Question: This assignment focuses on arrays and file/text processing. Turn in a file named DNA.java. You will also need the two input files dna.txt and ecoli.txt
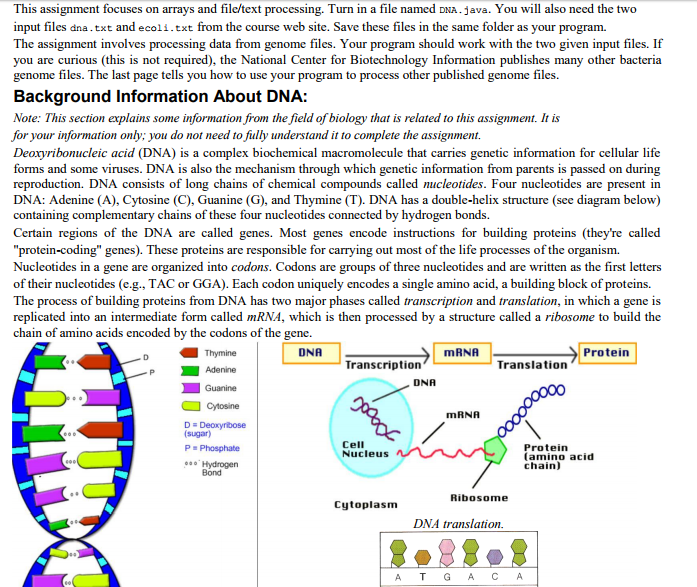






This assignment focuses on arrays and file/text processing. Turn in a file named DNA.java. You will also need the two input files dna.txt and ecoli.txt from the course web site. Save these files in the same folder as your program. The assignment involves processing data from genome files. Your program should work with the two given input files. If you are curious (this is not required), the National Center for Biotechnology Information publishes many other bacteria genome files. The last page tells you how to use your program to process other published genome files. Background Information About DNA: Note: This section explains some information from the field of biology that is related to this assignment. It is for your information only; you do not need to fully understand it to complete the assignment. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a complex biochemical macromolecule that carries genetic information for cellular life forms and some viruses. DNA is also the mechanism through which genetic information from parents is passed on during reproduction. DNA consists of long chains of chemical compounds called nucleotides. Four nucleotides are present in DNA: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Thymine (T). DNA has a double-helix structure (see diagram below) containing complementary chains of these four nucleotides connected by hydrogen bonds. Certain regions of the DNA are called genes. Most genes encode instructions for building proteins (they're called "protein-coding" genes). These proteins are responsible for carrying out most of the life processes of the organism. Nucleotides in a gene are organized into codons. Codons are groups of three nucleotides and are written as the first letters of their nucleotides (e.g., TAC or GGA). Each codon uniquely encodes a single amino acid, a building block of proteins. The process of building proteins from DNA has two major phases called transcription and translation, in which a gene is replicated into an intermediate form called mRNA, which is then processed by a structure called a ribosome to build the chain of amino acids encoded by the codons of the gene. Thymine PAdenine Guanine Cytosine DNA MRNA Protein Transcription Translation DNA MRNA (sugar) P-Phosphate ... Hydrogen Cell Nucleus Protein (amino acid chain) Bond Ribosome Cytoplasm DNA translation A T G A C A This assignment focuses on arrays and file/text processing. Turn in a file named DNA.java. You will also need the two input files dna.txt and ecoli.txt from the course web site. Save these files in the same folder as your program. The assignment involves processing data from genome files. Your program should work with the two given input files. If you are curious (this is not required), the National Center for Biotechnology Information publishes many other bacteria genome files. The last page tells you how to use your program to process other published genome files. Background Information About DNA: Note: This section explains some information from the field of biology that is related to this assignment. It is for your information only; you do not need to fully understand it to complete the assignment. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a complex biochemical macromolecule that carries genetic information for cellular life forms and some viruses. DNA is also the mechanism through which genetic information from parents is passed on during reproduction. DNA consists of long chains of chemical compounds called nucleotides. Four nucleotides are present in DNA: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Thymine (T). DNA has a double-helix structure (see diagram below) containing complementary chains of these four nucleotides connected by hydrogen bonds. Certain regions of the DNA are called genes. Most genes encode instructions for building proteins (they're called "protein-coding" genes). These proteins are responsible for carrying out most of the life processes of the organism. Nucleotides in a gene are organized into codons. Codons are groups of three nucleotides and are written as the first letters of their nucleotides (e.g., TAC or GGA). Each codon uniquely encodes a single amino acid, a building block of proteins. The process of building proteins from DNA has two major phases called transcription and translation, in which a gene is replicated into an intermediate form called mRNA, which is then processed by a structure called a ribosome to build the chain of amino acids encoded by the codons of the gene. Thymine PAdenine Guanine Cytosine DNA MRNA Protein Transcription Translation DNA MRNA (sugar) P-Phosphate ... Hydrogen Cell Nucleus Protein (amino acid chain) Bond Ribosome Cytoplasm DNA translation A T G A C A
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


