Question: The overflow flag is set in a processor when twos complement signed integers give an answer that cannot possibly be correct. For example, overflow in
The overflow flag is set in a processor when twos complement signed integers give an answer that cannot possibly be correct. For example, overflow in addition might occur if the result of two negatives added together yields a positive or two positives added together give a negative. In this question consider 32 bit twos complement integers. You have access to the most significant bit (the bit worth 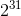 as
as 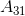 of one addend and
of one addend and 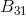 as the other addend.
as the other addend. 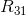 is the most significant bit of the result. The least significant bits (the ones place worth
is the most significant bit of the result. The least significant bits (the ones place worth 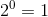 ) are accessed as
) are accessed as 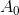 ,
, 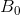 , and
, and 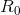 . You may access other elements as needed by using the proper subscripts (there are 96 total bits here).
. You may access other elements as needed by using the proper subscripts (there are 96 total bits here).
Make a Karnaugh Map (Hint: 96 bits are available but our K-Maps max out at 4) and create a simple equation to compute the overflow flag/bit for 32 bit integer addition. Overflow is 1 when the calculation is wrong. Overflow is 0 otherwise.
20 = 1 20 = 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


