Question: This is java Linear-probing distribution. Write a program, HashProbing.java, that inserts N/2 random int keys into an array of size N using the linear probing
This is java
Linear-probing distribution.
Write a program, HashProbing.java, that inserts N/2 random int keys into an array of size N using the linear probing strategy described in the context of hash tables. Note: we're not actually hashing an entry here, just imagining that we've been given the results of some hash function for N/2 elements, where the hash function is randomly distributed.
Next, we wish to compute the average cost for a search miss in the resulting partly-filled array. In other words, suppose a new element that doesn't match one of the hashed elements is given to us, and the hash function maps it to a random location in the array; how many probes will be required to recognize that this entry does not have a match? (remember: once a hashed search lands on a filled cell, it must proceed along sequential positions until it finds an empty one)
Do this for N = 103, 104, 105, 106. Discuss the extent to which your results validate Proposition M in the book (p 473): In a linear-probing hash table with M lists and N = M keys, the average number of probes (under Assumption J) required is
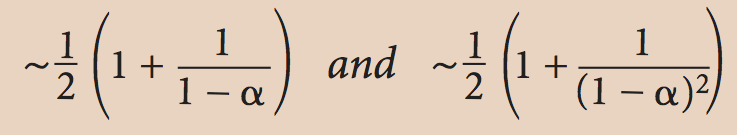
for search hits and search misses (or inserts), respectively. Capture your discussion in the README file.
and 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


