafNode(int nodeid){
if (arrayOfBTNodes[nodeid].getLeftChildPtr() == null && arrayOfBTNodes[nodeid].getRightChildPtr() == null)
return true;
return false;
}
public int getNodeHeight(int nodeid){
if (nodeid == -1)
return -1;
if (isLeafNode(nodeid) )
return 0;
int leftChildID = arrayOfBTNodes[nodeid].getLeftChildID(); // -1 if not exist
int rightChildID = arrayOfBTNodes[nodeid].getRightChildID(); // -1 if not exist
int heightOfLeftChild = getNodeHeight(leftChildID);
int heightOfRightChild = getNodeHeight(rightChildID);
return Math.max(heightOfLeftChild, heightOfRightChild) + 1;
}
public int getTreeHeight(){
return getNodeHeight(0);
}
public boolean checkHeightBalancedTree(){
// Implement this function to determine whether for each internal node, the absolute difference
// between the height of the left child and the right child is at most 1. If it is true for each internal ndoe, the
// binary tree is said to be height-balanced. Even if one internal node is not height-balanced, the
// whole binary tree is considered not height-balanced.
}
}
class BinaryTreeImplementation{
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String filename;
System.out.print("Enter a file name: ");
filename = input.next();
int numNodes;
System.out.print("Enter number of nodes: ");
numNodes = input.nextInt();
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree(numNodes);
FileReader fr = new FileReader(filename);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String line = null;
while ( (line = br.readLine()) != null){
StringTokenizer stk = new StringTokenizer(line, ",: ");
int upstreamNodeID = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
int childIndex = 0;
while (stk.hasMoreTokens()){
int downstreamNodeID = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
if (childIndex == 0 && downstreamNodeID != -1)
binaryTree.setLeftLink(upstreamNodeID, downstreamNodeID);
if (childIndex == 1 && downstreamNodeID != -1)
binaryTree.setRightLink(upstreamNodeID, downstreamNodeID);
childIndex++;
}
}
System.out.println("Tree Height: " + binaryTree.getTreeHeight() );
if (binaryTree.checkHeightBalancedTree())
System.out.println("The tree is height balanced..");
else
System.out.println("The tree is not height balanced..");
}
catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
}The code which is given is following(java):
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class BTNode{
private int nodeid;
private int data;
private int levelNum;
private BTNode leftChildPtr;
private BTNode rightChildPtr;
public BTNode(){}
public void setNodeId(int id){
nodeid = id;
}
public int getNodeId(){
return nodeid;
}
public void setData(int d){
data = d;
}
public int getData(){
return data;
}
public void setLevelNum(int level){
levelNum = level;
}
public int getLevelNum(){
return levelNum;
}
public void setLeftChildPtr(BTNode ptr){
leftChildPtr = ptr;
}
public void setRightChildPtr(BTNode ptr){
rightChildPtr = ptr;
}
public BTNode getLeftChildPtr(){
return leftChildPtr;
}
public BTNode getRightChildPtr(){
return rightChildPtr;
}
public int getLeftChildID(){
if (leftChildPtr == null)
return -1;
return leftChildPtr.getNodeId();
}
public int getRightChildID(){
if (rightChildPtr == null)
return -1;
return rightChildPtr.getNodeId();
}
}
class BinaryTree{
private int numNodes;
private BTNode arrayOfBTNodes[];
public BinaryTree(int n){
numNodes = n;
arrayOfBTNodes = new BTNode[numNodes];
for (int id = 0; id
arrayOfBTNodes[id] = new BTNode();
arrayOfBTNodes[id].setNodeId(id);
arrayOfBTNodes[id].setLevelNum(-1);
arrayOfBTNodes[id].setLeftChildPtr(null);
arrayOfBTNodes[id].setRightChildPtr(null);
}
}
public void setLeftLink(int upstreamNodeID, int downstreamNodeID){
arrayOfBTNodes[upstreamNodeID].setLeftChildPtr(arrayOfBTNodes[downstreamNodeID]);
}
public void setRightLink(int upstreamNodeID, int downstreamNodeID){
arrayOfBTNodes[upstreamNodeID].setRightChildPtr(arrayOfBTNodes[downstreamNodeID]);
}
public void printLeafNodes(){
for (int id = 0; id
if (arrayOfBTNodes[id].getLeftChildPtr() == null && arrayOfBTNodes[id].getRightChildPtr() == null)
System.out.print(id + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public boolean isLeafNode(int nodeid){
if (arrayOfBTNodes[nodeid].getLeftChildPtr() == null && arrayOfBTNodes[nodeid].getRightChildPtr() == null)
return true;
return false;
}
public int getNodeHeight(int nodeid){
if (nodeid == -1)
return -1;
if (isLeafNode(nodeid) )
return 0;
int leftChildID = arrayOfBTNodes[nodeid].getLeftChildID(); // -1 if not exist
int rightChildID = arrayOfBTNodes[nodeid].getRightChildID(); // -1 if not exist
int heightOfLeftChild = getNodeHeight(leftChildID);
int heightOfRightChild = getNodeHeight(rightChildID);
return Math.max(heightOfLeftChild, heightOfRightChild) + 1;
}
public int getTreeHeight(){
return getNodeHeight(0);
}
public boolean checkHeightBalancedTree(){
// Implement this function to determine whether for each internal node, the absolute difference
// between the height of the left child and the right child is at most 1. If it is true for each internal ndoe, the
// binary tree is said to be height-balanced. Even if one internal node is not height-balanced, the
// whole binary tree is considered not height-balanced.
