Question: This case study has been divided into three (3) components. You are to design a network, research and source appropriate devices justifying choices (feasibility,

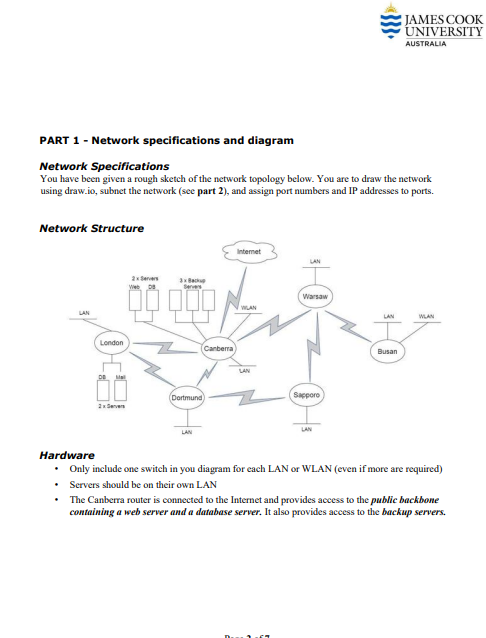
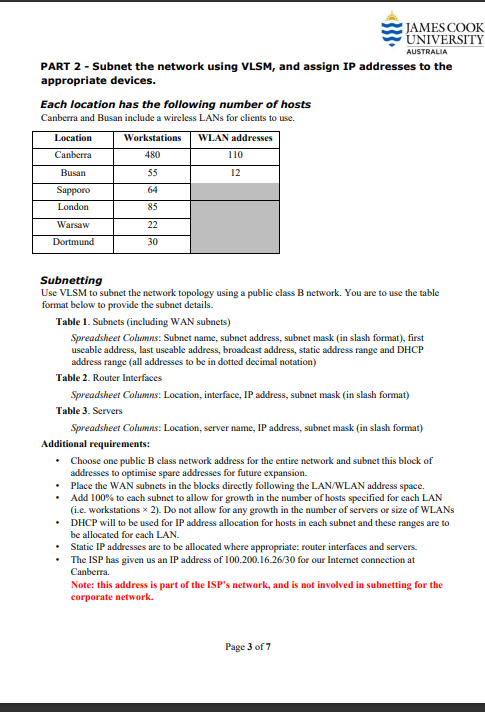

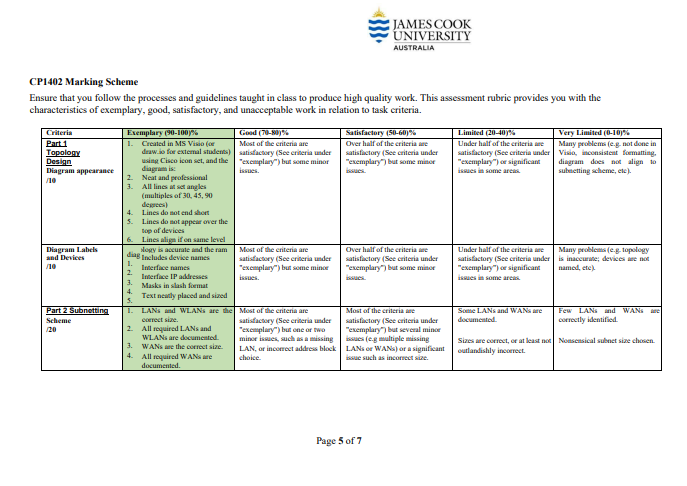
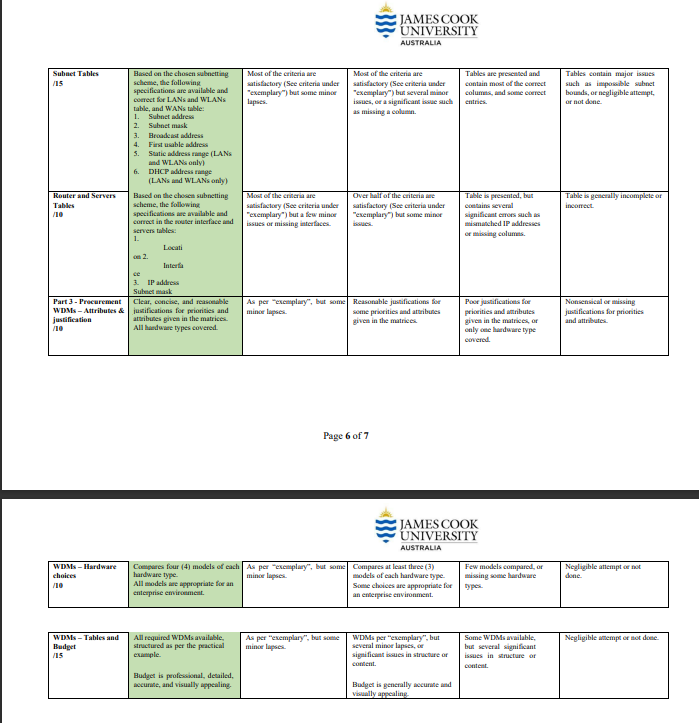
This case study has been divided into three (3) components. You are to design a network, research and source appropriate devices justifying choices (feasibility, efficiency, etc.), subnet the network, assign IP addresses to the appropriate devices, Note: This is not a group project. Each student must individually complete all parts of their submission. Students must start with a new document and they must not have another person's file in their possession at any time. Students may discuss the task with each other, but each student must write their assignment independently and not show their work to other students. Deliverables 1. A single Word document (.docx) - containing all parts Assignment breakdown Scenario MyNetwork Services Inc., a data analytics company, has asked you to assess and redesign their network. They are opening a new branch in Busan, which will require new equipment. They have existing contracts and hardware to maintain fibre-optic leased line WAN links between sites. PART 1- Network diagram PART 2 - Subnet the network and assign IP addresses to the appropriate devices PART 3 - Research and source appropriate devices justifying choices (feasibility, efficiency, etc.) with a Weighted Scoring Model (WSM) PART 1 - Network specifications and diagram Network Specifications You have been given a rough sketch of the network topology below. You are to draw the network using draw.io, subnet the network (see part 2), and assign port numbers and IP addresses to ports. Network Structure LAN London DB Ma 2x Server 3xBackup Servers Canberra (Dortmund) LAN Internet LAN LAN Warsaw Sapporo LAN LAN JAMES COOK UNIVERSITY AUSTRALIA Busan WLAN Hardware Only include one switch in you diagram for each LAN or WLAN (even if more are required) Servers should be on their own LAN The Canberra router is connected to the Internet and provides access to the public backbone containing a web server and a database server. It also provides access to the backup servers. AUSTRALIA PART 2 - Subnet the network using VLSM, and assign IP addresses to the appropriate devices. Each location has the following number of hosts Canberra and Busan include a wireless LANs for clients to use. Location Canberra Busan Sapporo London Warsaw Dortmund Workstations WLAN addresses 480 55 64 85 22 30 110 12 JAMES COOK UNIVERSITY Subnetting Use VLSM to subnet the network topology using a public class B network. You are to use the table format below to provide the subnet details. Table 1. Subnets (including WAN subnets) Spreadsheet Columns: Subnet name, subnet address, subnet mask (in slash format), first useable address, last useable address, broadcast address, static address range and DHCP address range (all addresses to be in dotted decimal notation) Table 2. Router Interfaces Spreadsheet Columns: Location, interface, IP address, subnet mask (in slash format) Table 3. Servers Spreadsheet Columns: Location, server name, IP address, subnet mask (in slash format) Additional requirements: Choose one public B class network address for the entire network and subnet this block of addresses to optimise spare addresses for future expansion. Place the WAN subnets