Question: Thick - walled cylinder ( TWC ) tests ( as shown in the figure below ) is a commonly used experimental technique for determining the
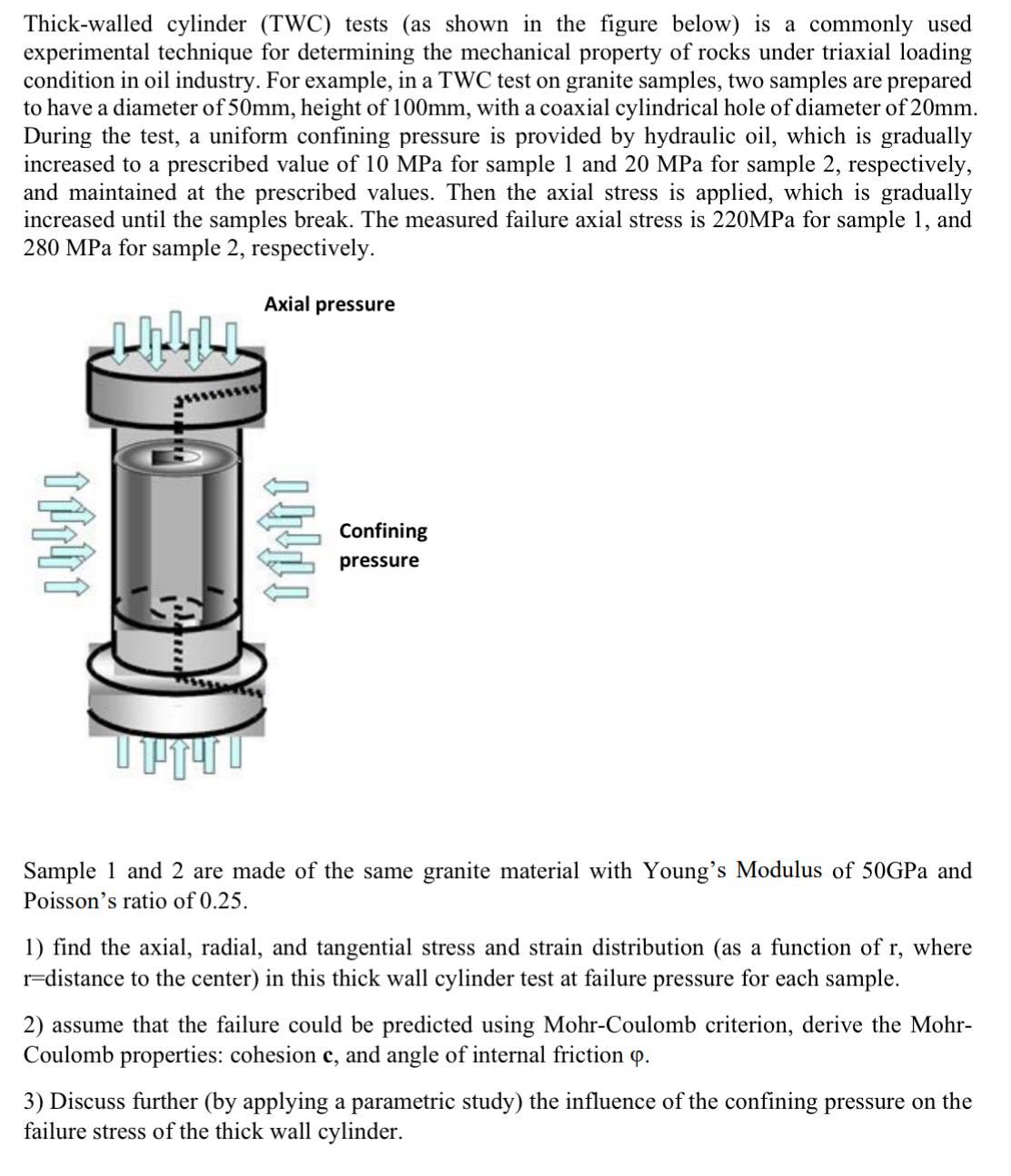
Thickwalled cylinder TWC tests as shown in the figure below is a commonly used experimental technique for determining the mechanical property of rocks under triaxial loading condition in oil industry. For example, in a TWC test on granite samples, two samples are prepared to have a diameter of mm height of mm with a coaxial cylindrical hole of diameter of mm During the test, a uniform confining pressure is provided by hydraulic oil, which is gradually increased to a prescribed value of MPa for sample and MPa for sample respectively, and maintained at the prescribed values. Then the axial stress is applied, which is gradually increased until the samples break. The measured failure axial stress is MPa for sample and MPa for sample respectively.
Sample and are made of the same granite material with Young's Modulus of GPa and Poisson's ratio of
find the axial, radial, and tangential stress and strain distribution as a function of r where distance to the center in this thick wall cylinder test at failure pressure for each sample.
assume that the failure could be predicted using MohrCoulomb criterion, derive the MohrCoulomb properties: cohesion and angle of internal friction
Discuss further by applying a parametric study the influence of the confining pressure on the failure stress of the thick wall cylinder.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


