Question: The recurrence relation T(n) = T(n/2) + nlogn then the time is Select one: O a. O(n log?n) 0 b. Onlogn) O C. on) 0


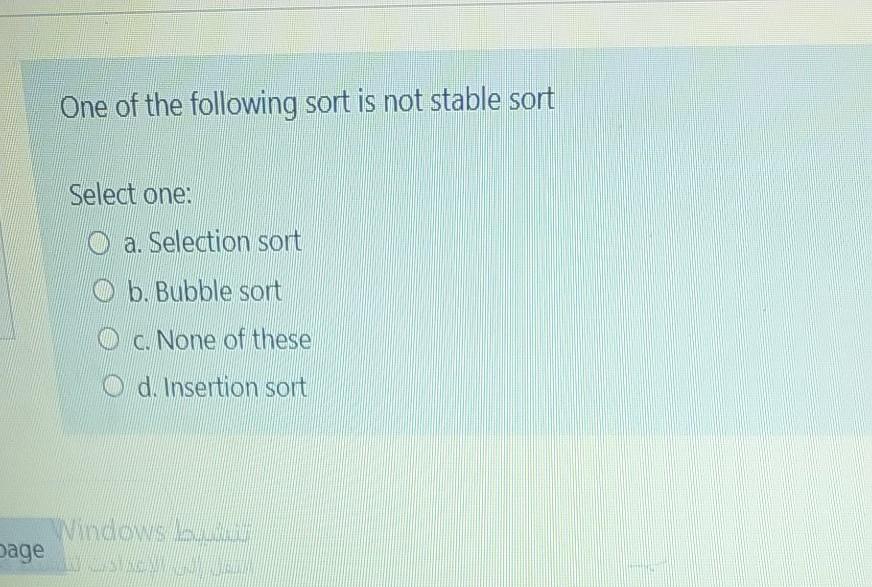
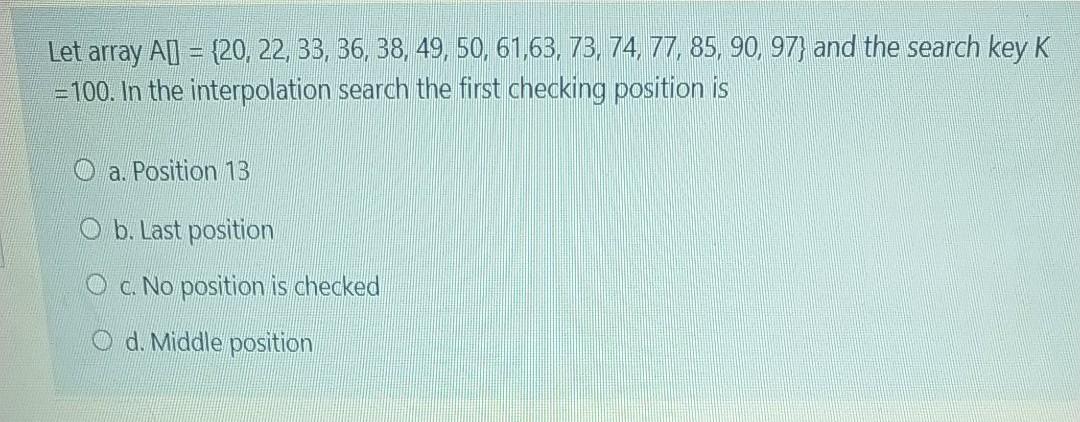

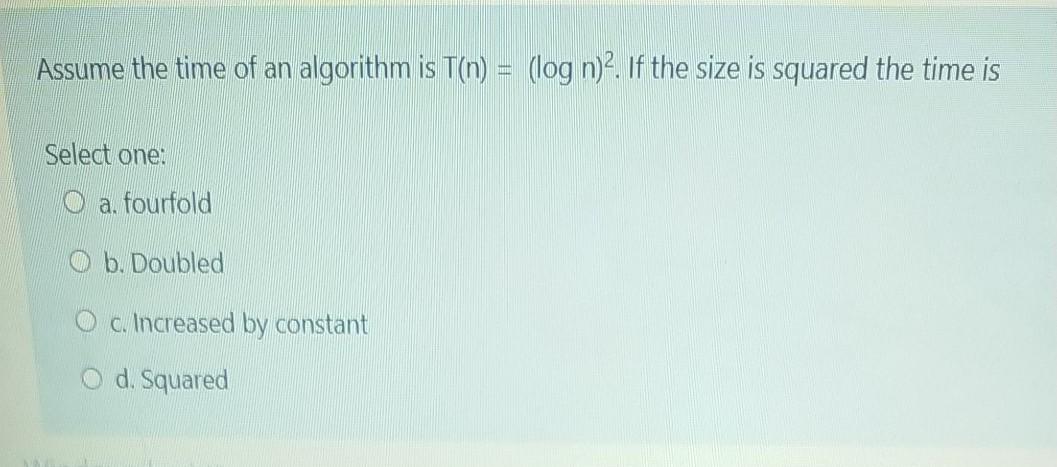
The recurrence relation T(n) = T(n/2) + nlogn then the time is Select one: O a. O(n log?n) 0 b. Onlogn) O C. on) 0 d. Onlogn) The average time complexity of the interpolation search is O an O b.log n c.vn O d. log log(n) One of the following sort is not stable sort Select one: O a. Selection sort ob. Bubble sort O c. None of these Od. Insertion sort Wees Dage Let array A[] = {20, 22, 33, 36, 38, 49, 50, 61,63, 73, 74, 77, 85, 90, 97} and the search key K =100. In the interpolation search the first checking position is O a. Position 13 O b. Last position O c. No position is checked O d. Middle position The closest pair problem belong to Select one: O a. Combinatorial problems O b. Numerical problems O e Geometric problems O d. Graph problems Assume the time of an algorithm is T(n) = (log n)2. If the size is squared the time is Select one: o a, fourfold O b. Doubled c. Increased by constant O d. Squared
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


