Question: The recognition that dividends are dependent on earnings, so a reliable dividend forecast is based on an underlying forecast of the firm's future sales, costs
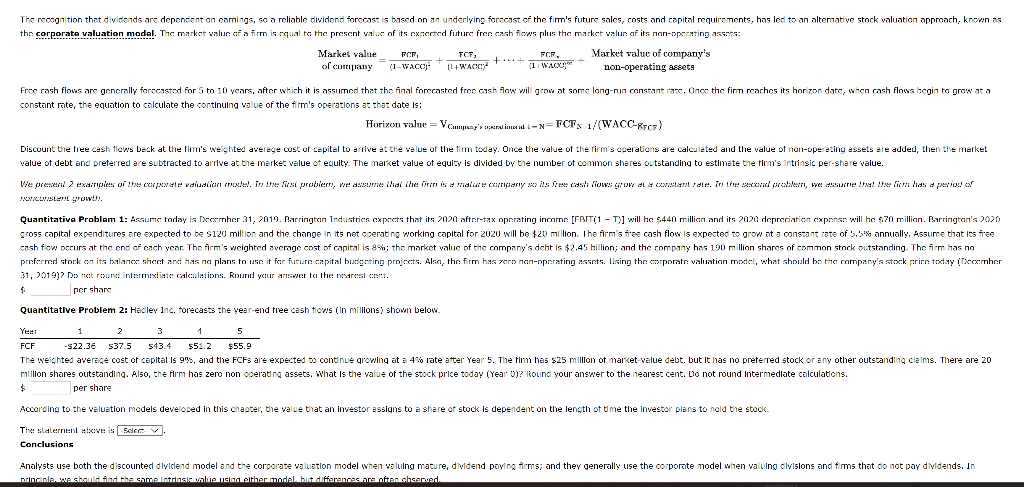
The recognition that dividends are dependent on earnings, so a reliable dividend forecast is based on an underlying forecast of the firm's future sales, costs and capital requirements, has led to an alternative stock valuation approach, known as the corporate valuation model. The market value of a firm is equal to the present value of its expected future free cash flows plus the market value of its non-operating assets:
Market value= FCF1 + FCF2 + .... + FCF00+ Market Value of Company's
of company (1+WACC)1 (1+WACC)2 (1+WACC)00 non-operating assets
Free cash flows are generally forecasted for 5 to 10 years, after which it is assumed that the final forecasted free cash flow will grow at some long-run constant rate. Once the firm reaches its horizon date, when cash flows begin to grow at a constant rate, the equation to calculate the continuing value of the firm's operations at that date is:
Horizon Value= V company operations at t=NFCF N+1/WACC-gFCF)
Discount the free cash flows back at the firm's weighted average cost of capital to arrive at the value of the firm today. Once the value of the firm's operations are calculated and the value of non-operating assets are added, then the market value of debt and preferred are subtracted to arrive at the market value of equity. The market value of equity is divided by the number of common shares outstanding to estimate the firm's intrinsic per-share value.
We present 2 examples of the corporate valuation model. In the first problem, we assume that the firm is a mature company so its free cash flows grow at a constant rate. In the second problem, we assume that the firm has a period of nonconstant growth.
Quantitative Problem 1: Assume today is December 31, 2019. Barrington Industries expects that its 2020 after-tax operating income [EBIT(1 T)] will be $440 million and its 2020 depreciation expense will be $70 million. Barrington's 2020 gross capital expenditures are expected to be $120 million and the change in its net operating working capital for 2020 will be $20 million. The firm's free cash flow is expected to grow at a constant rate of 5.5% annually. Assume that its free cash flow occurs at the end of each year. The firm's weighted average cost of capital is 8%; the market value of the company's debt is $2.45 billion; and the company has 190 million shares of common stock outstanding. The firm has no preferred stock on its balance sheet and has no plans to use it for future capital budgeting projects. Also, the firm has zero non-operating assets. Using the corporate valuation model, what should be the company's stock price today (December 31, 2019)? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest cent. $ _________ per share
Quantitative Problem 2: Hadley Inc. forecasts the year-end free cash flows (in millions) shown below.
| Year | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| FCF | -$22.36 | $37.5 | $43.4 | $51.2 | $55.9 |
The weighted average cost of capital is 9%, and the FCFs are expected to continue growing at a 4% rate after Year 5. The firm has $25 million of market-value debt, but it has no preferred stock or any other outstanding claims. There are 20 million shares outstanding. Also, the firm has zero non-operating assets. What is the value of the stock price today (Year 0)? Round your answer to the nearest cent. Do not round intermediate calculations. $ _______ per share
According to the valuation models developed in this chapter, the value that an investor assigns to a share of stock is dependent on the length of time the investor plans to hold the stock.
The statement above is (TRUE/FALSE)__________??
Free cash flows are generally forcenstod for 5 to 10 years, after which it is assumed that the final forceasted froe cash flow will grow at some lang-nun constant rate, Once the firm reaches its horizon date, when cash flows begin to grow at a constant rite, the equition to calculate the cortinuling vesulue of the firm's operations at that date is: Discount the tree cash thows beck at the tim's weghted averege cost of cepital to arnive at the velus of the fim tocay. Once the value of the firm's ceerations are calculated and the value of non-operating assets are added, then the market value of debt and preterred are subtracted to arive at the marke: value ot equity. The market value of equily is divided by the number of common shares outstandihn to estimate the tirm's intrinsic per-share value. cash few orcurs at the end of orch year. The firm's weighted evernge cost pf conpital is 8%; the market value of the company's debt is $2,45 billion; and the company has 190m illion shares of common stock outstanding. The fiem has no per share Quantitative Problem 2: Hacley 1nc. torecasts the year-end tree cash tows (in millionsy shown below. milllon shares outstand ha. A.150, the flim has zero non overatng assets. What is the value of the stock price today (Year of? hound your answer to the nearest cent. vo not round Intermedlate calculations. per share According to the valuation models develoced in this chadear, the value that an investor assians to a share of stock is dependent on the length of tme the investor plens to hold the stock. Ttere sideternent nixise is Conclusions Analysts use both the discounted dlyillend model ond the corborate waluation model when weluing mature, dividend paiyling firms; and they generally use the corporite model wien valuing slvislons and firms that do not pay diddends. In
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