in the blocks directly following the LAN/WLAN address space. Add 100% to each subnet to allow for growth in the number of hosts specified for each LAN (i.e. workstations x 2). Do not allow for any growth in the number of servers or size of WLANs DHCP will to be used for IP address allocation for hosts in each subnet and these ranges are to be allocated for each LAN. Static IP addresses are to be allocated where appropriate: router interfaces and servers. The ISP has given us an IP address of 100.200.16.26/30 for our Internet connection at Canberra. Note: this address is part of the ISP's network, and is not involved in subnetting for the corporate network. Page 3 of 7 PART 3 - Research and source appropriate devices justifying choices (feasibility, efficiency, etc.) JAMES COOK UNIVERSITY AUSTRALIA You are to research and submit a project procurement plan for the Busan network. The devices you must include are routers, switches, and wireless access points. Make sure the devices you select can handle the number of workstations required and provide a good quality of service to wired and wireless users. Devices should be enterprise-grade, not home or gaming equipment. Your project plan and final recommendations should be based on a Weighted Decision Matrix (like the WDM you did in the Procurement Practical). You are to compare four (4) devices from each category and to base the decision on reasonable and well-justified attributes. The budget for procurement is $4,000. You may exceed this if you can justify it well. Your project plan is to contain the following components: Weighted Decision Matrix - hardware resource requirements analysis Include a written justification for priorities and attributes given in the matrix Create your WDMs in Excel and copy and paste them into your Word doc Budget Create a well-presented table of the prices of all devices and the total cost Include hardware only, not labour Criteria Part 1 Topology Design Diagram appearance /10 CP1402 Marking Scheme Ensure that you follow the processes and guidelines taught in class to produce high quality work. This assessment rubric provides you with the characteristics of exemplary, good, satisfactory, and unacceptable work in relation to task criteria. Diagram Labels and Devices Part 2 Subnetting Scheme /20 Exemplary (90-100)% 1. Created in MS Visio (or draw.io for external students) using Cisco icon set, and the 2 3. 4. 5. nimiv 6. diag Includes device names 1. Interface names Interface IP addresses Masks in slash format 2 4. 5. Neat and professional All lines atset angles (multiples of 30, 45,90 degrees) Lines do not end short Lines do not appear over the top of devices 3. 4. Lines align if on same level slogy is accurate and the ram Text neatly placed and sized 1. LANs and WLANs are the correct size. 2. All required LANs and WLANs are documented. WANs are the correct size. All required WANs are documented. Good (70-80)% Most of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") but some minor issues. Most of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") but some minor issues. Most of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") but one or two minor issues, such as a missing LAN, or incorrect address block choice. JAMES COOK UNIVERSITY AUSTRALIA Satisfactory (50-60)% Over half of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") but some minor Over half of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") but some minor Page 5 of 7 Most