Question: The unit circle {(x, y) : x2 +y2 = 1} is divided into three arcs by choosing three random points A, B, C on the

The unit circle {(x, y) : x2 +y2 = 1} is divided into three arcs by choosing three random
points A, B, C on the circle (independently and uniformly), forming arcs between A and
B, between A and C, and between B and C. Let L be the length of the arc containing
the point (1, 0). What is E(L)? Study this by working through the following steps.
(a) Explain what is wrong with the following argument: "The total length of the arcs is
2?, the circumference of the circle. So by symmetry and linearity, each arc has length
2?/3 on average. Referring to the arc containing (1, 0) is just a way to specify one of
the arcs (it wouldn't matter if (1, 0) were replaced by (0,
A fair die is rolled, and then a coin with probability p of Heads is flipped as many times
as the die roll says, e.g., if the result of the die roll is a 3, then the coin is flipped 3
times. Let X be the result of the die roll and Y be the number of times the coin lands
Heads.
(a) Find the joint PMF of X and Y . Are they independent?
(b) Find the marginal PMFs of X and Y .
(c) Find the conditional PMFs of Y given X = x and of Y given X = x.
6. A committee of size k is chosen from a group of n women and m men. All possible
committees of size k are equally likely. Let X and Y be the numbers of women and men
on the committee, respectively.
(a) Find the joint PMF of X and Y . Be sure to specify the support.
(b) Find the marginal PMF of X in two di?erent ways: by doing a computation using
the joint PMF, and using a story.
(c) Find the conditional PMF of Y given that X = x.
7. A stick of length L (a positive constant) is broken at a uniformly random point X.
Given that X = x, another breakpoint Y is chosen uniformly on the interval [0, x].
(a) Find the joint PDF of X and Y . Be sure to specify the support.
(b) We already know that the marginal distribution of X is Unif(0, L). Check that
marginalizing out Y from the joint PDF agrees that this is the marginal distribution of
X.
(c) We already know that the conditional distribution of Y given X = x is Unif(0, x).
Check that using the definition of conditional PDFs (in terms of joint and marginal
PDFs) agrees that this is the conditional distribution of Y given X = x.
(d) Find the marginal PDF of Y .
(e) Find the conditional PDF of X given Y = y.
8. (a) Five cards are randomly chosen from a standard deck, one at a time with replacement.
Let X, Y, Z be the numbers of chosen queens, kings, and other cards. Find the joint PMF
of X, Y, Z.
(b) Find the joint PMF of X and Y .
Hint: In summing the joint PMF of X, Y, Z over the possible values of Z, note that most
terms are 0 because of the constraint that the number of chosen cards is five.
(c) Now assume instead that the sampling is without replacement (all 5-card hands are
equally likely). Find the joint PMF of X, Y, Z.
Hint: Use the naive definition of probability.
9. Let X and Y be i.i.d. Geom(p), and N = X

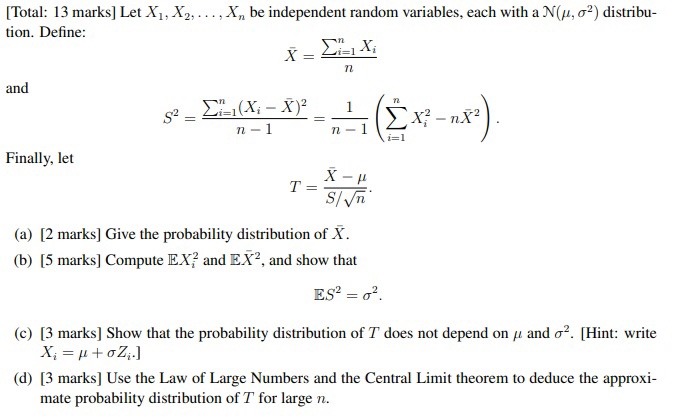

1. Let X be a random variable with probability distribution f(x). What is the mean if X is discrete or continuous? 3. Let X be a random variable with probability distribution f(x). Write the expected value of the random variable g(X) if X is discrete or continuous. 5. Let X and Y be random variables with joint probability distribution f(xy). Write the mean, or expected value, of the random variable g(X,Y) if X, and Y are discrete or continuous. 6. Let X be a random variable with probability distribution f(x) and mean p (mu). Write the variance of X for when X is discrete or continuous. 9. Let X and Y be random variables with covariance oxy and standard deviations ox and gy respectively. Write the correletion coefficient of X and Y. (P.125)[Total: 13 marks] Let X], X2, ..., X, be independent random variables, each with a N(/, o?) distribu- tion. Define: X = ZielXi 77 and 1 n - 1 Ex? -nx?) 7 - 1 i=1 Finally, let X - / T = S/ Vn (a) [2 marks] Give the probability distribution of X. (b) [5 marks] Compute EX, and EX, and show that ES' = 02. (c) [3 marks] Show that the probability distribution of T does not depend on / and o?. [Hint: write X; = p+oZ;.] (d) [3 marks] Use the Law of Large Numbers and the Central Limit theorem to deduce the approxi- mate probability distribution of T for large n.Part A. For two independent events A and B, suppose that P(A) = 0.2 and P(B) = 0.4. To find P(A /7 B), what probability rule/law, should you use? O Axioms of probability O Definition of the independent events O The law of total probability O The multiplication rule for P(A / B) O Definition of the conditional probability O Bayes' theorem O The addition rule Find P(A /) B). To find P(A U B), what probability rule/law, should you use? O The multiplication rule for P(A / B) O Definition of the conditional probability O Bayes' theorem O The law of total probability O The addition rule O Definition of the independent events O Axioms of probability Find P(A U B)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


