Question: The following algorithm PoT takes as input an integer n 0 and outputs the decimal expansion of 2n. (For two n-digit numbers A, B, you
The following algorithm PoT takes as input an integer n 0 and outputs the decimal expansion of 2n. (For two n-digit numbers A, B, you can assume that multiplyKS(A, B) returns their product in O(n^1.58) time and Add(A, B) returns their sum in O(n) time.)
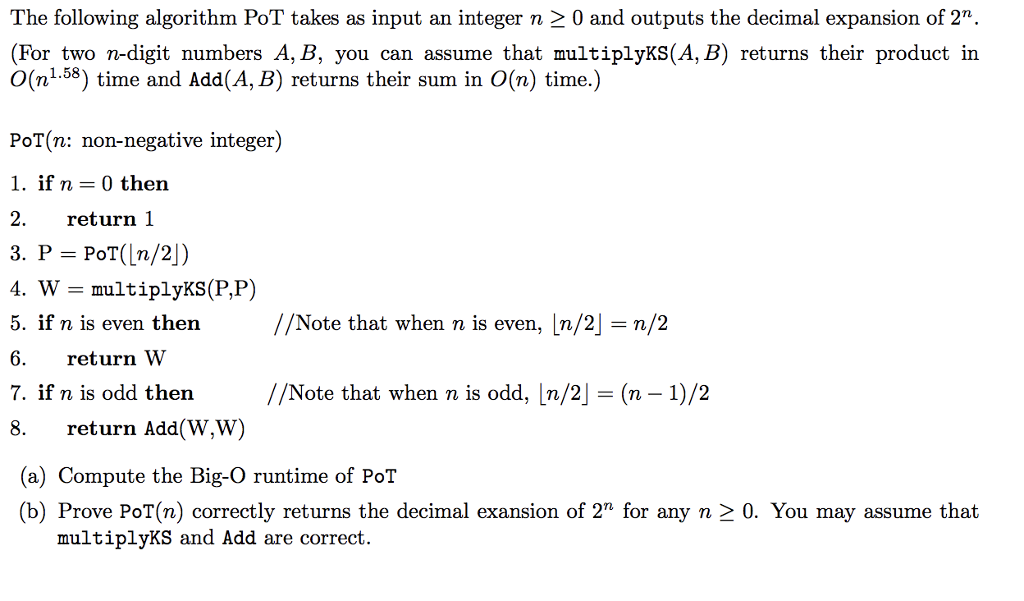
The following algorithm PoT takes as input an integer n 2 0 and outputs the decimal expansion of 2" (For two n-digit numbers A, B, you can assume that multiplyKS(A, B) returns their product in n58) ie and Add(A, B) returns their sum in O(n) time.) PoT(n: non-negative integer) 1, if n=0 then 2. return 1 3. P PoT(n/2|) 4. multiplyKS(P,P) 5. f n is even then //Note that when n is even, In/2] = n/2 6. return W 7 if n is odd then //Note that when n is odd, Ln/2= (n-1)/2 8. return Add(W,W) (a) Compute the Big-O runtime of PoT (b) Prove PoT(n) correctly returns the decimal exansion of 2" for any n 2 0. You may assume that multiplyKS and Add are correct
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


