Question: This is all that was given. 2. Consider a standard Cournot model with n firms (where the inverse demand function gives a price P =
This is all that was given.
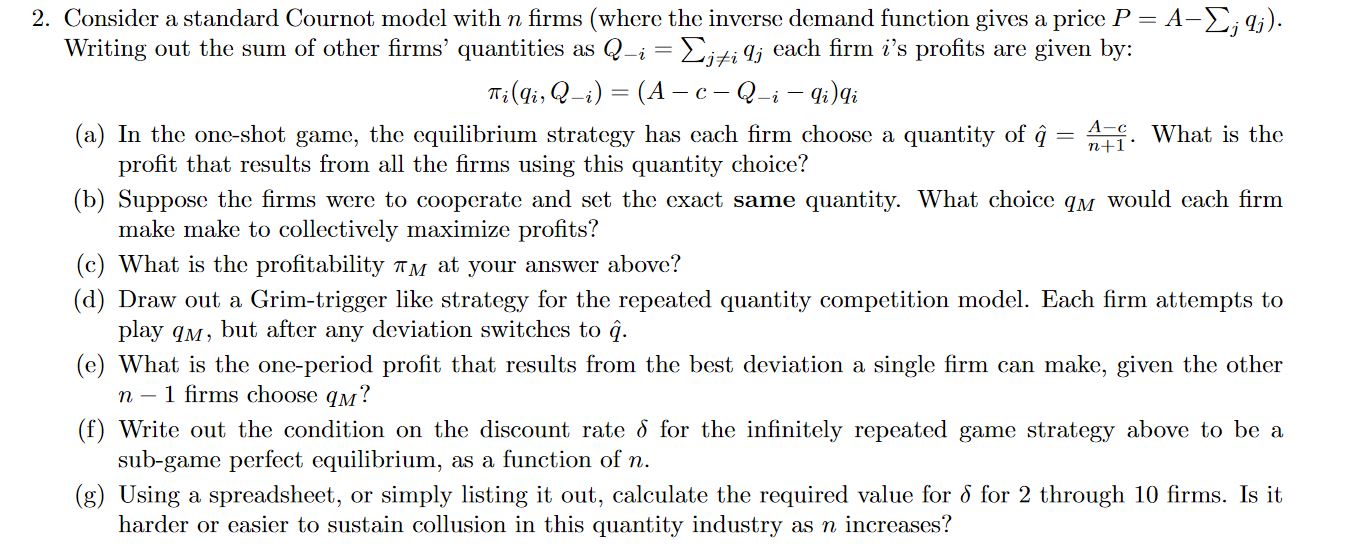
2. Consider a standard Cournot model with n firms (where the inverse demand function gives a price P = A-Z, q;). Writing out the sum of other firms' quantities as Q- = _, ; q; each firm i's profits are given by: mi(qi, Q-i) = (A -c - Q-i - qi)qi (a) In the one-shot game, the equilibrium strategy has each firm choose a quantity of q = 1. A-c. What is the profit that results from all the firms using this quantity choice? (b) Suppose the firms were to cooperate and set the exact same quantity. What choice am would each firm make make to collectively maximize profits? (c) What is the profitability TM at your answer above? (d) Draw out a Grim-trigger like strategy for the repeated quantity competition model. Each firm attempts to play qM, but after any deviation switches to q. (e) What is the one-period profit that results from the best deviation a single firm can make, given the other n - 1 firms choose qu? (f) Write out the condition on the discount rate o for the infinitely repeated game strategy above to be a sub-game perfect equilibrium, as a function of n. (g) Using a spreadsheet, or simply listing it out, calculate the required value for o for 2 through 10 firms. Is it harder or easier to sustain collusion in this quantity industry as n increases
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


