Question: This homework problem is designed to help you achieve the following course objective: Find roots of equations using bracketing and open methods; explain the differences
This homework problem is designed to help you achieve the following course objective:
Find roots of equations using bracketing and open methods; explain the differences between the two methods and point out the advantage of each method.
Problem Description: Develop a MATLAB function to find the root of a user-specified function using a user-specified computational method. Implement all of the following methods:
(a) the bisection method
(b) the false position method
(c) the built-in "fzero" function with an initial bracketing interval
(d) the fixed point iteration method
(e) the Newton-Raphson method
(f) the built-in "fzero" function with an initial guess
Read the function template for more details. Note that (c) and (f) have already been implemented in the template. Therefore you only need to enable (a), (b), (d) and (e).
Hint: You may re-use functions and subfunctions developed in the past.
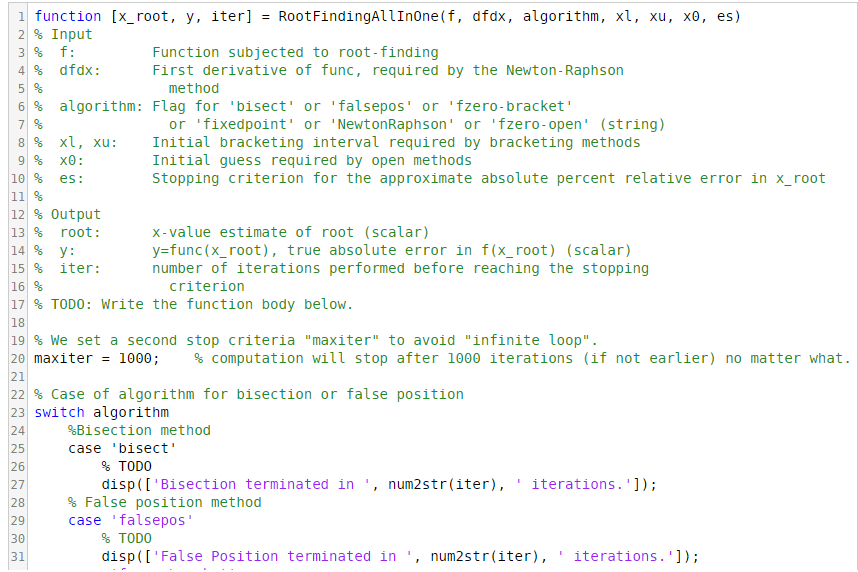
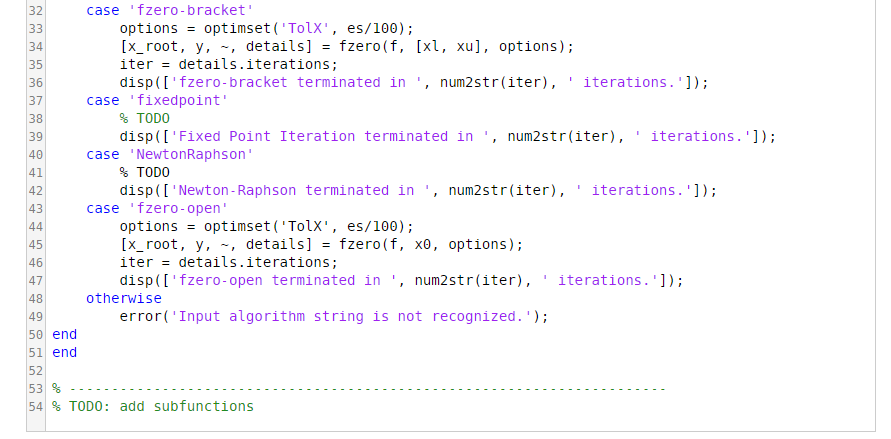
I function [s_root' y, iter) Root FindingAl11nOne(f, dfdx, algorithm, xl, xu, x0, es) 2% Input 3% f: 4 % dfdx : 5/% 6% algorithm : Flag for 'bisect' or 'falsepos' or 'fzero-bracket' 71 % Function subjected to root-finding First derivative of func, required by the Newton-Raphson method or 'fixedpoint' or 'NewtonRaphson' or'fzero-open' (string) Initial bracketing interval required by bracketing methods Initial guess required by open methods Stopping criterion for the approximate absolute percent relative error in x_root 11 % es : 11% 12| % Output 13 % root : 24% : 15 % iter: 161 % 17 % TODO: write the function body below 18 19% we set a second stop criteria "maxiter" to avoid "infinite loop". 20 maxiter-1000; 21 22% Case of algorithm for bisection or false position 23 switch algorithm x-value estimate of root (scalar) y-func(x_root), true absolute error in f(x_root) (scalar) number of iterations performed before reaching the stopping criterion % computation will stop after 1000 iterations (if not earlier) no matter what. %B1 section method case 'bisect 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 % TODO disp(['Bisection terminated in ', num2str(iter), iterations.); ' % False position method case 'falsepos" % TODO disp([' False Position terminated in . num2str(iter), iterations.']); I function [s_root' y, iter) Root FindingAl11nOne(f, dfdx, algorithm, xl, xu, x0, es) 2% Input 3% f: 4 % dfdx : 5/% 6% algorithm : Flag for 'bisect' or 'falsepos' or 'fzero-bracket' 71 % Function subjected to root-finding First derivative of func, required by the Newton-Raphson method or 'fixedpoint' or 'NewtonRaphson' or'fzero-open' (string) Initial bracketing interval required by bracketing methods Initial guess required by open methods Stopping criterion for the approximate absolute percent relative error in x_root 11 % es : 11% 12| % Output 13 % root : 24% : 15 % iter: 161 % 17 % TODO: write the function body below 18 19% we set a second stop criteria "maxiter" to avoid "infinite loop". 20 maxiter-1000; 21 22% Case of algorithm for bisection or false position 23 switch algorithm x-value estimate of root (scalar) y-func(x_root), true absolute error in f(x_root) (scalar) number of iterations performed before reaching the stopping criterion % computation will stop after 1000 iterations (if not earlier) no matter what. %B1 section method case 'bisect 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 % TODO disp(['Bisection terminated in ', num2str(iter), iterations.); ' % False position method case 'falsepos" % TODO disp([' False Position terminated in . num2str(iter), iterations.'])
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


