Question: The fourth project involves modifying the semantic analyzer for the attached compiler by adding checks for semantic errors. The static semantic rules of this language
The fourth project involves modifying the semantic analyzer for the attached compiler by adding checks for semantic errors. The static semantic rules of this language are the following: Variables and parameter names have local scope. The scope rules require that all names be declared and prohibit duplicate names within the same scope. The type correspondence rules are as follows:
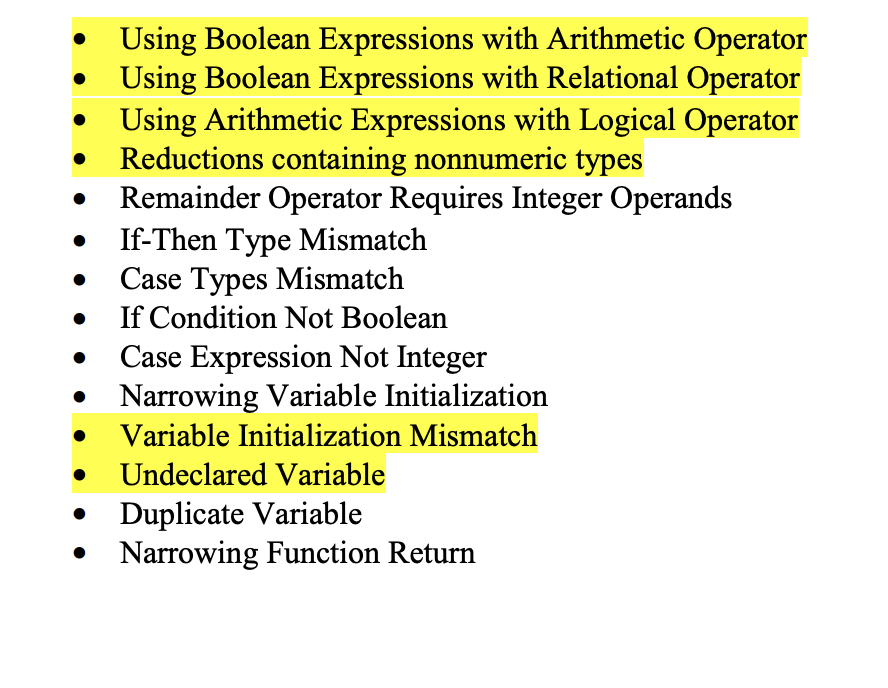
- Boolean expressions cannot be used with arithmetic or relational operators.
- Arithmetic expressions cannot be used with logical operators.
- Reductions can only contain numeric types.
- Only integer operands can be used with the remainder operator.
- The two statements in an if statement must match in type. No coercion is performed.
- All the statements in a case statement must match in type. No coercion is performed.
- The type of the if expression must be Boolean.
- The type of the case expression must be Integer
- A narrowing variable initialization or function return occurs when a real value is being forced into integer. Widening is permitted.
- Boolean types cannot be mixed with numeric types in variable initializations or function returns.
Type coercion from an integer to a real type is performed within arithmetic expressions. You must make the following semantic checks. Those highlighted in yellow are already performed by the code that you have been provided, although you are must make minor modifications to account for the addition of real types and the need to perform type coercion and to handle the additional arithmetic and logical operators.
