Question: The net present value (NPV) method estimates how much a potential project will contribute to , and it is the best selection criterion. The -Select-
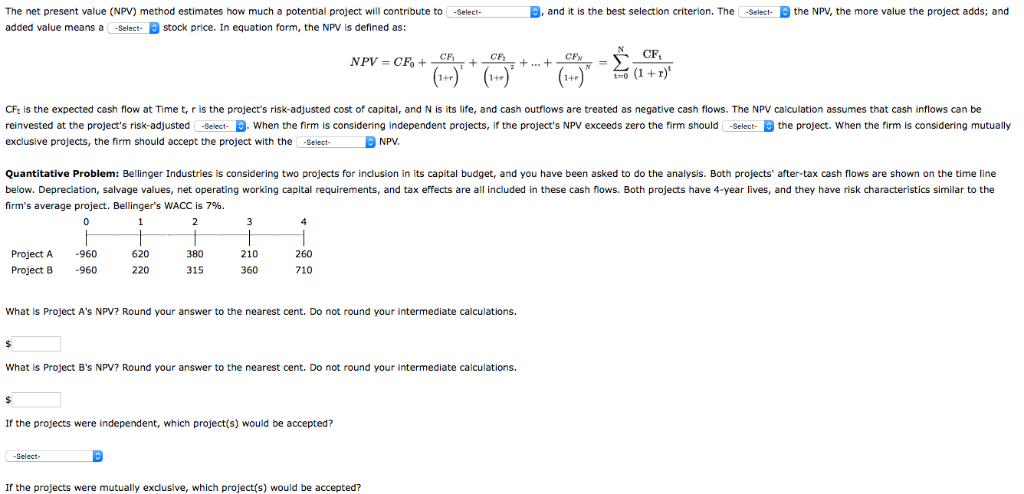
The net present value (NPV) method estimates how much a potential project will contribute to , and it is the best selection criterion. The -Select- the NPV, the more value the project adds; and -Select- added value means a -Select- stock price. In equation form, the NPV is defined as: CF t-0 1+ 1+ CFt is the expected cash flow at Time t, r is the project's risk-adjusted cost of capital, and N is its life, and cash outflows are treated as negative cash flows. The NPv calculation assumes that cash inflows can be reinvested at the project's risk-adjusted -Select-. When the firm is considering independent projects, if the project's NPV exceeds zero the firm should Select-the project. When the firm is considering mutually exclusive projects, the firm should accept the project with the -Select NPV Quantitative Problem: Bellinger Industries is considering two projects for inclusion in its capital budget, and you have been asked to do the analysis. Both projects' after-tax cash flows are shown on the time line below. Depreciation, salvage values, net operating working capital requirements, and tax effects are all included in these cash fiows. Both projects have 4-year lives, and they have risk characteristics similar to the firm's average project. Bellinger's WACC is 7%. 620 220 Project A -960 Project 8 -960 380 315 210 260 710 360 What is Project A's NPV? Round your answer to the nearest cent. Do not round your intermediate calculations. What is Project B's NPV? Round your answer to the nearest cent. Do not round your intermediate calculations. If the projects were independent, which project(s) would be accepted? Select- If the projects were mutually exdusive, which project(s) would be accepted
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