of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") but several minor issues (eg multiple missing LANs or WAN) or a significant issue such as incorrect size. Limited (20-40)% Under half of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") or significant issues in some areas. Under half of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") or significant issues in some areas. Some LANs and WANs are documented. Very Limited (0-10)% Many problems (e.g. not done in Visio, inconsistent formatting. diagram does not align to subnetting scheme, etc). Many problems (e.g. topology is inaccurate; devices are not named, etc). Few LANs and WANs are correctly identified. Sizes are correct, or at least not Nonsensical subnet size chosen. outlandishly incorrect. Subnet Tables /15 Router and Servers Tables /10 Part3 - Procurement WDMs-Attributes & justification /10 choices /10 Based on the chosen subnetting scheme, the following specifications are available and correct for LANs and WLANS table, and WANs table: Subnet address 1. 2. Subnet mask 3. Broadcast address 4. First usable address 5. WDMs - Tables and Budget /15 Static address range (LAN and WLANS only) 6. DHCP address range (LAN and WLANs only) Based on the chosen subnetting scheme, the following specifications are available and correct in the router interface and servers tables: on 2. Locati Interfa WDMs-Hardware Compares four (4) models of each hardware type. All models are appropriate for an enterprise environment. ce 3. IP address Subnet mask Clear, concise, and reasonable justifications for priorities and attributes given in the matrices. All hardware types covered. All required WDMs available, structured as per the practical example. Budget is professional, detailed, accurate, and visually appealing. Most of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") but some minor lapses. Most of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") but a few minor issues or missing interfaces. JAMES COOK UNIVERSITY AUSTRALIA Most of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") but several minor issues, or a significant lsue such as missing a column. Page 6 of 7 As per "exemplary", but some minor lapses. Over half of the criteria are satisfactory (See criteria under "exemplary") but some minor As per "exemplary", but some Reasonable justifications for minor lapses. some priorities and attributes given in the matrices AUSTRALIA As per "exemplary", but some Compares at least three (3) minor lapses. models of each hardware type. Some choices are appropriate for an enterprise environment. JAMES COOK UNIVERSITY WDMs per "exemplary", but several minor lapses, or significant issues in structure or content. Tables are presented and contain most of the correct columns, and some correct entries. Budget is generally accurate and visually appealing. Table is presented, but contains several significant errors such as mismatched IP addresses ce amouissing, columams. Poor justifications for priorities and attributes given in the matrices, or only one hardware type covered. Few models compared, or missing some hardware types. Some WDMs available, but several significant issues in structure or Tables contain major issues such as impossible subnet bounds, or negligible attempt, or not done Table is generally incomplete or incorrect Nonsensical or missing justifications for priorities and attributes. Negligible attempt or not done. Negligible attempt or not done.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