This project requires modification to the bison input file, so that it defines the additional semantic checks necessary to produce these errors and addition of functions to the library of type checking functions already provided in types.cc. You must also make some modifications to the functions provided. You need to add a check to the checkAssignment function for mismatched types in the case that Boolean and numeric types are mixed. You need to also add code to the checkArithmetic function to coerce integers to reals when the types are mixed and the error message must be modified to indicate that numeric rather than only integer types are permitted
The provided code includes a template class Symbols that defines the symbol table. It already includes a check for undeclared identifiers. You need to add a check for duplicate identifiers. Like the lexical and syntax errors, the compiler should display the semantic errors in the compilation listing, after the line in which they occur. An example of compilation listing output containing semantic errors is shown below:

listing.cc
// This file contains the bodies of the functions that produces the compilation
// listing
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include "listing.h"
static int lineNumber;
static string error = "";
static int totalErrors = 0;
static void displayErrors();
void firstLine()
{
lineNumber = 1;
printf(" %4d ",lineNumber);
}
void nextLine()
{
displayErrors();
lineNumber++;
printf("%4d ",lineNumber);
}
int lastLine()
{
printf(" ");
displayErrors();
printf(" ");
return totalErrors;
}
void appendError(ErrorCategories errorCategory, string message)
{
string messages[] = { "Lexical Error, Invalid Character ", "",
"Semantic Error, ", "Semantic Error, Duplicate Identifier: ",
"Semantic Error, Undeclared " };
error = messages[errorCategory] + message;
totalErrors++;
}
void displayErrors()
{
if (error != "")
printf("%s ", error.c_str());
error = "";
}
listing.h
// This file contains the function prototypes for the functions that produce the
// compilation listing
enum ErrorCategories {LEXICAL, SYNTAX, GENERAL_SEMANTIC, DUPLICATE_IDENTIFIER,
UNDECLARED};
void firstLine();
void nextLine();
int lastLine();
void appendError(ErrorCategories errorCategory, string message);
parser.y
%{
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include "types.h"
#include "listing.h"
#include "symbols.h"
int yylex();
void yyerror(const char* message);
Symbols
%}
%error-verbose
%union
{
CharPtr iden;
Types type;
}
%token
%token
%token ADDOP MULOP RELOP ANDOP
%token BEGIN_ BOOLEAN END ENDREDUCE FUNCTION INTEGER IS REDUCE RETURNS
%type
factor primary
%%
function:
function_header optional_variable body ;
function_header:
FUNCTION IDENTIFIER RETURNS type ';';
optional_variable:
variable |
;
variable:
IDENTIFIER ':' type IS statement_
{checkAssignment($3, $5, "Variable Initialization");
symbols.insert($1, $3);} ;
type:
INTEGER {$$ = INT_TYPE;} |
BOOLEAN {$$ = BOOL_TYPE;} ;
body:
BEGIN_ statement_ END ';' ;
statement_:
statement ';' |
error ';' {$$ = MISMATCH;} ;
statement:
expression |
REDUCE operator reductions ENDREDUCE {$$ = $3;} ;
operator:
ADDOP |
MULOP ;
reductions:
reductions statement_ {$$ = checkArithmetic($1, $2);} |
{$$ = INT_TYPE;} ;
expression:
expression ANDOP relation {$$ = checkLogical($1, $3);} |
relation ;
relation:
relation RELOP term {$$ = checkRelational($1, $3);}|
term ;
term:
term ADDOP factor {$$ = checkArithmetic($1, $3);} |
factor ;
factor:
factor MULOP primary {$$ = checkArithmetic($1, $3);} |
primary ;
primary:
'(' expression ')' {$$ = $2;} |
INT_LITERAL |
IDENTIFIER {if (!symbols.find($1, $$)) appendError(UNDECLARED, $1);} ;
%%
void yyerror(const char* message)
{
appendError(SYNTAX, message);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
firstLine();
yyparse();
lastLine();
return 0;
}
scanner.I
/* This file contains flex input file */
%{
#include
using namespace std;
#include "types.h"
#include "listing.h"
#include "tokens.h"
%}
%option noyywrap
ws [ \t ]+
comment \-\-.*
line [ ]
id [A-Za-z][A-Za-z0-9]*
digit [0-9]
int {digit}+
punc [\(\),:;]
%%
{ws} { ECHO; }
{comment} { ECHO; nextLine();}
{line} { ECHO; nextLine();}
"
"+" { ECHO; return(ADDOP); }
"*" { ECHO; return(MULOP); }
begin { ECHO; return(BEGIN_); }
boolean { ECHO; return(BOOLEAN); }
end { ECHO; return(END); }
endreduce { ECHO; return(ENDREDUCE); }
function { ECHO; return(FUNCTION); }
integer { ECHO; return(INTEGER); }
is { ECHO; return(IS); }
reduce { ECHO; return(REDUCE); }
