Question: This is a doubly linked list. Please implement the following functions, in C, provided below. Do not modify the signatures ( names and arguments )
This is a doubly linked list. Please implement the following functions, in C, provided below. Do not modify the signatures ( names and arguments ) of these functions just provide the implementation (i.e. body of code).
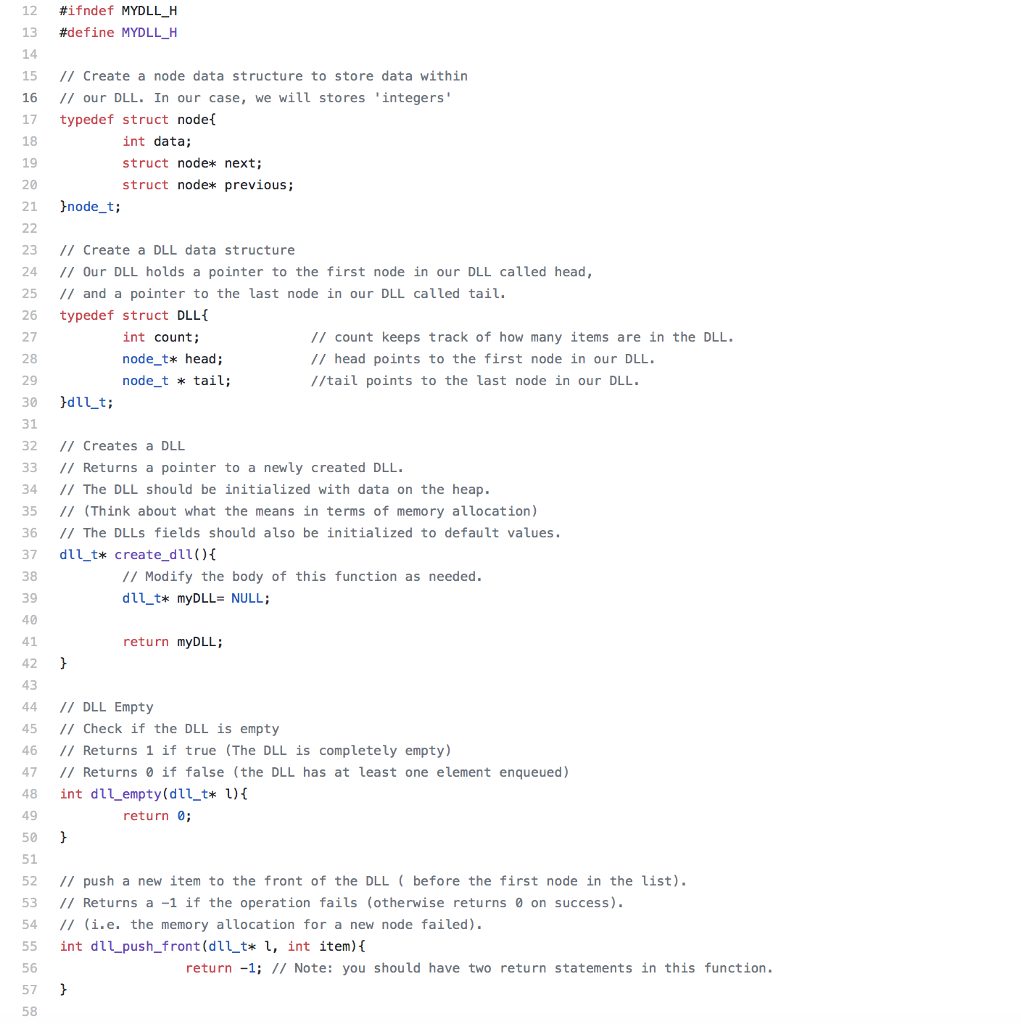


12 #ifndefMYDLLH 13 #define MYDLL_A 14 15 II Create a node data structure to store data within 16 I/ our DLL. In our case, we will stores 'integers 17 typedef struct nodet 18 19 20 21 node_t; int data; struct node* next; struct node* previous; 23 II Create a DLL data structure 24 I/Our DLL holds a pointer to the first node in our DLL called head, 25 II and a pointer to the last node in our DLL called tail. 26 typedef struct DLL 27 28 29 30 dll t; 31 32 // Creates a DLL 33 II Returns a pointer to a newly created DLL. 34 IIThe DLL should be initialized with data on the heap. 35 II (Think about what the means in terms of memory allocation) 36 I/ The DLLs fields should also be initialized to default values. 37 dll t create dll) 38 39 40 41 42 43 44// DLL Empty 45 // Check if the DLL is empty 46 I/ Returns 1 if true (The DLL is completely empty) 47 //Returns if false (the DLL has at least one element enqueued) 48 int dll empty(dll_t* ) int count; node_t* head; node t tail: // count keeps track of how many items are in the DLL. // head points to the first node in our DLL. //tail points to the last node in our DLL. // Modify the body of this function as needed dll_t* myDLL NULL; return myDLL; return 0; 50 51 52 II push a new item to the front of the DLL (before the first node in the list) 53 I/ Returns a -1 if the operation fails (otherwise returns 0 on success) 54 11 (i.e. the memory allocation for a new node failed) 55 int dll push front (dllt* 1, int item) 56 57 58 return -1; Note: you should have two return statements in this function // push a new item to the end of the DLL(after the last node in the list) /Returns a -1 if the operation fails (otherwise returns on success) // (i.e. the memory allocation for a new node failed) int dll-push, back(du.t* , int item){ return -1; // Note: you should have two return statements in this function. // Returns the first item in the DLL // Removes an item from the DLL. //Removing from an empty DLL should crash the program, call exit(1) int dllpop_front(dll t* t) return 9999999; II Note: This line is a 'filler' so the code compiles. // Returns the last item in the DLL // Removes the last item from the DLL. /Removing from an empty DLL should crash the program, call exit(1). int dll pop_back(dll_t* t)f return 9999999; // Note: This line is a 'filler' so the code compiles // Inserts a new node before the node at the specified position. // Returns a -1 if the operation fails (otherwise returns 0 on success). // (i.e. the memory allocation for a new node failed or trying to insert at a negative position or at /a position past the size of the DLL) int dllinsert (dll t* 1, int pos, int item) return -1 / Note: you should have two return statements in this function. /Returns the item at position pos starting at(ebeing the first item) // Returns-1 if the position is negative or trying to retrive an item at or past the size, /1 or the list is empty int dllget(dllt*1, int pos) return -1; // Note: you should have two return statements in this function. /Removes the item at position pos starting at0(ebeing the first item) // Returns-1 if the position is negative or trying to remove an item at or past the size, // or if the list is empty int dllremove(dll t* 1, int pos)( return -1; // Note: you should have two return statements in this function. /IDLL Size // Queries the current size of a DLL // A DLL that has not been previously created will crash the program. // (i.e. A NULL DLL cannot return the size) unsigned int dll_size(dll t* t) return 0; // Free DLL // Removes a DLL and ALL of its elements from memory. // This should be called before the proram terminates. void free_dll(dll_t* t) #endif
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


