Question: The Implementation Phase During the implementation, a major scope change was formally authorized and performed. The change was the expansion of the power units in

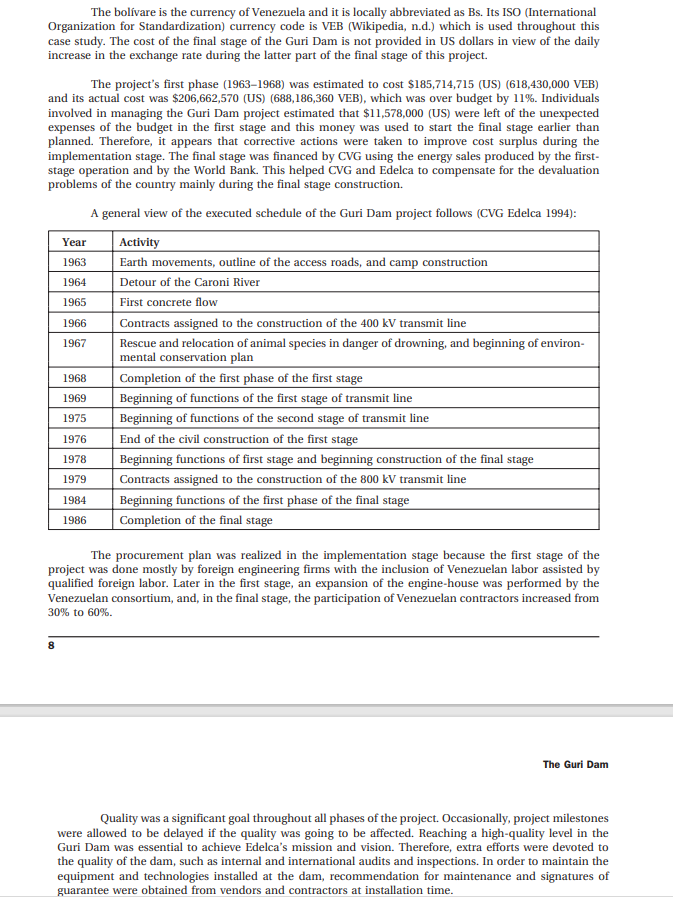
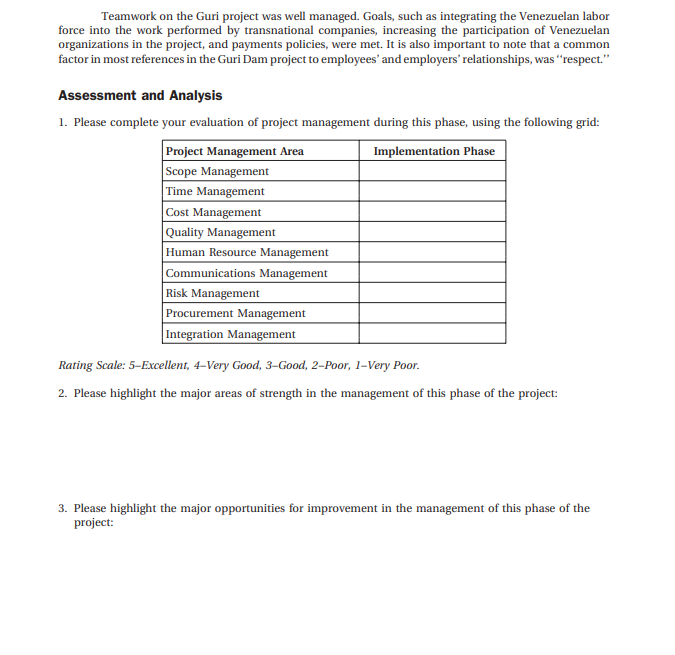
The Implementation Phase During the implementation, a major scope change was formally authorized and performed. The change was the expansion of the power units in the first stage from 5 to 10 units. The change was a consequence of the phase one success in functionality in the first stage, and of the fast-growing demand for electric power by the developments in the Guayana Region and of the country. According to a World Bank report on this scope change, the changes were implemented within the time and budget expected (The World Bank 1976). The scope described in the first stage was designed to have the capacity for generating 2,865MW with 10 generation units and a reservoir with a maximum elevation of 705ft(215m) above sea level. The scope of the final stage included the following tasks: - Increasing the height of the gravity dam and overflow weir to an elevation of 892ft (272m) above sea level; - Building two gravity dams on both riverbanks; - Building a second engine-house that would hold 10 units of 730MW each; - Digging a second spillway channel; - Building two earth-fill and rock-fill dams on both riverbanks; - Building the bulkhead dams. The volume of the main works of the Guri project was: 7 The Guri Dam The actual cost of the Guri Dam project is difficult to calculate because during the project's implementation, Venezuela went through an economical crisis during which the national currency had different exchange values with the dollar. At the project start date in 1963, the exchange rate was 3.33 bolivares (VEB) per dollar until 1973, when it became 4.30 VEB per dollar. Then in 1982, the devaluation exploded and the exchange rate increased daily. An Edelca information brochure about the Guri Dam (CVG Edelca 1994) states that the project's actual costs were: - First stage-1,388.6 million VEB (\$417 million (US)) - Final stage-21,163.6 million VEB The bolvare is the currency of Venezuela and it is locally abbreviated as Bs. Its ISO (International Organization for Standardization) currency code is VEB (Wikipedia, n.d.) which is used throughout this case study. The cost of the final stage of the Guri Dam is not provided in US dollars in view of the daily increase in the exchange rate during the latter part of the final stage of this project. The project's first phase (1963-1968) was estimated to cost $185,714,715 (US) (618,430,000 VEB) and its actual cost was $206,662,570 (US) (688,186,360 VEB), which was over budget by 11%. Individuals involved in managing the Guri Dam project estimated that $11,578,000 (US) were left of the unexpected expenses of the budget in the first stage and this money was used to start the final stage earlier than planned. Therefore, it appears that corrective actions were taken to improve cost surplus during the implementation stage. The final stage was financed by CVG using the energy sales produced by the firststage operation and by the World Bank. This helped CVG and Edelca to compensate for the devaluation problems of the country mainly during the final stage construction. A general view of the executed schedule of the Guri Dam project follows (CVG Edelca 1994): The procurement plan was realized in the implementation stage because the first stage of the project was done mostly by foreign engineering firms with the inclusion of Venezuelan labor assisted by qualified foreign labor. Later in the first stage, an expansion of the engine-house was performed by the Venezuelan consortium, and, in the final stage, the participation of Venezuelan contractors increased from 30% to 60%. 8 The Guri Dam Quality was a significant goal throughout all phases of the project. Occasionally, project milestones were allowed to be delayed if the quality was going to be affected. Reaching a high-quality level in the Guri Dam was essential to achieve Edelca's mission and vision. Therefore, extra efforts were devoted to the quality of the dam, such as internal and international audits and inspections. In order to maintain the equipment and technologies installed at the dam, recommendation for maintenance and signatures of guarantee were obtained from vendors and contractors at installation time. Teamwork on the Guri project was well managed. Goals, such as integrating the Venezuelan labor force into the work performed by transnational companies, increasing the participation of Venezuelan organizations in the project, and payments policies, were met. It is also important to note that a common factor in most references in the Guri Dam project to employees' and employers' relationships, was "respect." Assessment and Analysis 1. Please complete your evaluation of project management during this phase, using the following grid: Rating Scale: 5-Excellent, 4-Very Good, 3-Good, 2-Poor, 1-Very Poor. 2. Please highlight the major areas of strength in the management of this phase of the project: 3. Please highlight the major opportunities for improvement in the management of this phase of the project
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


