Question: The modulo result is 152. There are some other useful resources: The Hamming Distance between two sequences of bits is the total number of bits

The modulo result is 152. There are some other useful resources:
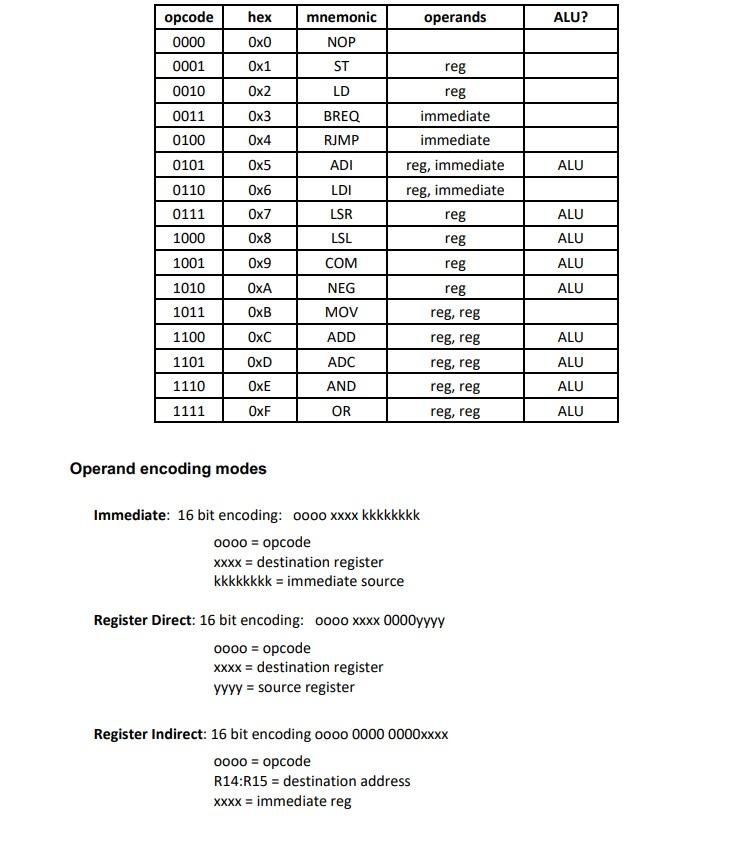


The Hamming Distance between two sequences of bits is the total number of bits positions in which the two sequences differ. For example, 01011010 and 01111000 have a Hamming Distance of 2 because they differ in two positions. Using the subset of the AVR assembly used by the simplified CPU (whose definition is in the Appendix), write a program that performs the following actions: (1) initialises RO and R1 to 0x3F and your student ID modulo 28 respectively (ii) calculates the Hamming Distance between the sequences of 8 bits contained in RO and R1 (iii) returns the result in the registers R2 (iv) stops executing any other operation The first 10 instructions of the program should be encoded and relocated at address Ox0100. The candidate should demonstrate that the program works as intended by providing a table or a timing diagram indicating the value of the instruction pointer and one of the registers in the Register File shortly after the rising edge of each clock for at least 5 clocks after RESET. Vec W Fm MCU INTO INT1 Volume up buttono Volume down button 1 Atmega32 Figure 1 hex operands ALU? opcode 0000 mnemonic NOP ST LD Ox1 Ox2 Ox3 BREQ RUMP Ox4 reg reg immediate immediate reg, immediate reg, immediate reg Ox5 ADI ALU 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 ALU Ox6 Ox7 Ox8 Ox9 LDI LSR LSL reg ALU COM ALU NEG ALU OXA OxB MOV OxC ADD reg reg reg, reg reg, reg reg, reg reg, reg reg, reg ALU OxD ADC ALU ALU OxE AND 1111 OxF OR ALU Operand encoding modes Immediate: 16 bit encoding: 0000 xxxx kkkkkkkk 0000 = opcode XXXX = destination register kkkkkkkk = immediate source Register Direct: 16 bit encoding: 0000 XXXX 0000yyyy 0000 = opcode xXxx = destination register YYYY = source register Register Indirect: 16 bit encoding 0000 0000 0000xxxx 0000 = opcode R14:R15 = destination address XXXX = immediate reg Instruction Set of Simple CPU NOP - No operation syntax: NOP The CPU does nothing for one clock cycle ST-Store in address space syntax: ST reg The CPU stores the source reg in address space at address specified in R14:15 LD - Load from address space syntax: LD reg The CPU loads the source reg in address space at address specified in R14:15 BREQ - Branching if equal syntax: BREQ immediate The CPU updates the IP adding immediate considered a two-complement number if the Z flag is zero. RUMP - Relative jump syntax: RJJMP immediate The CPU updates the IP adding immediate considered a two-complement number if the Z flag is zero. ADI - Add immediate syntax: ADI reg, immediate The CPU adds the immediate source and to destination registers and copies the result into the register. LDI - Load Immediate syntax: LDI reg, immediate The CPU stores the immediate into reg LSR - Logical Shift Right syntax: LSR reg The CPU shifts right one position all bits in the register reg inserting a zero in the MSB of the result. The Cflag in SREG receives the LSB of reg. LSL - Logical Shift Left syntax: LSL reg The CPU shifts left one position all bits in the register reg inserting the Cflag in the LSB of the result. The C flag in SREG is update with the MSB of reg. COM - One's complement syntax: COM reg The CPU calculates the one complement of register reg NEG - Negate syntax: NEGreg The CPU calculates the two's complement of register reg MOV - Copy register syntax: MOV destination, source The CPU copies the source into the destination register ADD - Addition syntax: ADD source, destination The CPU adds the source and destination registers and copies the result into the destination register. The Z flag and the C flags in SREG are also updated. ADC - Addition with carry syntax: ADC reg1 The CPU adds the source, destination registers and the carry bit and copies the result into the source register. The Z flag and the C flags in SREG are also updated. AND - Bitwise AND syntax: AND source, destination. The CPU calculates the logical bit-wise AND between source and destination registers. The Z flag in SREG is also updated. OR - Bitwise OR syntax: OR reg1 The CPU calculates