Question: The theme of this mandatory exercise is memory usage and how the operating system manages this resource. It is important to use a virtual machine
The theme of this mandatory exercise is memory usage and how the operating system manages this resource. It is important to use a virtual machine with Linux for this exercise, as Windows or Mac might handle memory differently. Some of the tasks will use almost all available memory, so use a VM
Task
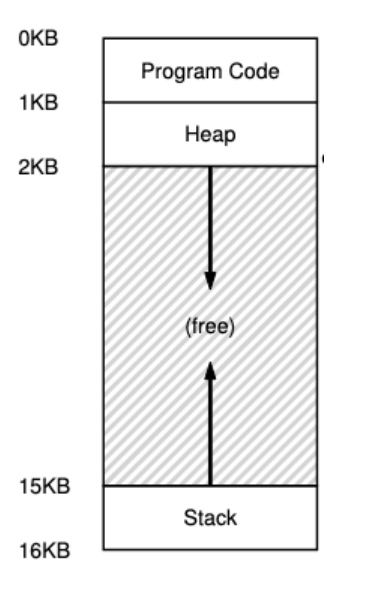
In this task, you will investigate what the virtual memory area of a program looks like. More precisely, you will find the virtual memory addresses of these parts of the program:
The stack
The heap
The program code
Global variables
Write a small C file named "addresses.c where you print out the addresses of various functionsvariables to find this information. Upload this file to CodeGrade.
Setup
As a security measure, some randomization of the virtual memory area takes place. To reproduce the results, we want to disable this for this task. There is a simple way to do this by using the setarch command.
When compiling, be careful not to use optimization, as we dont want the compiler to optimize anything away. You can also include static to include libraries in the executable file.
Submission
Once you have collected the values, you should also upload a text file named addresses.txt where you show, using ASCII characters, what the memory area looks like. Use the memory addresses you got, and the order should roughly follow the layout in the book. You can either create the file manually or let addresses.c generate it Either way, the file should be uploaded separately.
Format:
markdown
Kopier kode
addressname of the areaaddressname of the area Unused addressname of the area
You should also submit the code you have written and an explanation of where the values you found come from. Below are more details about what is expected from the different parts of the program.
The Stack
For the stack, we want to know the memory address of a variable on the stack, but also in which direction the stack grows. You can use a recursive function to see how the addresses change as the stack grows. You can start with a function like this:
void fint i if i return; Your code here fi ;
The Heap
Allocate a relatively large amount of memory MB and see what memory address you get. You dont need to investigate the heap further for now; that will come in the next task.
The Program Code
It is not immediately obvious where the program code is located, but there are several ways to find out. For example, you can print out the address of a function in the program or use a debugger.
Global Variables
Finally, find out where global variables end up Does it matter if they are initialized or not? Does it matter if they are marked as const or not?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


