Question: The permanent action ( G ) ( including self - weight ) applied to a beam is 1 5 kN / m and the imposed
The permanent action Gincluding selfweight applied to a beam is kNm and the imposed load Q is kNm The loads to use for a strength limit state analysis, and to calculate the short term deflection of a beam in an office respectively are: a None of the other answers is correctb w kNm; Ws kNm c w kNm; Ws kNmd w kNm; Ws kNme w kNm; Ws kNm
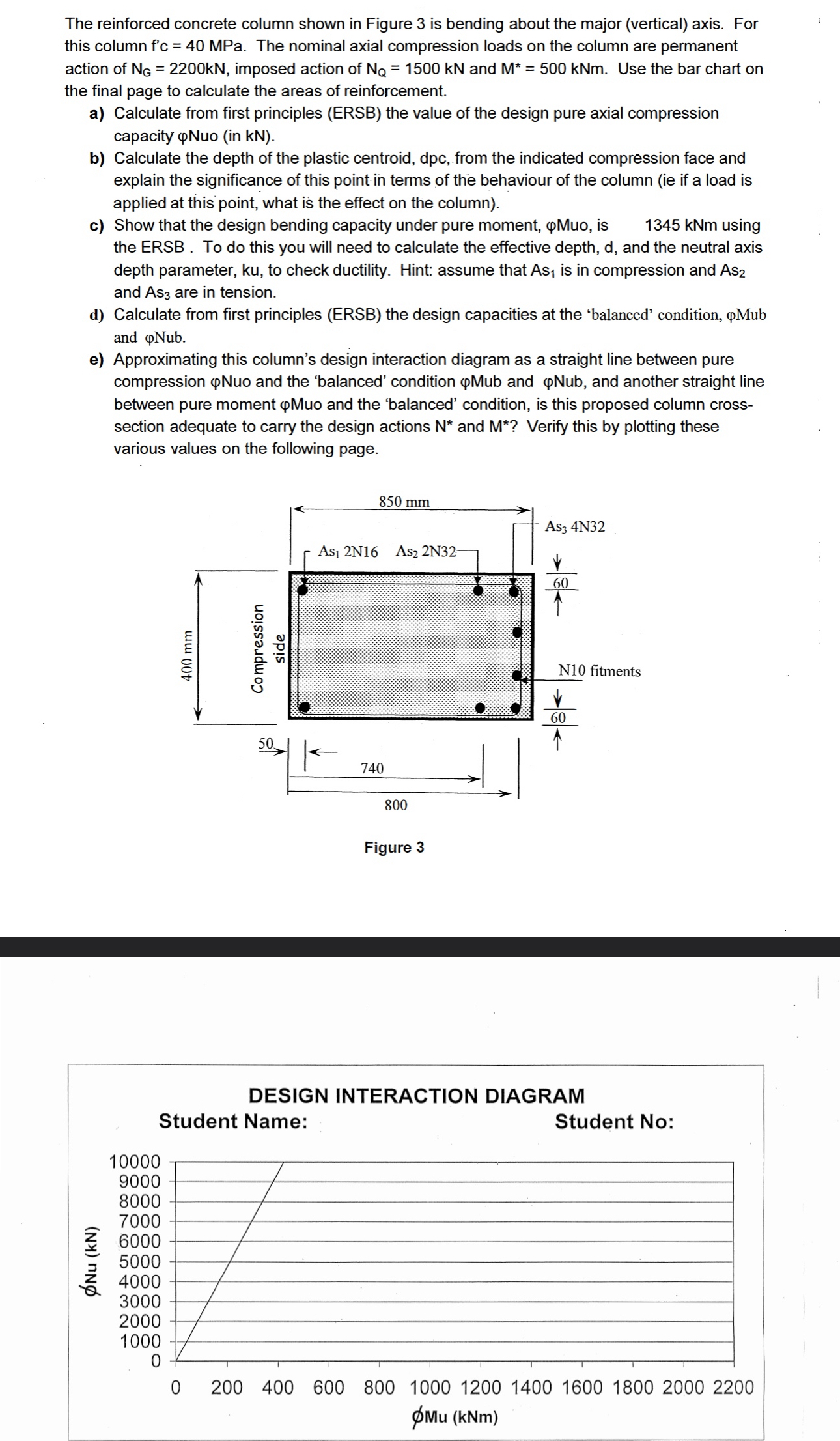
a Calculate from first principles ERSB the value of the design pure axial compression
capacity in kN
b Calculate the depth of the plastic centroid, dpc from the indicated compression face and
explain the significance of this point in terms of the behaviour of the column ie if a load is
applied at this point, what is the effect on the column
c Show that the design bending capacity under pure moment, Muo, is kNm using
the ERSB. To do this you will need to calculate the effective depth, d and the neutral axis
depth parameter, ku to check ductility. Hint: assume that is in compression and
and are in tension.
d Calculate from first principles ERSB the design capacities at the 'balanced' condition, Mub
and Nub.
e Approximating this column's design interaction diagram as a straight line between pure
compression Nuo and the 'balanced' condition and and another straight line
between pure moment Muo and the 'balanced' condition, is this proposed column cross
section adequate to carry the design actions and Verify this by plotting these
various values on the following page.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


