Question: These equations may be useful: Coating metals with paint typically requires solvents, which are significant sources of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Many states have significantly

These equations may be useful:
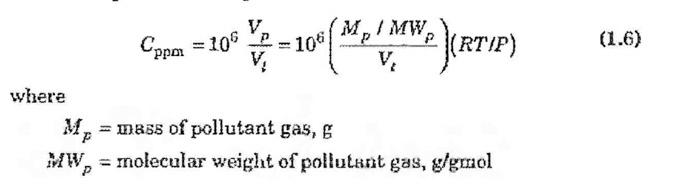
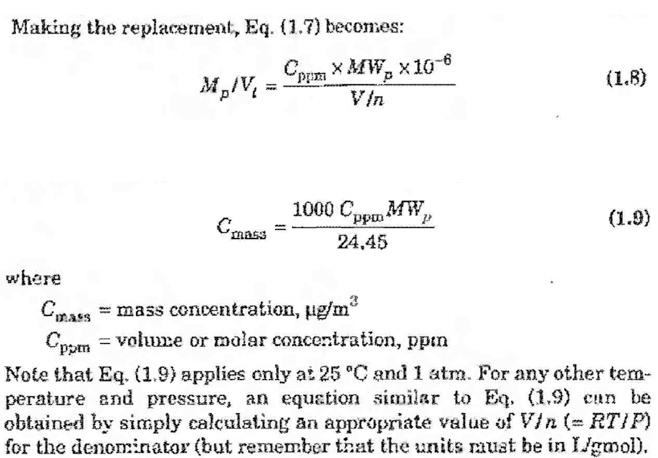
Coating metals with paint typically requires solvents, which are significant sources of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Many states have significantly restricted the use of solvents as oxides of nitrogen have dropped in an effort to curb ozone formation. Consider a car body manufacturer at sea level that passes painted doors through a drying oven. The air is heated to 50C at atmospheric pressure. The solvent carrying the paint pigment, which has a molecular weight of 90, dries at a rate of 0.83 g/hr into air that is flowing at a rate of 500 m3/min. The air is drawn in from outdoors, passed through the oven, and emitted back outdoors through a short stack. The temperature of the air outdoors is 25C. a. What is the molecular weight of the air? b. What is the concentration of the solvent in the exhaust in parts per million? Copa 200 -100(0,55MW ) RTUP) 2 ( = (1.6) Vi V / / = V. where Mo = mass of pollutant gas, & MW, = molecular weight of pollutant gas, gmol Making the replacement, Eq. (1.7) becomes: MA/V = Oppima XA1W, X10-6 (1.8) 3 1000 Cppo MW, (1.9) 24.45 where Comass = mass concentration, ug/m2 Cppen = volume or malar concentration, ppn , Note that Eq. (1.9) applies only a: 25 C and 1 atm. For any other tem- perature and pressure, an equation similar to Eq. (1.9) can be obtained by simply calculating an appropriate value of Vin (= RT/P) for the denominator (but remember that the units must be in Imol)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


