Question: THERBLIG: A therblig is a basic motion element, the basic building block of virtually all manual work. The 17 therligs were defined by Frank Gilbreth,
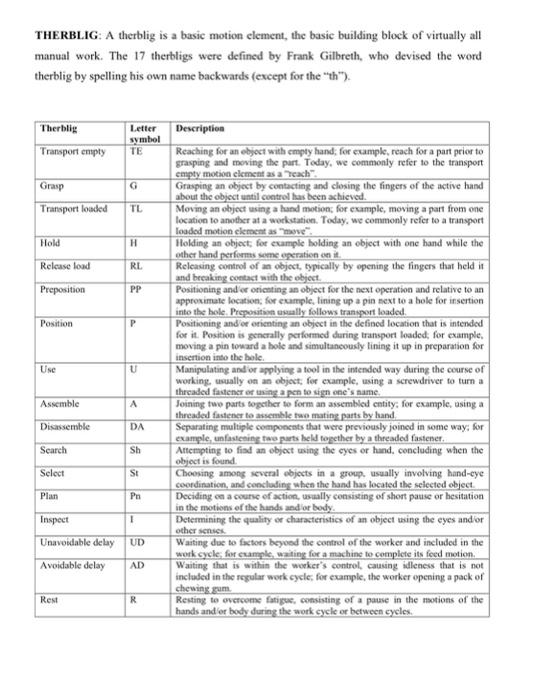
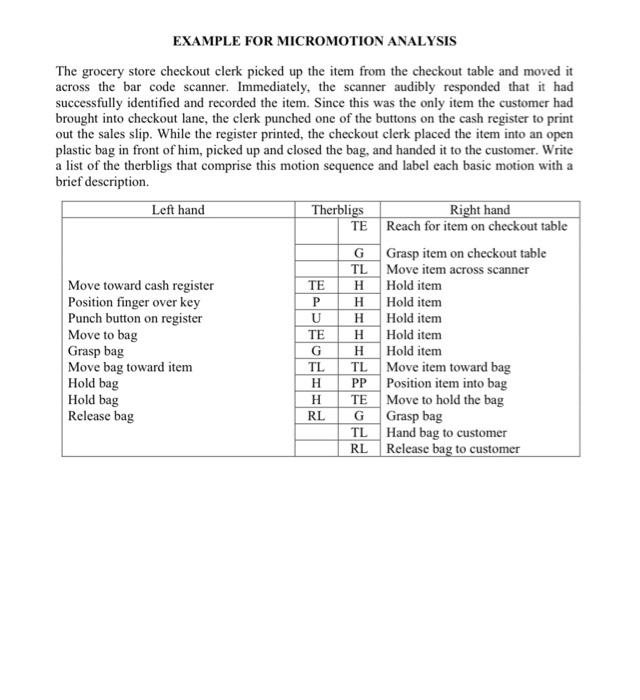
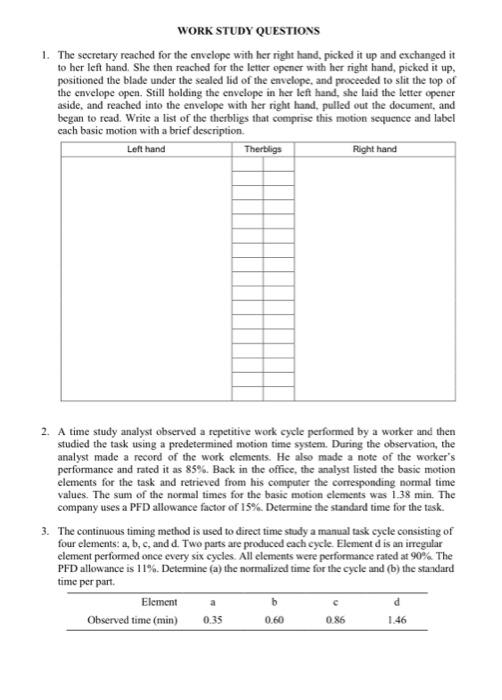
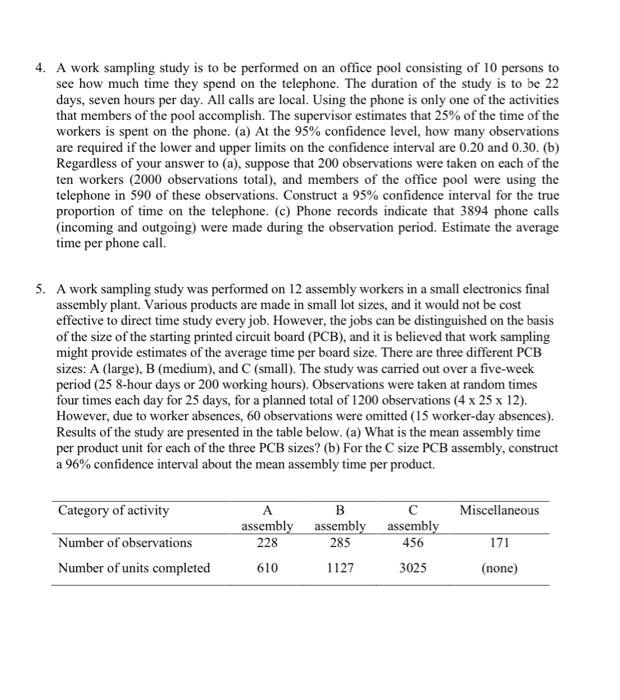
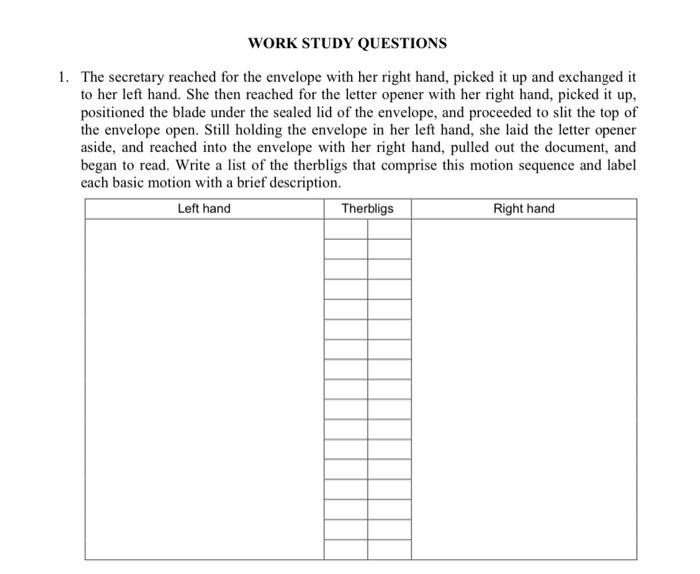
THERBLIG: A therblig is a basic motion element, the basic building block of virtually all manual work. The 17 therligs were defined by Frank Gilbreth, who devised the word therblig by spelling his own name backwards (except for the "th"). Letter Therlig Transport empty symbol TE Grasp G Transport loaded TL Hold H Release load RL Preposition PP Position P Use U Description Reaching for an objoet with empty hand, for example, reach for a part prior to grasping and moving the part. Today, we commonly refer to the transport cmply motion clement as a reach Grasping an object by contacting and closing the fingers of the active hand about the object until control has been achieved. Moving an object using a hand motion for example, moving a part from one location to another at a workstation. Today, we commonly refer to a transport loaded motion clement as me Holding an object, for example holding an object with one hand while the other hand performs some operation on it Releasing control of an object, typically by opening the fingers that held in and breaking contact with the object. Positioning and or orienting an object for the next operation and relative to an approximate location for example, lining up a pin next to a hole for insertion into the hole. Preposition usually follows transport loaded Positioning and or orienting an object in the defined location that is intended for it. Position is generally performed during transport loaded, for example, moving a pin toward a hole and simultaneousiy lining it up in preparation for insertion into the hole. Manipulating and or applying a tool in the intended way during the course of working, usually on an object, for example, using a screwdriver to turn a threaded fastener or using a pen to sign one's name Joining two parts together to form an assembled entity, for example, using a threaded fastener to assemble two mating parts by hand Separating multiple components that were previously joined in some way, for example, unfastening the parts held together by a threaded fastener Attempting to find an object using the eyes or hand, concluding when the object is found Choosing among several objects in a group. usually involving hand-eye coordination, and concluding when the hand has located the scieeted object Deciding on a course of action, usually consisting of short pause or hesitation in the motions of the hands and for body Determining the quality or characteristics of an object using the eyes and or other sche Waiting due to factors beyond the control of the worker and included in the work cycle, for example, waiting for a machine to complete its foed motion Waiting that is within the worker's control, causing idleness that is not included in the regular work cycle, for example, the worker opening a pack of chewing gum Resting to overcome fatigue, consisting of a pause in the motions of the hands and for body during the work cycle or between cycles. Assemble A Disassemble DA Search Sh Select St Plan Pn Inspect 1 Unavoidable delay UD Avoidable delay AD Rest R EXAMPLE FOR MICROMOTION ANALYSIS The grocery store checkout clerk picked up the item from the