Question: The Photoelectric Effect Here are some data collected on a sample of cesium exposed to various energies of light. Electrons are emitted from the surface
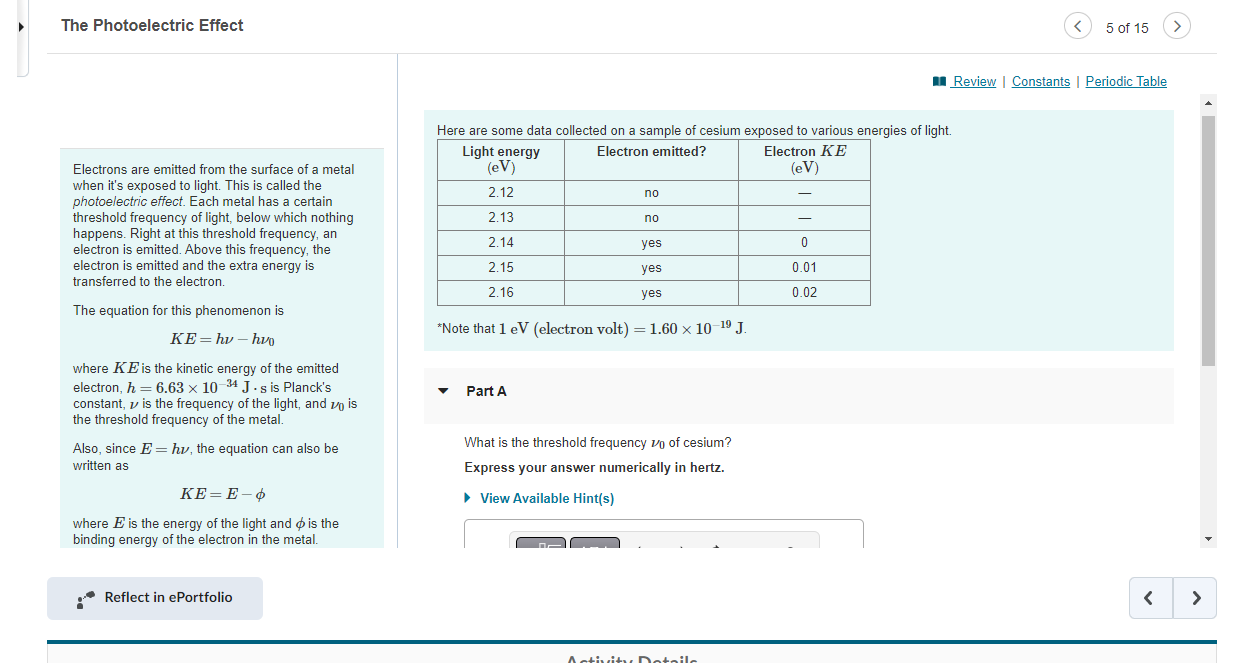
The Photoelectric Effect Here are some data collected on a sample of cesium exposed to various energies of light. Electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal when it's exposed to light. This is called the photoelectric effect. Each metal has a certain threshold frequency of light, below which nothing happens. Right at this threshold frequency, an electron is emitted. Above this frequency, the electron is emitted and the extra energy is transferred to the electron. The equation for this phenomenon is KE=hh0 Note that 1eV( electron volt )=1.601019J. where KE is the kinetic energy of the emitted electron, h=6.631034Js is Planck's constant, is the frequency of the light, and 0 is Part A the threshold frequency of the metal. Also, since E=h, the equation can also be What is the threshold frequency 0 of cesium? written as Express your answer numerically in hertz. KE=E where E is the energy of the light and is the binding energy of the electron in the metal
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


