Question: The following data are from a completely randomized design. Treatment Treatment Treatment A 32 44 B 33 30 43 36 30 44 35 26
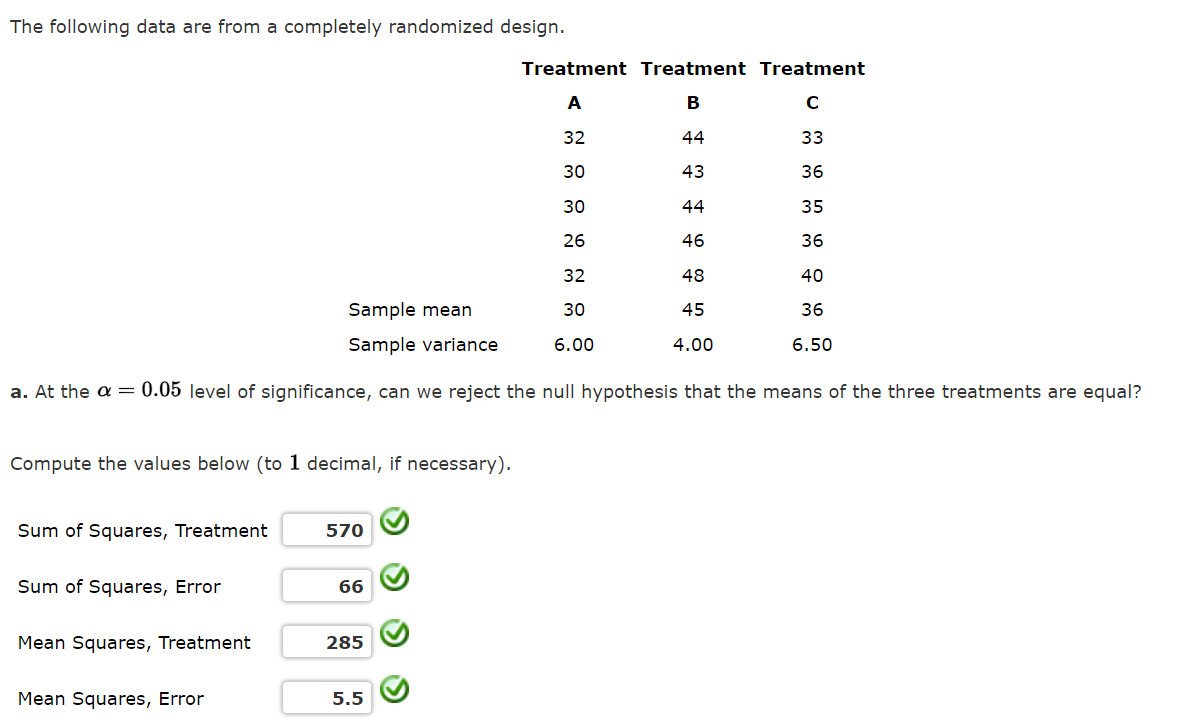
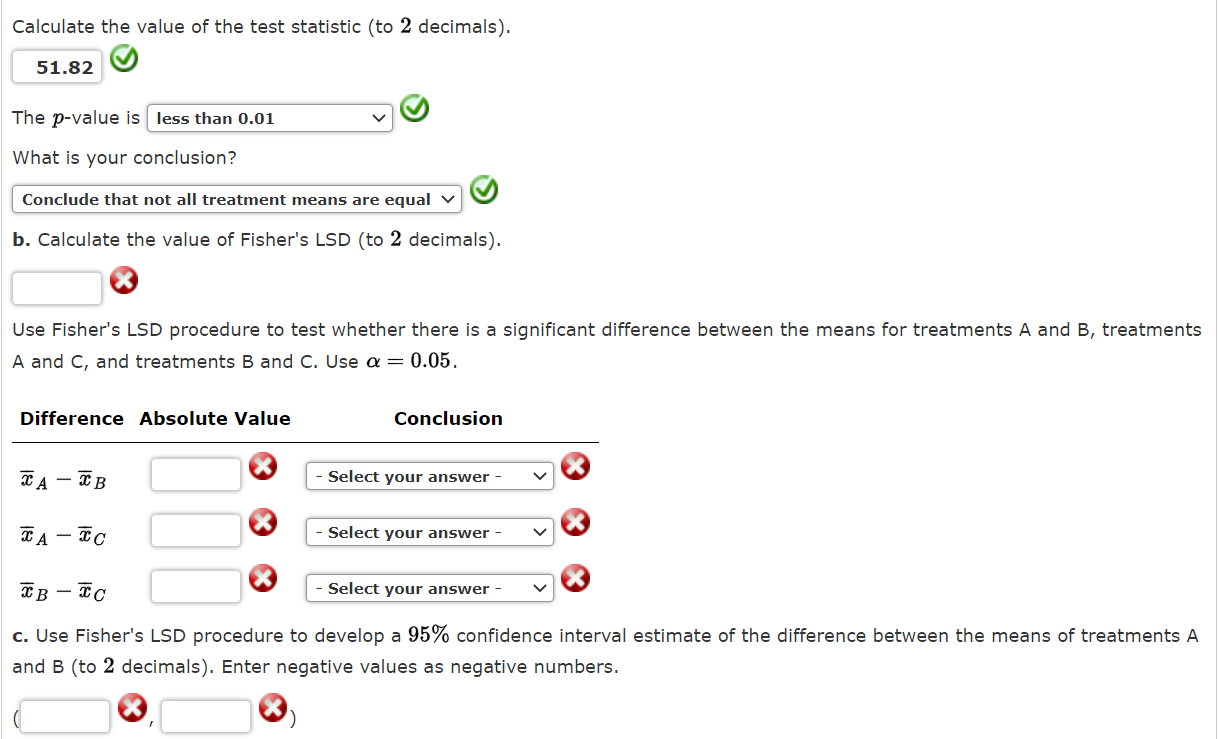
The following data are from a completely randomized design. Treatment Treatment Treatment A 32 44 B 33 30 43 36 30 44 35 26 46 36 32 48 40 Sample mean 30 45 36 Sample variance 6.00 4.00 6.50 a. At the = 0.05 level of significance, can we reject the null hypothesis that the means of the three treatments are equal? Compute the values below (to 1 decimal, if necessary). Sum of Squares, Treatment 570 Sum of Squares, Error 66 Mean Squares, Treatment 285 Mean Squares, Error 5.5 Calculate the value of the test statistic (to 2 decimals). 51.82 The p-value is less than 0.01 What is your conclusion? Conclude that not all treatment means are equal b. Calculate the value of Fisher's LSD (to 2 decimals). Use Fisher's LSD procedure to test whether there is a significant difference between the means for treatments A and B, treatments A and C, and treatments B and C. Use a = 0.05. Difference Absolute Value Conclusion A-C T B-C Select your answer - - Select your answer - - Select your answer - c. Use Fisher's LSD procedure to develop a 95% confidence interval estimate of the difference between the means of treatments A and B (to 2 decimals). Enter negative values as negative numbers.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


