Question: This information is also given for help Answer all parts of this question. a) Consider a cooling tower of height 25 metres containing water droplets

This information is also given for help
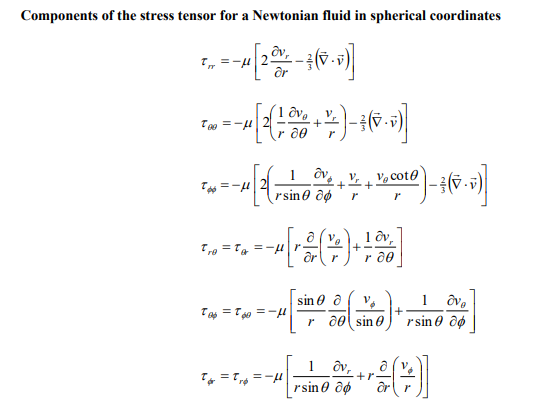
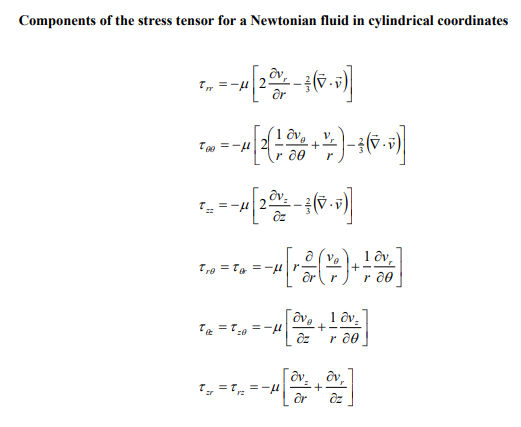
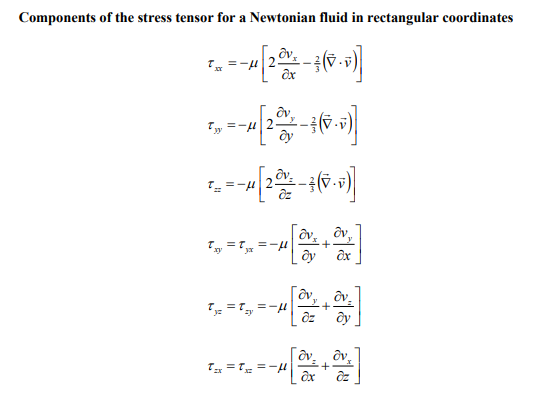

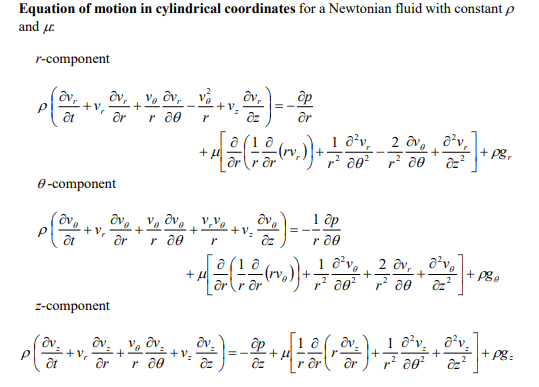
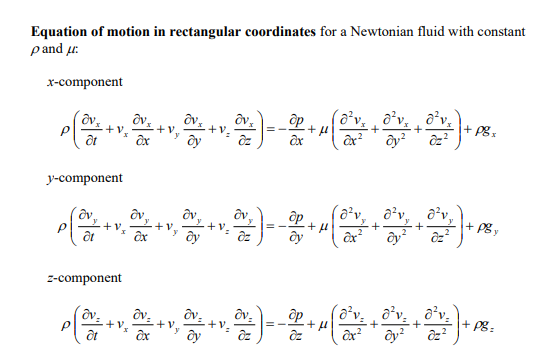
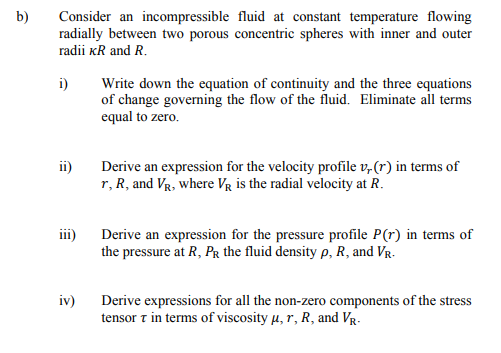
Answer all parts of this question. a) Consider a cooling tower of height 25 metres containing water droplets with diameter equal to 0.5mm and density equal to 1gcm3. The viscosity of air is equal to 0.018cp(1cp=0.001Pas). Assume the air is at atmospheric pressure, behaves as an ideal gas at 298K, and only contains oxygen and nitrogen where the mole fraction of oxygen is equal to 0.21 . The molecular weight of oxygen is 32gmol1 and nitrogen is 28gmol1. i) Estimate the terminal velocity of the water droplet using the Stokes' law to calculate the drag force on the droplet. ii) How long does it take for a droplet to fall from the top of the cooling tower to the ground when there is an upward air velocity equal to 3ms1. Assume the droplet diameter remains constant during the fall. ii) Is the assumption to use Stokes' law valid? Consider an incompressible fluid at constant temperature flowing radially between two porous concentric spheres with inner and outer radii R and R. i) Write down the equation of continuity and the three equations of change governing the flow of the fluid. Eliminate all terms equal to zero. ii) Derive an expression for the velocity profile vr(r) in terms of r,R, and VR, where VR is the radial velocity at R. iii) Derive an expression for the pressure profile