Question: The following data are from a completely randomized design. Sample mean Sample variance Treatment A B 162 142 126 142 156 122 165 124

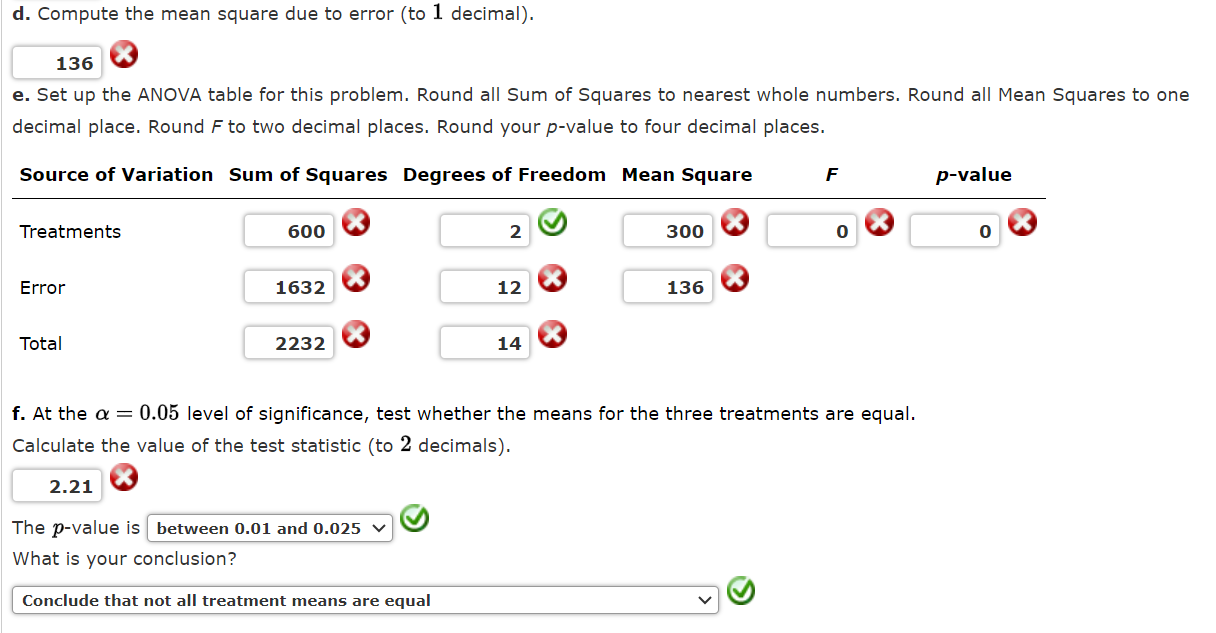
The following data are from a completely randomized design. Sample mean Sample variance Treatment A B 162 142 126 142 156 122 165 124 138 145 142 140 148 136 150 174 152 128 156 142 134 164.4 131.2 110.4 a. Compute the sum of squares between treatments (to the nearest whole number). 600 b. Compute the mean square between treatments (to 1 decimal). 300 c. Compute the sum of squares due to error (to the nearest whole number). 1632 Hint(s) Check My Work d. Compute the mean square due to error (to 1 decimal). 136 e. Set up the ANOVA table for this problem. Round all Sum of Squares to nearest whole numbers. Round all Mean Squares to one decimal place. Round F to two decimal places. Round your p-value to four decimal places. Source of Variation Sum of Squares Degrees of Freedom Mean Square Treatments 600 2 300 Error 1632 12 136 Total 2232 14 F p-value 0 0 f. At the = 0.05 level of significance, test whether the means for the three treatments are equal. Calculate the value of the test statistic (to 2 decimals). 2.21 The p-value is between 0.01 and 0.025 What is your conclusion? Conclude that not all treatment means are equal
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


