Question: The rational expectations model Suppose the U . S . economy is in equilibrium at a potential output of $ 1 2 trillion so that
The rational expectations model
Suppose the US economy is in equilibrium at a potential output of $ trillion so that unemployment is at the natural rate. At the beginning of the
year, the Federal Reserve announces that its monetary policy will aim to maintain output at potential output and sustain the current price level
throughout the year. Firms and workers negotiate annual wage and resource price agreements based on the belief that the Fed is committed to price
stability.
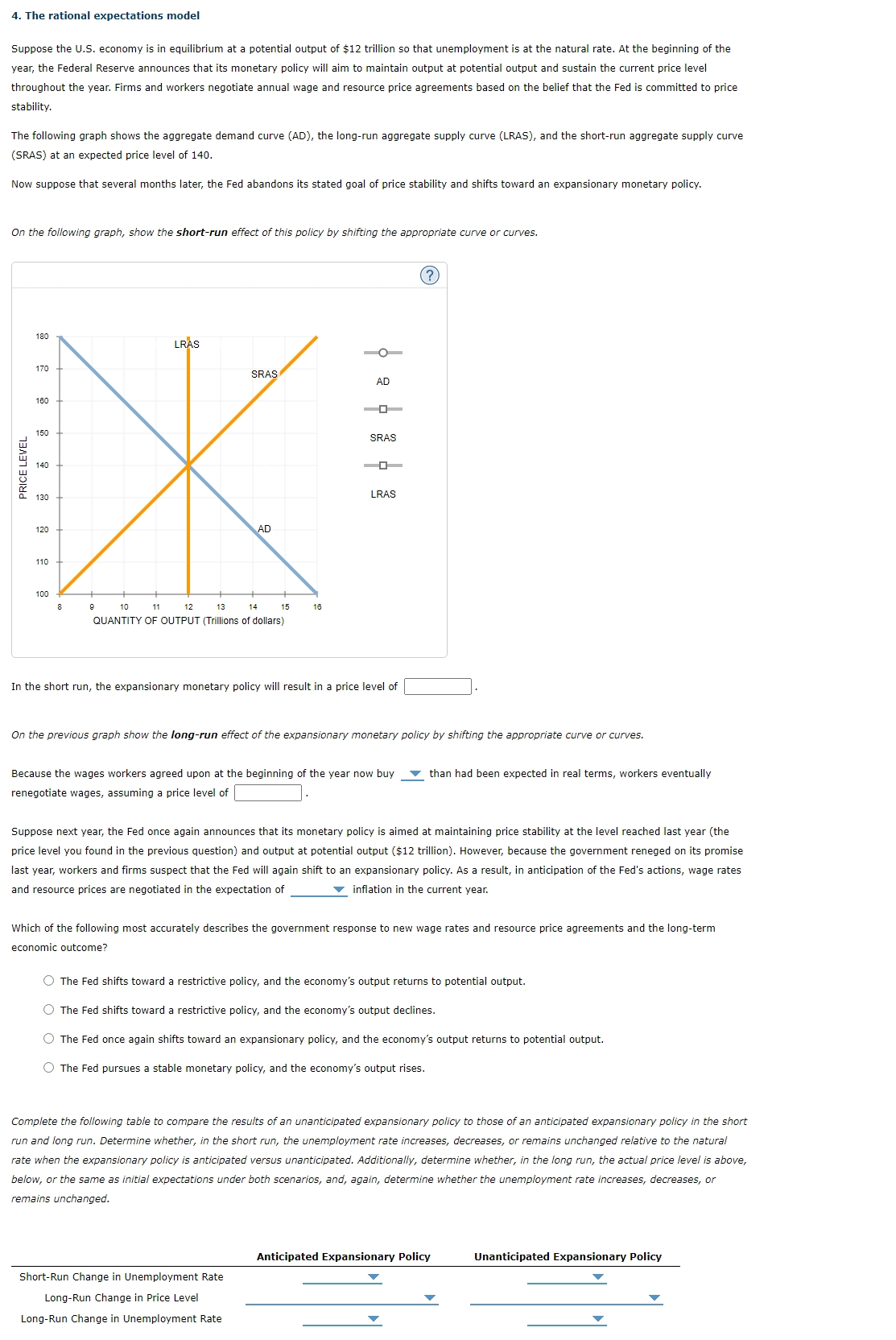
The following graph shows the aggregate demand curve AD the longrun aggregate supply curve LRAS and the shortrun aggregate supply curve
SRAS at an expected price level of
Now suppose that several months later, the Fed abandons its stated goal of price stability and shifts toward an expansionary monetary policy.
On the following graph, show the shortrun effect of this policy by shifting the appropriate curve or curves.
In the short run, the expansionary monetary policy will result in a price level of
On the previous graph show the longrun effect of the expansionary monetary policy by shifting the appropriate curve or curves.
Because the wages workers agreed upon at the beginning of the year now buy
than had been expected in real terms, workers eventually
renegotiate wages, assuming a price level of
Suppose next year, the Fed once again announces that its monetary policy is aimed at maintaining price stability at the level reached last year the
price level you found in the previous question and output at potential output $ trillion However, because the government reneged on its promise
last year, workers and firms suspect that the Fed will again shift to an expansionary policy. As a result, in anticipation of the Fed's actions, wage rates
and resource prices are negotiated in the expectation of inflation in the current year.
Which of the following most accurately describes the government response to new wage rates and resource price agreements and the longterm
economic outcome?
The Fed shifts toward a restrictive policy, and the economy's output returns to potential output.
The Fed shifts toward a restrictive policy, and the economy's output declines.
The Fed once again shifts toward an expansionary policy, and the economy's output returns to potential output.
The Fed pursues a stable monetary policy, and the economy's output rises.
Complete the following table to compare the results of an unanticipated expansionary policy to those of an anticipated expansionary policy in the short
run and long run. Determine whether, in the short run, the unemployment rate increases, decreases, or remains unchanged relative to the natural
rate when the expansionary policy is anticipated versus unanticipated. Additionally, determine whether, in the long run, the actual price level is above,
below, or the same as initial expectations under both scenarios, and, again, determine whether the unemployment rate increases, decreases, or
remains unchanged.
ShortRun Change in Unemployment Rate
Drop down answer choices
lessmore
lowerhigher
Short run change in unemp. decreaseincreaseno change
Long run change in price level lower than initial expectations, higher than initial expectations, same as initial expectations
Long run change in unemployment rate decreaseincreaseno change
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