the logical bit-wise AND between source and destination registers. The Z flag in SREG is also updated. The Hamming Distance between two sequences of bits is the total number of bits positions in which the two sequences differ. For example, 01011010 and 01111000 have a Hamming Distance of 2 because they differ in two positions. Using the subset of the AVR assembly used by the simplified CPU (whose definition is in the Appendix), write a program that performs the following actions: (1) initialises RO and R1 to 0x3F and your student ID modulo 28 respectively (ii) calculates the Hamming Distance between the sequences of 8 bits contained in RO and R1 (iii) returns the result in the registers R2 (iv) stops executing any other operation The first 10 instructions of the program should be encoded and relocated at address Ox0100. The candidate should demonstrate that the program works as intended by providing a table or a timing diagram indicating the value of the instruction pointer and one of the registers in the Register File shortly after the rising edge of each clock for at least 5 clocks after RESET. Vec W Fm MCU INTO INT1 Volume up buttono Volume down button 1 Atmega32 Figure 1 hex operands ALU? opcode 0000 mnemonic NOP ST LD Ox1 Ox2 Ox3 BREQ RUMP Ox4 reg reg immediate immediate reg, immediate reg, immediate reg Ox5 ADI ALU 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 ALU Ox6 Ox7 Ox8 Ox9 LDI LSR LSL reg ALU COM ALU NEG ALU OXA OxB MOV OxC ADD reg reg reg, reg reg, reg reg, reg reg, reg reg, reg ALU OxD ADC ALU ALU OxE AND 1111 OxF OR ALU Operand encoding modes Immediate: 16 bit encoding: 0000 xxxx kkkkkkkk 0000 = opcode XXXX = destination register kkkkkkkk = immediate source Register Direct: 16 bit encoding: 0000 XXXX 0000yyyy 0000 = opcode xXxx = destination register YYYY = source register Register Indirect: 16 bit encoding 0000 0000 0000xxxx 0000 = opcode R14:R15 = destination address XXXX = immediate reg Instruction Set of Simple CPU NOP - No operation syntax: NOP The CPU does nothing for one clock cycle ST-Store in address space syntax: ST reg The CPU stores the source reg in address space at address specified in R14:15 LD - Load from address space syntax: LD reg The CPU loads the source reg in address space at address specified in R14:15 BREQ - Branching if equal syntax: BREQ immediate The CPU updates the IP adding immediate considered a two-complement number if the Z flag is zero. RUMP - Relative jump syntax: RJJMP immediate The CPU updates the IP adding immediate considered a two-complement number if the Z flag is zero. ADI - Add immediate syntax: ADI reg, immediate The CPU adds the immediate source and to destination registers and copies the result into the register. LDI - Load Immediate syntax: LDI reg, immediate The CPU stores the immediate into reg LSR - Logical Shift Right syntax: LSR reg The CPU shifts right one position all bits in the register reg inserting a zero in the MSB of the result. The Cflag in SREG receives the LSB of reg. LSL - Logical Shift Left syntax: LSL reg The CPU shifts left one position all bits in the register reg inserting the Cflag in the LSB of the result. The C flag in SREG is update with the MSB of reg. COM - One's complement syntax: COM reg The CPU calculates the one complement of register reg NEG - Negate syntax: NEGreg The CPU calculates the two's complement of register reg MOV - Copy register syntax: MOV destination, source The CPU copies the source into the destination register ADD - Addition syntax: ADD source, destination The CPU adds the source and destination registers and copies the result into the destination register. The Z flag and the C flags in SREG are also updated. ADC - Addition with carry syntax: ADC reg1 The CPU adds the source, destination registers and the carry bit and copies the result into the source register. The Z flag and the C flags in SREG are also updated. AND - Bitwise AND syntax: AND source, destination. The CPU calculates the logical bit-wise AND between source and destination registers. The Z flag in SREG is also updated. OR - Bitwise OR syntax: OR reg1 The CPU calculates the logical bit-wise AND between source and destination registers. The Z flag in SREG is also updated
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


