Question: This information is also given for help 3. Consider the pressure-driven flow of an incompressible Newtonian fluid in the annular region between two coaxial cylinders

This information is also given for help

![flow conditions, rz=2LPLR[(Rr)2(rR)] where the constant is determined by the condition that](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f8e51276be2_60266f8e5120a8c9.jpg)
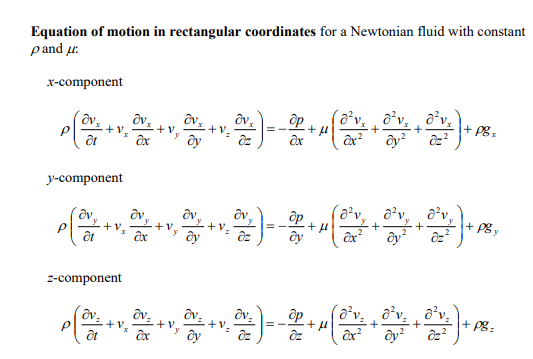
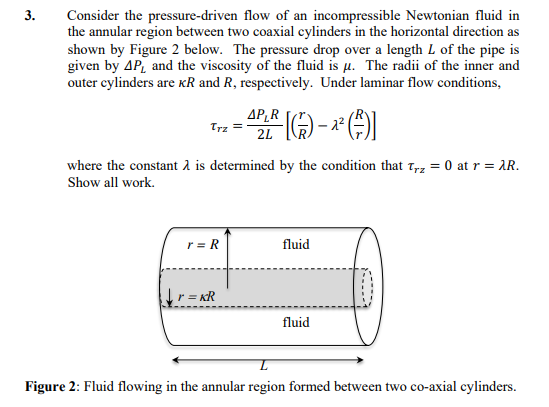
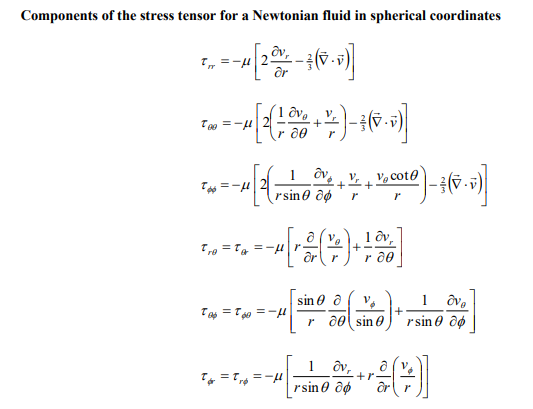
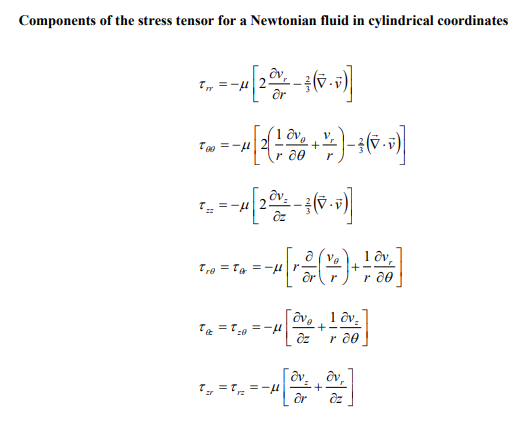
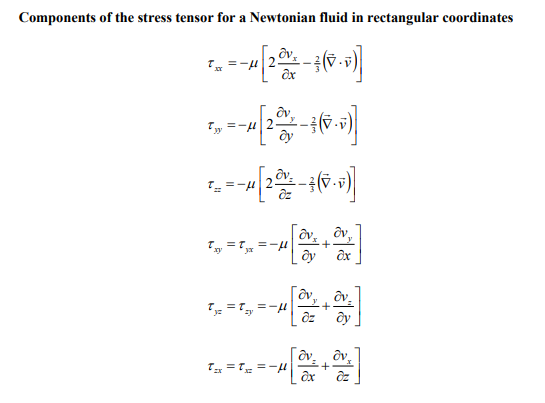
3. Consider the pressure-driven flow of an incompressible Newtonian fluid in the annular region between two coaxial cylinders in the horizontal direction as shown by Figure 2 below. The pressure drop over a length L of the pipe is given by PL and the viscosity of the fluid is . The radii of the inner and outer cylinders are R and R, respectively. Under laminar flow conditions, rz=2LPLR[(Rr)2(rR)] where the constant is determined by the condition that rz=0 at r=R. Show all work. Figure 2: Fluid flowing in the annular region formed between two co-axial cylinders. a) What are the boundary conditions for this problem? b) Derive an expression for the velocity profile vz in terms of L,,R,r, , and PL. c) Determine the maximum velocity vz,max in terms of L,,R,, and PL d) Calculate the force exerted by the fluid on the inner cylinder and on the outer cylinder. The final answer should be expressed in terms of R,, and PL. e) Determine the volumetric flowrate Q in terms of L,,R,, and PL. Components of the stress tensor for a Newtonian fluid in spherical coordinates rr=[2rvr32(v)]=[2(r1v+rvr)32(v)]=[2(rsin1v+rvr+rvcot)32(v)]r==[rr(rv)+r1vr]==[rsin(sinv)+rsin1v]=r=[rsin1vr+rr(rv)] Components of the stress tensor for a Newtonian fluid in cylindrical coordinates rr=[2rvr32(v)]=[2(r1v+rvr)32(v)]zz=[2zvz32(v)]r=r=[rr(rv)+r1vr]z=z=[zv+r1vz]zr=rz=[rvz+zvr] Components of the stress tensor for a Newtonian fluid in rectangular coordinates xx=[2xvx32(v)]yy=[2yvy32(v)]zz=[2zvz32(v)]xy=yx=[yvx+xvy]yz=zy=[zvy+yvz]zx=xz=[xvz+zvx] Equation of motion in spherical coordinates for a Newtonian fluid with constant and . r-component (tvr+vrrvr+rvvr+rsinvvrrv2+v2)=rp+[r21r22(r2vr)+r2sin1(sinvr)+r2sin2122vr]+gr -component (tv+vrrv+rvv+rsinvv+rvrvrv2cot)=r1p+[r21r(r2rv)+r21(sin1(vsin))+r2sin2122v+r22vrr2sin22cosv]+g -component (tv+vrrv+rvv+rsinvv+rvvr+rvvcot)=rsin1p+[r21r(r2rv)+r21(sin1(vsin))+r2sin2122v+r2sin2vr+r2sin22cosv]+g Equation of motion in cylindrical coordinates for a Newtonian fluid with constant and . r-component (tvr+vrrvr+rvvrrv2+vzzvr)=rp+[r(r1r(rvr))+r2122vrr22v+z22vr]+gr -component (tv+vrrv+rvv+rvrv+vzzv)=r1p+[r(r1r(rv))+r2122v+r22vr+z22v]+gz-component(tvz+vrrvz+rvvz+vzzvz)=zp+[r1r(rrvz)+r2122vz+z22vz]+gz Equation of motion in rectangular coordinates for a Newtonian fluid with constant and : x-component (tvx+vxxvx+vyyvx+vzzvx)=xp+(x22vx+y22vx+z22vx)+gx y-component (tvy+vxxvy+vyyvy+vzzvy)=yp+(x22vy+y22vy+z22vy)+gy z-component (tvz+vxxvz+vyyvz+vzzvz)=zp+(x22vz+y22vz+z22vz)+gz
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


