Question: this case, $0) and another total visits. Total visits is the sum from each place. Total Alabaster Beautiful Cornucopia Admission Cost Visiv Visits Cost/ Visit
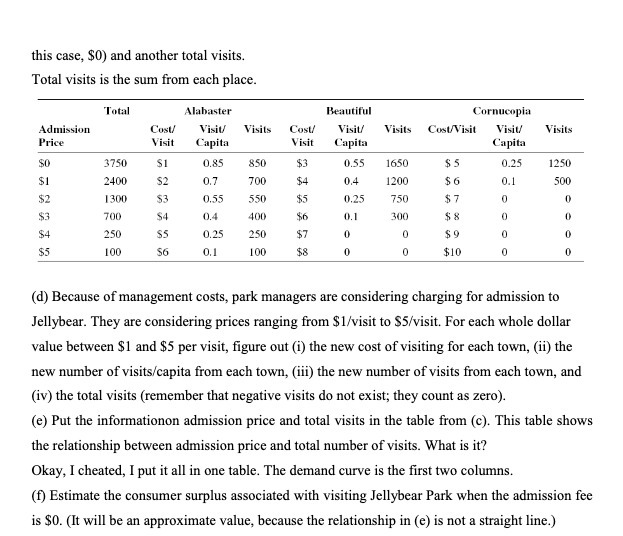
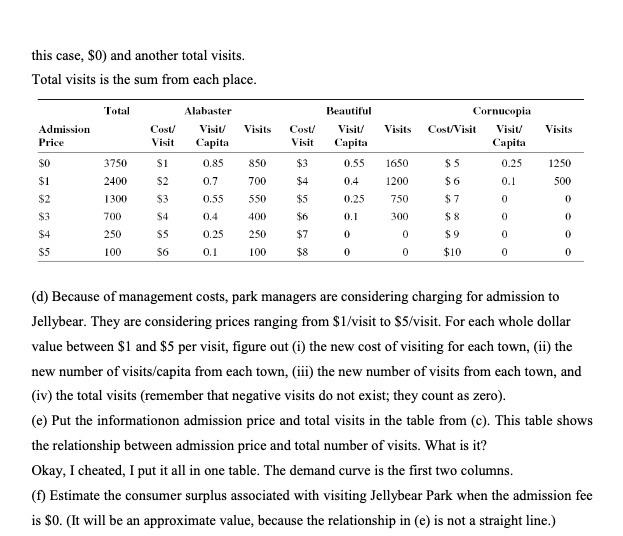
this case, $0) and another total visits. Total visits is the sum from each place. Total Alabaster Beautiful Cornucopia Admission Cost Visiv Visits Cost/ Visit Visits Cost/Visit Visiv Visits Price Visit Capita Visit Capita Capita 3750 $1 0.85 850 0.55 1650 $5 0.25 1250 $1 2400 $2 0,7 700 $4 0,4 1200 $G 0.1 500 $2 1300 $3 0,55 550 $5 0.25 750 $7 0 0 $3 700 0.4 400 $6 0.1 300 0 0 $4 250 0.25 250 $7 0 $9 $5 100 0.1 100 $8 $10 (d) Because of management costs, park managers are considering charging for admission to Jellybear. They are considering prices ranging from $1/visit to $5/visit. For each whole dollar value between $1 and $5 per visit, figure out (i) the new cost of visiting for each town, (ii) the new number of visits/capita from each town, (iii) the new number of visits from each town, and (iv) the total visits (remember that negative visits do not exist; they count as zero). (e) Put the informationon admission price and total visits in the table from (c). This table shows the relationship between admission price and total number of visits. What is it? Okay, I cheated, I put it all in one table. The demand curve is the first two columns. (f) Estimate the consumer surplus associated with visiting Jellybear Park when the admission fee is $0. (It will be an approximate value, because the relationship in (e) is not a straight line.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