}
}
class BinaryTreeImplementation{
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String filename;
System.out.print("Enter a file name: ");
filename = input.next();
int numNodes;
System.out.print("Enter number of nodes: ");
numNodes = input.nextInt();
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree(numNodes);
FileReader fr = new FileReader(filename);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String line = null;
while ( (line = br.readLine()) != null){
StringTokenizer stk = new StringTokenizer(line, ",: ");
int upstreamNodeID = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
int childIndex = 0;
while (stk.hasMoreTokens()){
int downstreamNodeID = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
if (childIndex == 0 && downstreamNodeID != -1)
binaryTree.setLeftLink(upstreamNodeID, downstreamNodeID);
if (childIndex == 1 && downstreamNodeID != -1)
binaryTree.setRightLink(upstreamNodeID, downstreamNodeID);
childIndex++;
}
}
System.out.println("Tree Height: " + binaryTree.getTreeHeight() );
if (binaryTree.checkHeightBalancedTree())
System.out.println("The tree is height balanced..");
else
System.out.println("The tree is not height balanced..");
}
catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
}
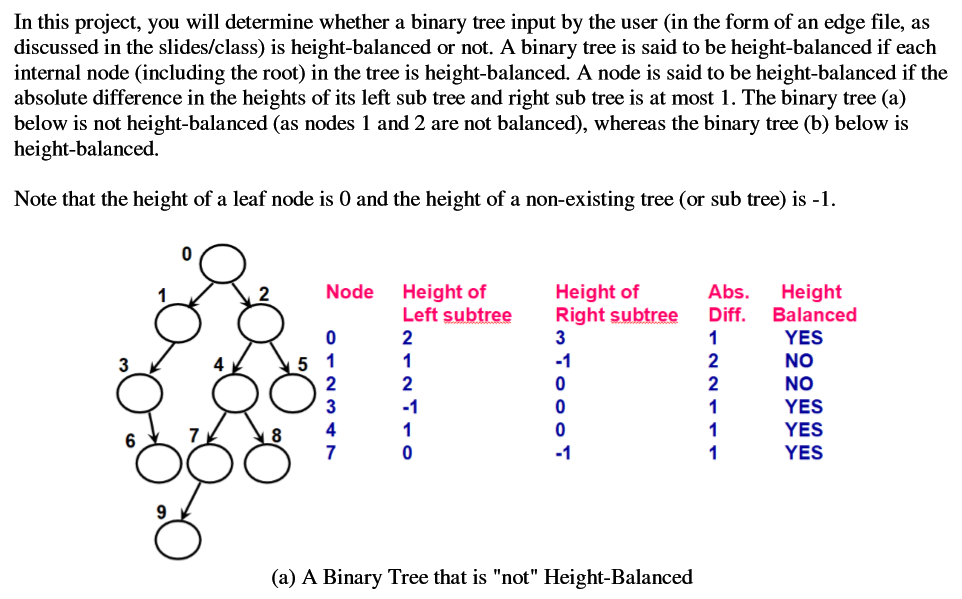
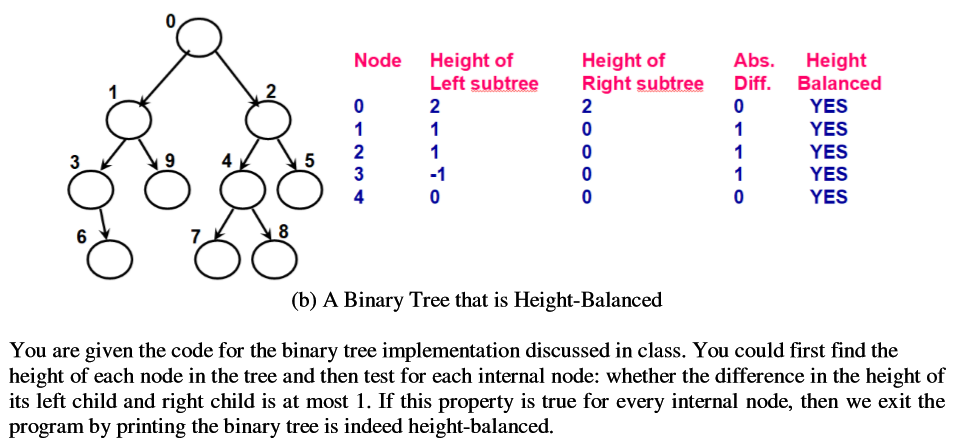
In this project, you will determine whether a binary tree input by the user (in the form of an edge file, a:s discussed in the slides/class) is height-balanced or not. A binary tree is said to be height-balanced if each internal node (including the root) in the tree is height-balanced. A node is said to be height-balanced if the absolute difference in the heights of its left sub tree and right sub tree is at most 1. The binary tree (a) below is not height-balanced (as nodes 1 and 2 are not balanced), whereas the binary tree (b) below is height-balanced. Note that the height of a leaf node is 0 and the height of a non-existing tree (or sub tree) is -1. Node Height of Height of Abs. Height Left subtree Right subtree Diff. Balanced 2 YES No No YES YES YES 2 2 3 2 2 4 (a) A Binary Tree that is "not" Height-Balanced
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


