Question: The perceptron algorithm considers the hinge loss function over the training data (31, X1),..., (yn, Xn), with the hinge being at 0. The loss
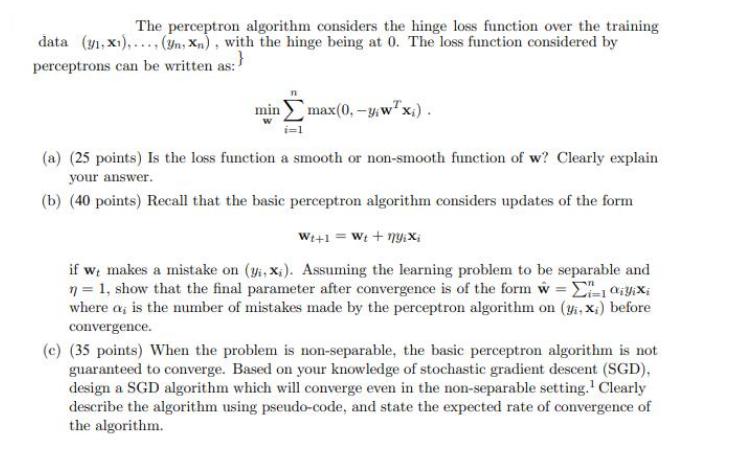
The perceptron algorithm considers the hinge loss function over the training data (31, X1),..., (yn, Xn), with the hinge being at 0. The loss function considered by perceptrons can be written as:} min max(0, -y,wx;). (a) (25 points) Is the loss function a smooth or non-smooth function of w? Clearly explain your answer. (b) (40 points) Recall that the basic perceptron algorithm considers updates of the form W+1 = Wt + nyixi if we makes a mistake on (yi, x). Assuming the learning problem to be separable and n = 1, show that the final parameter after convergence is of the form w = Ei=1iYixi where a, is the number of mistakes made by the perceptron algorithm on (y,x;) before convergence. (c) (35 points) When the problem is non-separable, the basic perceptron algorithm is not guaranteed to converge. Based on your knowledge of stochastic gradient descent (SGD), design a SGD algorithm which will converge even in the non-separable setting. Clearly describe the algorithm using pseudo-code, and state the expected rate of convergence of the algorithm.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