checkout table and moved it across the bar code scanner. Immediately, the scanner audibly responded that it had successfully identified and recorded the item. Since this was the only item the customer had brought into checkout lane, the clerk punched one of the buttons on the cash register to print out the sales slip. While the register printed, the checkout clerk placed the item into an open plastic bag in front of him, picked up and closed the bag, and handed it to the customer. Write a list of the therbligs that comprise this motion sequence and label each basic motion with a brief description Left hand Therbligs Right hand TE Reach for item on checkout table Grasp item on checkout table TL Move item across scanner Move toward cash register TE H Hold item Position finger over key H Hold item Punch button on register H Hold item Move to bag TE H Hold item Grasp bag G H Hold item Move bag toward item TL TL Move item toward bag Hold bag PP Position item into bag Hold bag Move to hold the bag Release bag Grasp bag Hand bag to customer RL Release bag to customer G P U ! H H RL TE G TL WORK STUDY QUESTIONS 1. The secretary reached for the envelope with her right hand, picked it up and exchanged it to her left hand. She then reached for the letter opener with her right hand, picked it up, positioned the blade under the scaled lid of the envelope, and proceeded to slit the top of the envelope open. Still holding the envelope in her left hand, she laid the letter opener aside, and reached into the envelope with her right hand, pulled out the document, and began to read. Write a list of the therbligs that comprise this motion sequence and label cach basic motion with a brief description Left hand Therligs Right hand 2. A time study analyst observed a repetitive work cycle performed by a worker and then studied the task using a predetermined motion time system. During the observation, the analyst made a record of the work elements. He also made a note of the worker's performance and rated it as 85%. Back in the office, the analyst listed the basic motion elements for the task and retrieved from his computer the corresponding normal time values. The sum of the normal times for the basic motion elements was 1.38 min. The company uses a PFD allowance factor of 15%. Determine the standard time for the task. 3. The continuous timing method is used to direct time study a manual task cycle consisting of four elements: a, b, c, and d. Two parts are produced each cycle. Element dis an irregular element performed once every six cycles. All elements were performance rated at 90%. The PFD allowance is 11%. Determine (a) the normalized time for the cycle and (b) the standard time per part Element b Observed time (min) 1.46 c d 0.35 0.60 0.86 4. A work sampling study is to be performed on an office pool consisting of 10 persons to see how much time they spend on the telephone. The duration of the study is to be 22 days, seven hours per day. All calls are local. Using the phone is only one of the activities that members of the pool accomplish. The supervisor estimates that 25% of the time of the workers is spent on the phone. (a) At the 95% confidence level, how many observations are required if the lower and upper limits on the confidence interval are 0.20 and 0.30. (b) Regardless of your answer to (a), suppose that 200 observations were taken on each of the ten workers (2000 observations total), and members of the office pool were using the telephone in 590 of these observations. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the true proportion of time on the telephone. (c) Phone records indicate that 3894 phone calls (incoming and outgoing) were made during the observation period. Estimate the average time per phone call. 5. A work sampling study was performed on 12 assembly workers in a small electronics final assembly plant. Various products are made in small lot sizes, and it would not be cost effective to direct time study every job. However, the jobs can be distinguished on the basis of the size of the starting printed circuit board (PCB), and it is believed that work sampling might provide estimates of the average time per board size. There are three different PCB sizes: A (large), B (medium), and C (small). The study was carried out over a five-week period (25 8-hour days or 200 working hours). Observations were taken at random times four times each day for 25 days, for a planned total of 1200 observations (4 x 25 x 12). However, due to worker absences, 60 observations were omitted (15 worker-day absences). Results of the study are presented in the table below. (a) What is the mean assembly time per product unit for each of the three PCB sizes? (b) For the size PCB assembly, construct a 96% confidence interval about the mean assembly time per product. Miscellaneous Category of activity Number of observations Number of units completed A B assembly assembly 228 285 610 1127 assembly 456 3025 171 (none) WORK STUDY QUESTIONS 1. The secretary reached for the envelope with her right hand, picked it up and exchanged it to her left hand. She then reached for the letter opener with her right hand, picked it up, positioned the blade under the scaled lid of the envelope, and proceeded to slit the top of the envelope open. Still holding the envelope in her left hand, she laid the letter opener aside, and reached into the envelope with her right hand, pulled out the document, and began to read. Write a list of the therbligs that comprise this motion sequence and label cach basic motion with a brief description Left hand Therligs Right hand 2. A time study analyst observed a repetitive work cycle performed by a worker and then studied the task using a predetermined motion time system. During the observation, the analyst made a record of the work elements. He also made a note of the worker's performance and rated it as 85%. Back in the office, the analyst listed the basic motion elements for the task and retrieved from his computer the corresponding normal time values. The sum of the normal times for the basic motion elements was 1.38 min. The company uses a PFD allowance factor of 15%. Determine the standard time for the task. 3. The continuous timing method is used to direct time study a manual task cycle consisting of four elements: a, b, c, and d. Two parts are produced each cycle. Element dis an irregular element performed once every six cycles. All elements were performance rated at 90%. The PFD allowance is 11%. Determine (a) the normalized time for the cycle and (b) the standard time per part Element b Observed time (min) 1.46 c d 0.35 0.60 0.86 4. A work sampling study is to be performed on an office pool consisting of 10 persons to see how much time they spend on the telephone. The duration of the study is to be 22 days, seven hours per day. All calls are local. Using the phone is only one of the activities that members of the pool accomplish. The supervisor estimates that 25% of the time of the workers is spent on the phone. (a) At the 95% confidence level, how many observations are required if the lower and upper limits on the confidence interval are 0.20 and 0.30. (b) Regardless of your answer to (a), suppose that 200 observations were taken on each of the ten workers (2000 observations total), and members of the office pool were using the telephone in 590 of these observations. