Question: the structs are given as: / / DO NOT CHANGE THE NAME OF THIS STRUCT struct set { struct node * tree; / / DO
the structs are given as: DO NOT CHANGE THE NAME OF THIS STRUCT
struct set
struct node tree; DO NOT MODIFYREMOVE THIS FIELD
You may add more fields here if needed
;
DO NOT CHANGE THE NAME OF THIS STRUCT
struct node
int item; DO NOT MODIFYREMOVE THIS FIELD
struct node left; DO NOT MODIFYREMOVE THIS FIELD
struct node right; DO NOT MODIFYREMOVE THIS FIELD
You may add more fields here if needed
;
You may define more structs here if needed
Cursors
struct cursor
You may add more fields here if needed
;
The interface is given as: DO NOT MODIFY THIS FILE
#ifndef SETH
#define SETH
#include
#include
#include
#define UNDEFINED INTMIN
typedef struct set Set;
Basic Set Operations
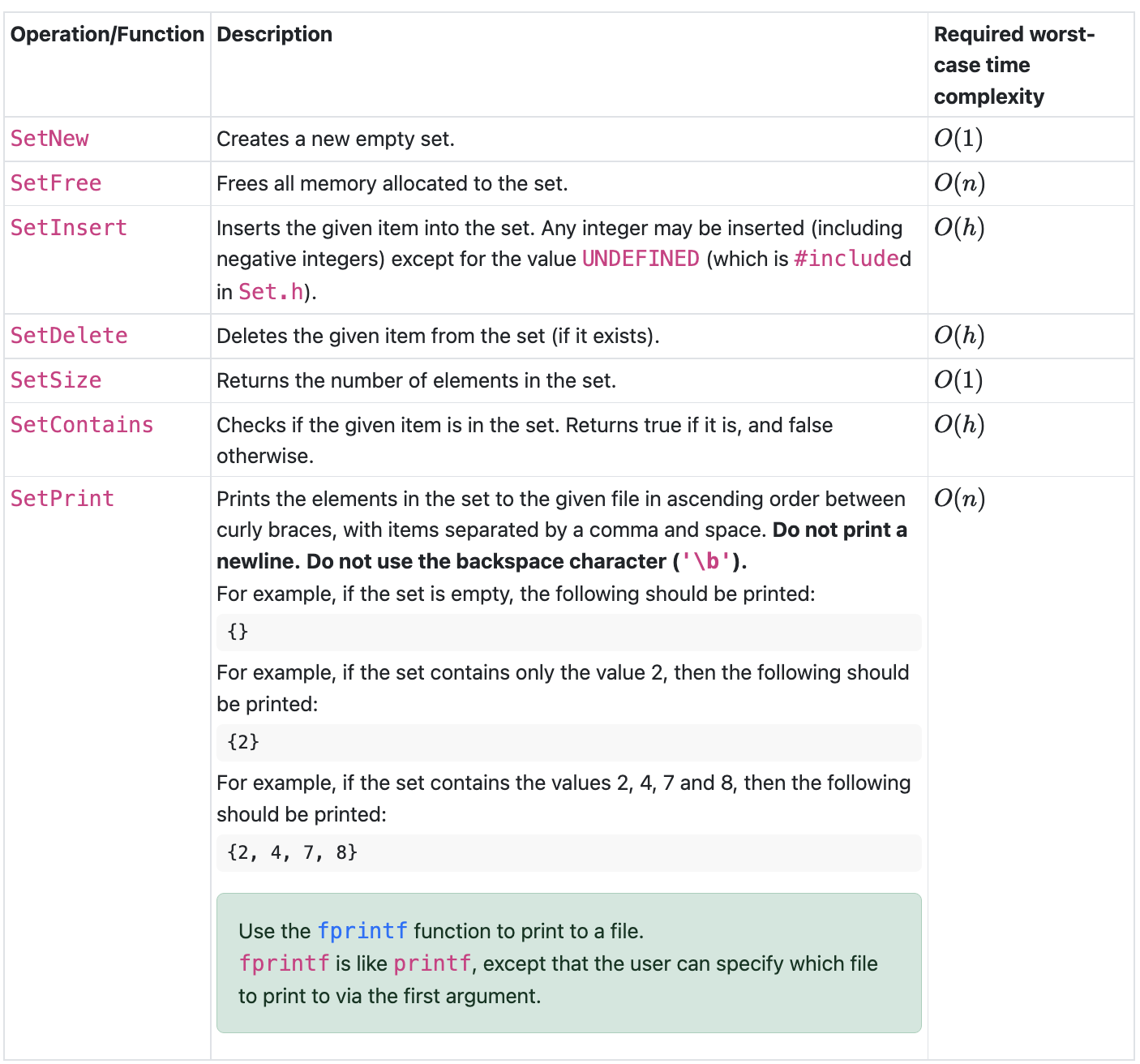
Creates a new empty set
Set SetNewvoid;
Frees all memory allocated to the set
void SetFreeSet s;
Inserts an item into the set
void SetInsertSet s int item;
Deletes an item from the set
void SetDeleteSet s int item;
Returns the number of elements in the set
int SetSizeSet s;
Returns true if the set contains the given item, and false otherwise
bool SetContainsSet s int item;
Prints the elements in the set to the given file in ascending order
between curly braces, with items separated by a comma and space
void SetPrintSet s FILE out;
Common Set Operations
Returns a new set representing the union of the two sets
Set SetUnionSet s Set s;
Returns a new set representing the intersection of the two sets
Set SetIntersectionSet s Set s;
Returns true if the two sets are equal, and false otherwise
bool SetEqualsSet s Set s;
Returns true if set s is a subset of set s and false otherwise
bool SetSubsetSet s Set s;
Index Operations
Returns the element at the given index, or UNDEFINED if the given
index is outside the range n where n is the size of the set
int SetAtIndexSet s int index;
Returns the index of the given element in the set if it exists, and
otherwise
int SetIndexOfSet s int elem;
Cursor Operations
typedef struct cursor SetCursor;
Creates a new cursor positioned at the start of the set
see the spec for details
SetCursor SetCursorNewSet s;
Frees all memory allocated to the given cursor
void SetCursorFreeSetCursor cur;
Returns the element at the cursor's position, or UNDEFINED if the
cursor is positioned at the start or end of the set
int SetCursorGetSetCursor cur;
Moves the cursor to the next greatest element, or to the end of the
set if there is no next greatest element. Does not move the cursor if
it is already at the end. Returns false if the cursor is at the end
after this operation, and true otherwise.
bool SetCursorNextSetCursor cur;
Moves the cursor to the next smallest element, or to the start of the
set if there is no next smallest element. Does not move the cursor if
it is already at the start. Returns false if the cursor is at the
start after this operation, and true otherwise.
bool SetCursorPrevSetCursor cur;
#endif. Implement the following functions using this info.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


