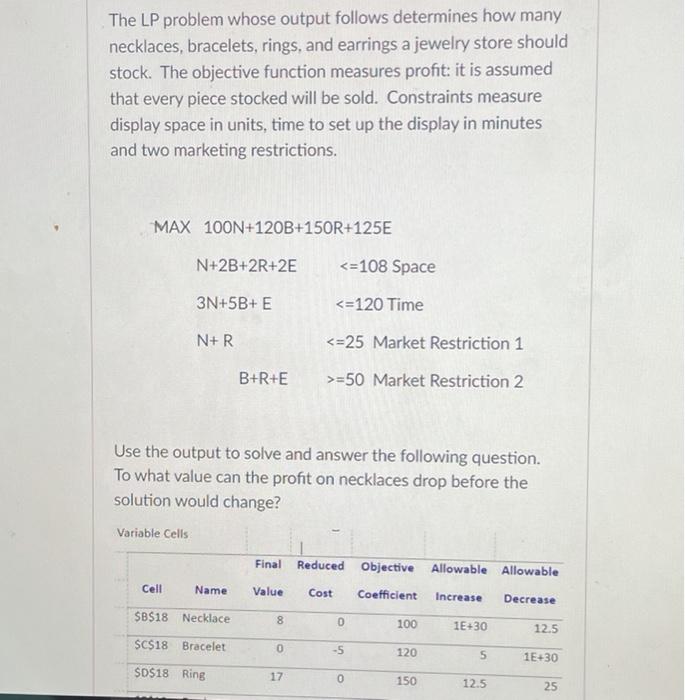
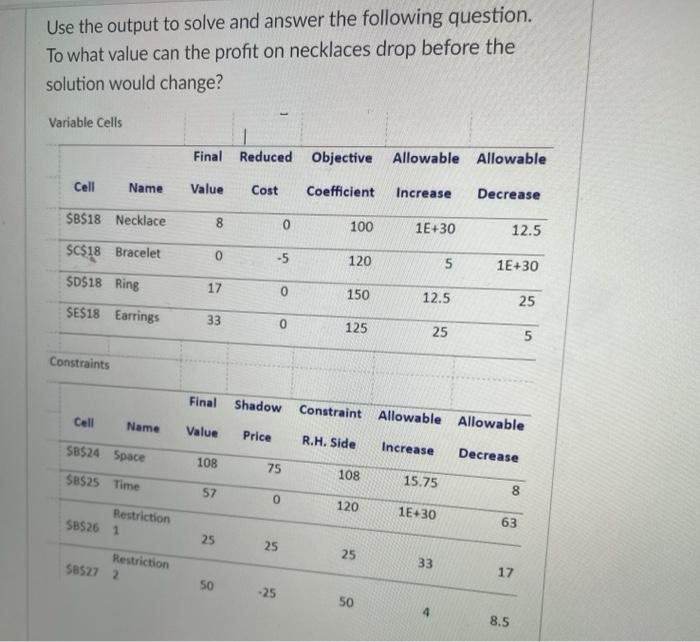
Question: The LP problem whose output follows determines how many necklaces, bracelets, rings, and earrings a jewelry store should stock. The objective function measures profit: it
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


