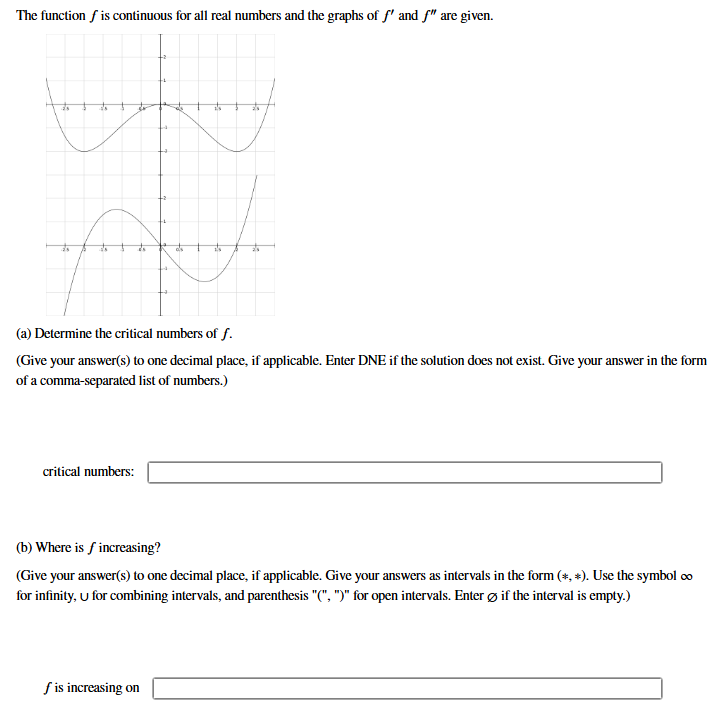
Question: The function f is continuous for all real numbers and the graphs of f ^ ( ' ) and f ^ ( ' ' )
The function f is continuous for all real numbers and the graphs of f and f are given.
a Determine the critical numbers of f
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Enter DNE if the solution does not exist. Give your answer in the form
of a commaseparated list of numbers.
critical numbers
b Where is f increasing?
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Give your answers as intervals in the form Use the symbol oo
for infinity, u for combining intervals, and parenthesis for open intervals. Enter O if the interval is empty.
f is increasing on:
c Where is f decreasing?
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Give your answers as intervals in the form Use the symbol oo
for infinity, U for combining intervals, and parenthesis for open intervals. Enter O if the interval is empty.
f is decreasing on
d At what numbers x if any, does f have a local minimum?
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Enter DNE if the solution does not exist. Give your answer in the form
of a commaseparated list of numbers.
local minimum at the numbers:
e At what numbers x if any, does f have a local maximum?
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Enter DNE if the solution does not exist. Give your answer in the form
of a commaseparated list of numbers.
local maximum at the numbers:
f Where is f concave up
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Give your answers as intervals in the form Use the symbol oo
for infinity, U for combining intervals, and parenthesis for open intervals. Enter O if the interval is empty.
f is concave up on
g Where is f concave down?
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Give your answers as intervals in the form Use the symbol oo
for infinity, U for combining intervals, and parenthesis for open intervals. Enter O if the interval is empty.
f is concave down on
h List the xcoordinates of any inflection points.
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Enter DNE if the solution does not exist. Give your answer in the form
of a commaseparated list of numbers. The function f is continuous for all real numbers and the graphs of fprime and fprime prime are given.
a Determine the critical numbers of f
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Enter DNE if the solution does not exist. Give your answer in the form of a commaseparated list of numbers.
critical numbers
b Where is f increasing?
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Give your answers as intervals in the form Use the symbol infty for infinity, u for combining intervals, and parenthesis for open intervals. Enter varnothing if the interval is empty.
f is increasing on c Where is f decreasing?
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Give your answers as intervals in the form Use the symbol infty for infinity, U for combining intervals, and parenthesis for open intervals. Enter varnothing if the interval is empty.
f is decreasing on
d At what numbers x if any, does f have a local minimum?
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Enter DNE if the solution does not exist. Give your answer in the form of a commaseparated list of numbers.
local minimum at the numbers:
e At what numbers x if any, does f have a local maximum?
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Enter DNE if the solution does not exist. Give your answer in the form of a commaseparated list of numbers.
local maximum at the numbers: f Where is f concave up
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Give your answers as intervals in the form Use the symbol infty for infinity, U for combining intervals, and parenthesis for open intervals. Enter varnothing if the interval is empty.
f is concave up on
g Where is f concave down?
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Give your answers as intervals in the form Use the symbol infty for infinity, U for combining intervals, and parenthesis for open intervals. Enter varnothing if the interval is empty.
f is concave down on
h List the x coordinates of any inflection points.
Give your answers to one decimal place, if applicable. Enter DNE if the solution does not exist. Give your answer in the form of a commaseparated list of numbers.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