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the true proportion of time on the telephone. (c) Phone records indicate that 3894 phone calls (incoming and outgoing) were made during the observation period. Estimate the average time per phone call. 5. A work sampling study was performed on 12 assembly workers in a small electronics final assembly plant. Various products are made in small lot sizes, and it would not be cost effective to direct time study every job. However, the jobs can be distinguished on the basis of the size of the starting printed circuit board (PCB), and it is believed that work sampling might provide estimates of the average time per board size. There are three different PCB sizes: A (large), B (medium), and C (small). The study was carried out over a five-week period (25 8-hour days or 200 working hours). Observations were taken at random times four times each day for 25 days, for a planned total of 1200 observations (4 x 25 x 12). However, due to worker absences, 60 observations were omitted (15 worker-day absences). Results of the study are presented in the table below. (a) What is the mean assembly time per product unit for each of the three PCB sizes? (b) For the size PCB assembly, construct a 96% confidence interval about the mean assembly time per product. Miscellaneous Category of activity Number of observations Number of units completed A B assembly assembly assembly 228 285 456 610 1127 3025 171 (none) WORK STUDY QUESTIONS 1. The secretary reached for the envelope with her right hand, picked it up and exchanged it to her left hand. She then reached for the letter opener with her right hand, picked it up, positioned the blade under the sealed lid of the envelope, and proceeded to slit the top of the envelope open. Still holding the envelope in her left hand, she laid the letter opener aside, and reached into the envelope with her right hand, pulled out the document, and began to read. Write a list of the therbligs that comprise this motion sequence and label each basic motion with a brief description. Left hand Therbligs Right hand 2. A time study analyst observed a repetitive work cycle performed by a worker and then studied the task using a predetermined motion time system. During the observation, the analyst made a record of the work elements. He also made a note of the worker's performance and rated it as 85%. Back in the office, the analyst listed the basic motion elements for the task and retrieved from his computer the corresponding normal time values. The sum of the normal times for the basic motion elements was 1.38 min. The company uses a PFD allowance factor of 15%. Determine the standard time for the task. 3. The continuous timing method is used to direct time study a manual task cycle consisting of four elements: a, b, c, and d. Two parts are produced each cycle. Element d is an irregular element performed once every six cycles. All elements were performance rated at 90%. The PFD allowance is 11%. Determine (a) the normalized time for the cycle and (b) the standard time per part Element b d Observed time (min) 0.35 0.60 0.86 1.46 a