Question: The MM Problem Read the problem below and answer the questions. Bailey discusses a connection between the MM Theorem and the Put- Call Parity relation

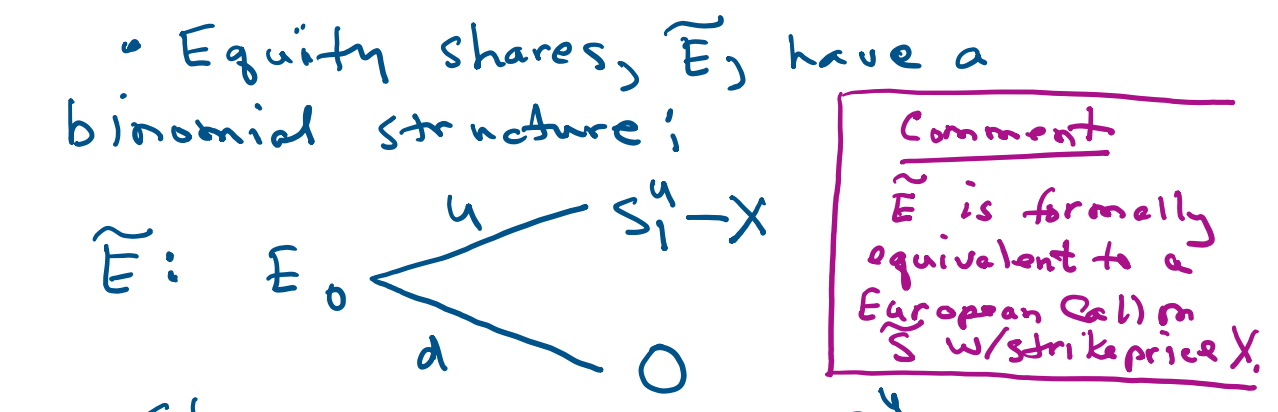
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