P(r) in terms of the pressure at R,PR the fluid density ,R, and VR. iv) Derive expressions for all the non-zero components of the stress tensor in terms of viscosity ,r,R, and VR. Components of the stress tensor for a Newtonian fluid in spherical coordinates rr=[2rvr32(v)]=[2(r1v+rvr)32(v)]=[2(rsin1v+rvr+rvcot)32(v)]r==[rr(rv)+r1vr]==[rsin(sinv)+rsin1v]=r=[rsin1vr+rr(rv)] Components of the stress tensor for a Newtonian fluid in cylindrical coordinates rr=[2rvr32(v)]=[2(r1v+rvr)32(v)]zz=[2zvz32(v)]r=r=[rr(rv)+r1vr]z=z=[zv+r1vz]zr=rz=[rvz+zvr] Components of the stress tensor for a Newtonian fluid in rectangular coordinates xx=[2xvx32(v)]yy=[2yvy32(v)]zz=[2zvz32(v)]xy=yx=[yvx+xvy]yz=zy=[zvy+yvz]zx=xz=[xvz+zvx] Equation of motion in spherical coordinates for a Newtonian fluid with constant and . r-component (tvr+vrrvr+rvvr+rsinvvrrv2+v2)=rp+[r21r22(r2vr)+r2sin1(sinvr)+r2sin2122vr]+gr -component (tv+vrrv+rvv+rsinvv+rvrvrv2cot)=r1p+[r21r(r2rv)+r21(sin1(vsin))+r2sin2122v+r22vrr2sin22cosv]+g -component (tv+vrrv+rvv+rsinvv+rvvr+rvvcot)=rsin1p+[r21r(r2rv)+r21(sin1(vsin))+r2sin2122v+r2sin2vr+r2sin22cosv]+g Equation of motion in cylindrical coordinates for a Newtonian fluid with constant and . r-component (tvr+vrrvr+rvvrrv2+vzzvr)=rp+[r(r1r(rvr))+r2122vrr22v+z22vr]+gr -component (tv+vrrv+rvv+rvrv+vzzv)=r1p+[r(r1r(rv))+r2122v+r22vr+z22v]+gz-component(tvz+vrrvz+rvvz+vzzvz)=zp+[r1r(rrvz)+r2122vz+z22vz]+gz Equation of motion in rectangular coordinates for a Newtonian fluid with constant and : x-component (tvx+vxxvx+vyyvx+vzzvx)=xp+(x22vx+y22vx+z22vx)+gx y-component (tvy+vxxvy+vyyvy+vzzvy)=yp+(x22vy+y22vy+z22vy)+gy z-component (tvz+vxxvz+vyyvz+vzzvz)=zp+(x22vz+y22vz+z22vz)+gz
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


