Question: The function e^-x can be approximated by its McLaurin series expansion as follows (note the alternating + and -): Alternatively, note that e^-x = 1/(e^x).
The function e^-x can be approximated by its McLaurin series expansion as follows (note the alternating + and -):
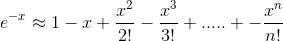
Alternatively, note that e^-x = 1/(e^x). Thus, e^-x can also be apporximated by 1 over the McLaurin series expansion of e^x. That is,
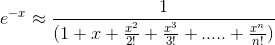
Approximate e^-2 using both approaches above for n = 1,2,...., 6 and compare each approximation to the true value of e^-2 = 0:135335..., using the true relative error. What conclusions can you make about the two approaches
x2 x3 In e 1-x+-----+ ..... +-- 21 31 n
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


