Question: This is answer, but I don't understand why, shouldn't Vt = -S in the HJM model? Where is Vtt used in the equation? Why is

This is answer, but I don't understand why, shouldn't Vt = -S in the HJM model? Where is Vtt used in the equation? Why is Vt = S(T-t)? I thought Vt(T,T) =0?
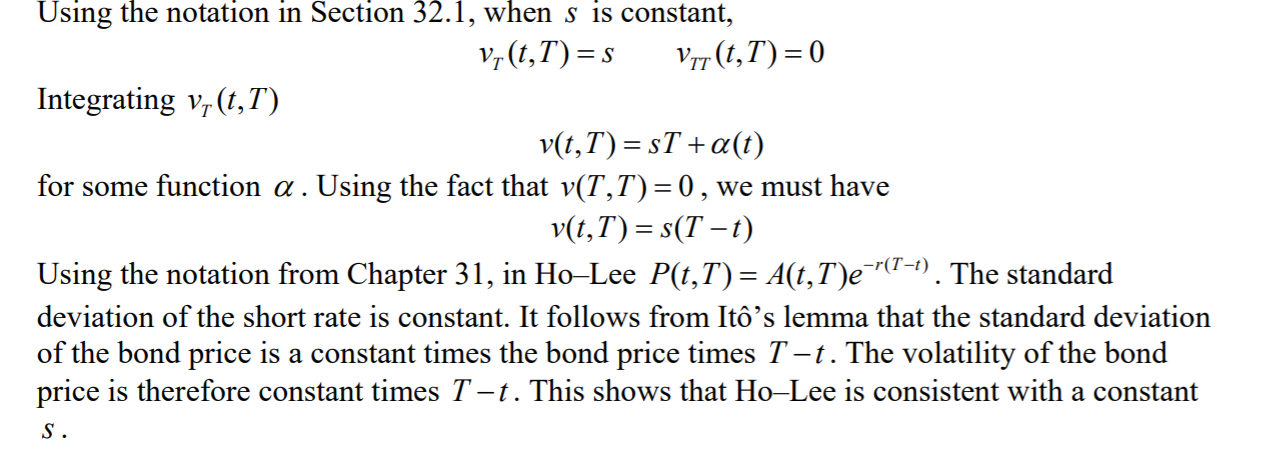
Using the notation in Section 32.1, when s is constant, v;(t,T)=s Vit,T)= 0 Integrating v;(t,T) v(t,T)= sT +a(t) for some function a . Using the fact that v(T,T)=0, we must have v(t,T) = s(T t) Using the notation from Chapter 31, in Ho-Lee P(t,T) = A(t,T)e="(T-1). The standard deviation of the short rate is constant. It follows from Ito's lemma that the standard deviation of the bond price is a constant times the bond price times T-t. The volatility of the bond price is therefore constant times T-t. This shows that Ho-Lee is consistent with a constant S. Using the notation in Section 32.1, when s is constant, v;(t,T)=s Vit,T)= 0 Integrating v;(t,T) v(t,T)= sT +a(t) for some function a . Using the fact that v(T,T)=0, we must have v(t,T) = s(T t) Using the notation from Chapter 31, in Ho-Lee P(t,T) = A(t,T)e="(T-1). The standard deviation of the short rate is constant. It follows from Ito's lemma that the standard deviation of the bond price is a constant times the bond price times T-t. The volatility of the bond price is therefore constant times T-t. This shows that Ho-Lee is consistent with a constant S
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


