Question: The feasible set of a linear programming problem and a mixed-integer problem is given in Figure 1. The feasible region depicts the area within
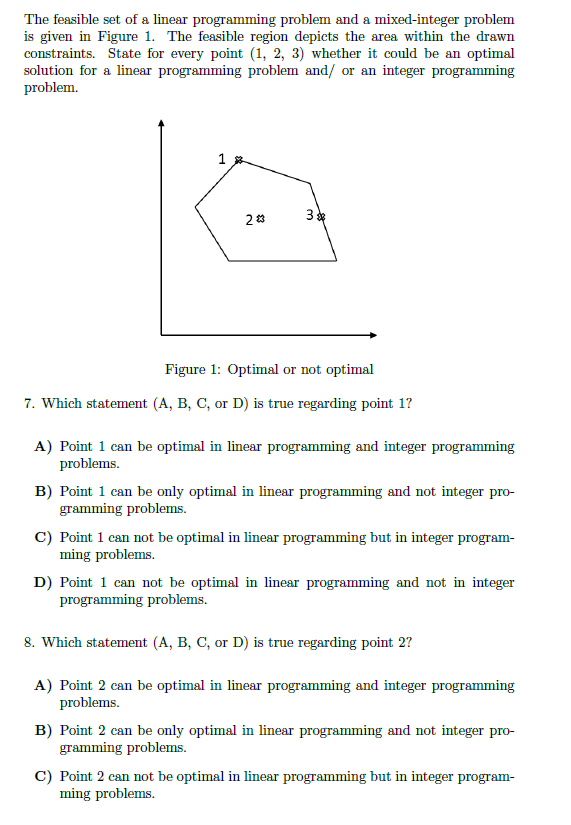

The feasible set of a linear programming problem and a mixed-integer problem is given in Figure 1. The feasible region depicts the area within the drawn constraints. State for every point (1, 2, 3) whether it could be an optimal solution for a linear programming problem and/ or an integer programming problem. 23 3* m Figure 1: Optimal or not optimal 7. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 1? A) Point 1 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 1 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 1 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 1 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems. 8. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 2? A) Point 2 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 2 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 2 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 2 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems. 9. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 37 A) Point 3 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 3 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 3 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 3 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems. The feasible set of a linear programming problem and a mixed-integer problem is given in Figure 1. The feasible region depicts the area within the drawn constraints. State for every point (1, 2, 3) whether it could be an optimal solution for a linear programming problem and/ or an integer programming problem. 23 3* m Figure 1: Optimal or not optimal 7. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 1? A) Point 1 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 1 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 1 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 1 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems. 8. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 2? A) Point 2 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 2 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 2 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 2 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems. 9. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 37 A) Point 3 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 3 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 3 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 3 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems.
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The skin friction coefficient Cf for a laminar boundary ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