returns { ECHO; return(RETURNS); }
and { ECHO; return(ANDOP); }
{id} { ECHO; yylval.iden = (CharPtr)malloc(yyleng + 1); strcpy(yylval.iden, yytext); return(IDENTIFIER);}
{int} { ECHO; yylval.type = INT_TYPE; return(INT_LITERAL); }
{punc} { ECHO; return(yytext[0]); }
. { ECHO; appendError(LEXICAL, yytext); }
%%
symbols.h
template typename T>
class Symbols
{
public:
void insert(char* lexeme, T entry);
bool find(char* lexeme, T& entry);
private:
map
};
template typename T>
void Symbols
{
string name(lexeme);
symbols[name] = entry;
}
template typename T>
bool Symbols
{
string name(lexeme);
typedef typename map
Iterator iterator = symbols.find(name);
bool found = iterator != symbols.end();
if (found)
entry = iterator->second;
return found;
}
types.cc
// This file contains the bodies of the type checking functions
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include "types.h"
#include "listing.h"
void checkAssignment(Types lValue, Types rValue, string message)
{
if (lValue != MISMATCH && rValue != MISMATCH && lValue != rValue)
appendError(GENERAL_SEMANTIC, "Type Mismatch on " + message);
}
Types checkArithmetic(Types left, Types right)
{
if (left == MISMATCH || right == MISMATCH)
return MISMATCH;
if (left == BOOL_TYPE || right == BOOL_TYPE)
{
appendError(GENERAL_SEMANTIC, "Integer Type Required");
return MISMATCH;
}
return INT_TYPE;
}
Types checkLogical(Types left, Types right)
{
if (left == MISMATCH || right == MISMATCH)
return MISMATCH;
if (left != BOOL_TYPE || right != BOOL_TYPE)
{
appendError(GENERAL_SEMANTIC, "Boolean Type Required");
return MISMATCH;
}
return BOOL_TYPE;
return MISMATCH;
}
Types checkRelational(Types left, Types right)
{
if (checkArithmetic(left, right) == MISMATCH)
return MISMATCH;
return BOOL_TYPE;
}
types.h
// This file contains type definitions and the function
// prototypes for the type checking functions
typedef char* CharPtr;
enum Types {MISMATCH, INT_TYPE, BOOL_TYPE};
void checkAssignment(Types lValue, Types rValue, string message);
Types checkArithmetic(Types left, Types right);
Types checkLogical(Types left, Types right);
Types checkRelational(Types left, Types right);
makefile
compile: scanner.o parser.o listing.o types.o
g++ -o compile scanner.o parser.o listing.o types.o
scanner.o: scanner.c types.h listing.h tokens.h
g++ -c scanner.c
scanner.c: scanner.l
flex scanner.l
mv lex.yy.c scanner.c
parser.o: parser.c types.h listing.h symbols.h
g++ -c parser.c
parser.c tokens.h: parser.y
bison -d -v parser.y
mv parser.tab.c parser.c
mv parser.tab.h tokens.h
listing.o: listing.cc listing.h
g++ -c listing.cc
types.o: types.cc types.h
g++ -c types.cc
Using Boolean Expressions with Arithmetic Operator Using Boolean Expressions with Relational Operator Using Arithmetic Expressions with Logical Operator Reductions containing nonnumeric types Remainder Operator Requires Integer Operands If-Then Type Mismatch Case Types Mismatch If Condition Not Boolean Case Expression Not Integer Narrowing Variable Initialization Variable Initialization Mismatch Undeclared Variable Duplicate Variable Narrowing Function Return 2; 1 Test of Multiple Semantic Errors 2 3 function test a: integer returns integer; 4 b: integer is 5 if a + 5 then 6 7 else 8 5; 9 endif; Semantic Error, If Expression Must Be Boolean 10 c: real is 9.8 - 2 + 8; 11 d: boolean is 7 = f; Semantic Error, Undeclared f 12 begin 13 case bis 14 when 1 => 4.5 + C; 15 when 2 => b; Semantic Error, Case Types Mismatch 16 others => C; 17 endcase; 18 end; Lexical Errors 0 Syntax Errors 0 Semantic Errors 3 Using Boolean Expressions with Arithmetic Operator Using Boolean Expressions with Relational Operator Using Arithmetic Expressions with Logical Operator Reductions containing nonnumeric types Remainder Operator Requires Integer Operands If-Then Type Mismatch Case Types Mismatch If Condition Not Boolean Case Expression Not Integer Narrowing Variable Initialization Variable Initialization Mismatch Undeclared Variable Duplicate Variable Narrowing Function Return 2; 1 Test of Multiple Semantic Errors 2 3 function test a: integer returns integer; 4 b: integer is 5 if a + 5 then 6 7 else 8 5; 9 endif; Semantic Error, If Expression Must Be Boolean 10 c: real is 9.8 - 2 + 8; 11 d: boolean is 7 = f; Semantic Error, Undeclared f 12 begin 13 case bis 14 when 1 => 4.5 + C; 15 when 2 => b; Semantic Error, Case Types Mismatch 16 others => C; 17 endcase; 18 end; Lexical Errors 0 Syntax Errors 0 Semantic Errors 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


