Question: This is my code currently but I'm getting several errors in CodeWarrior IDE (HCS12D Family -> MC9S12DG256B & Full chip simulation & Absolute Assembly) o
This is my code currently but I'm getting several errors in CodeWarrior IDE (HCS12D Family -> MC9S12DG256B & Full chip simulation & Absolute Assembly)
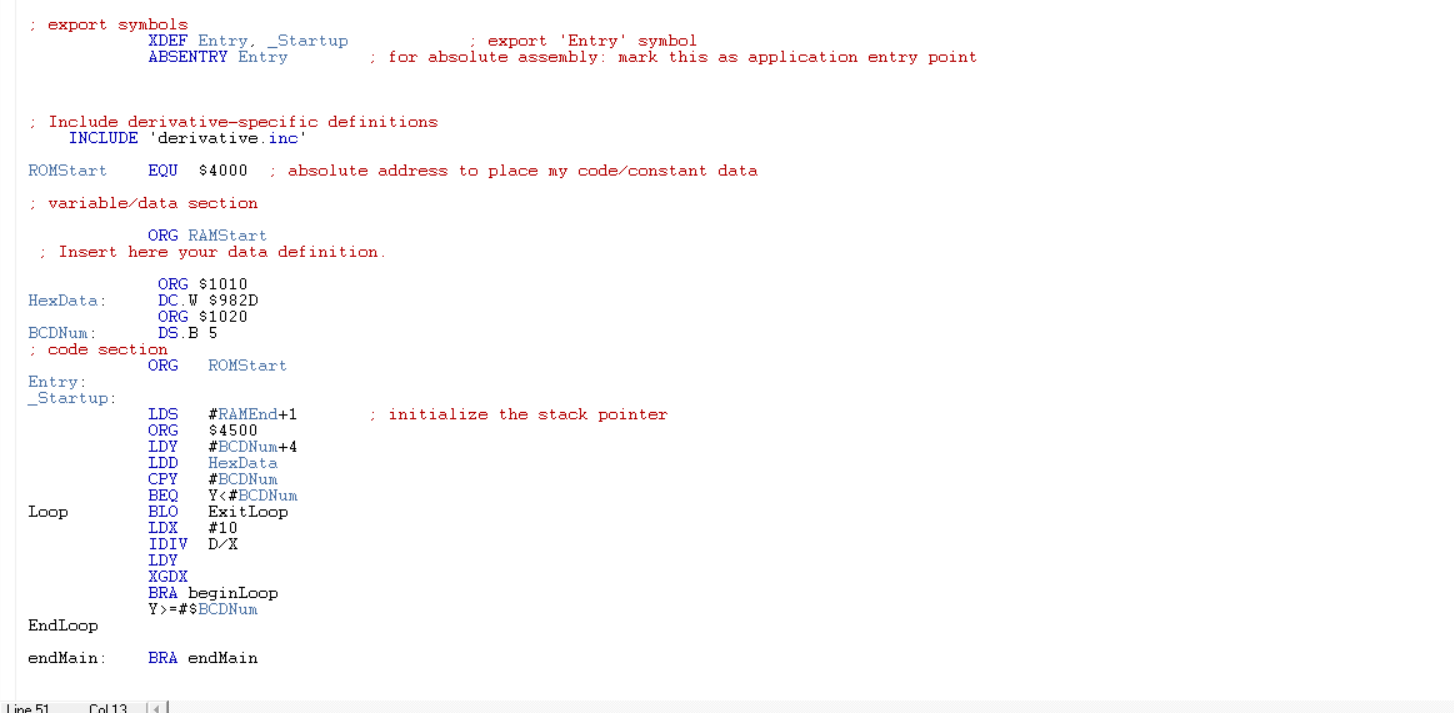
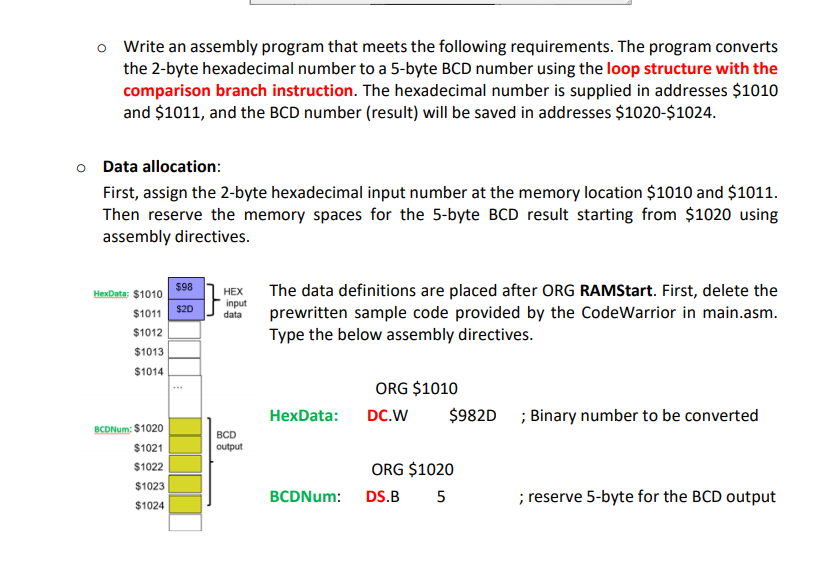
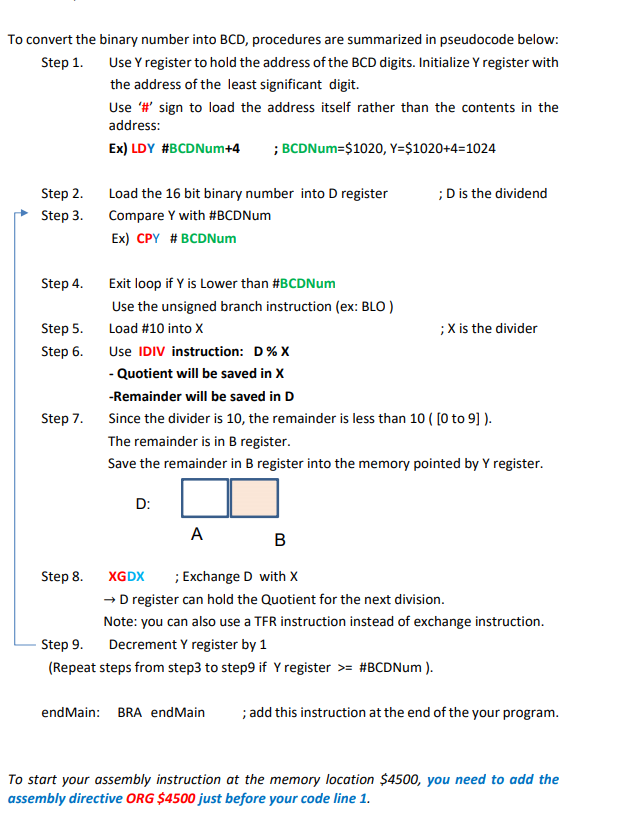
o Write an assembly program that meets the following requirements. The program converts the 2-byte hexadecimal number to a 5-byte BCD number using the loop structure with the comparison branch instruction. The hexadecimal number is supplied in addresses $1010 and $1011, and the BCD number (result) will be saved in addresses $1020-$1024. o Data allocation: First, assign the 2-byte hexadecimal input number at the memory location $1010 and $1011. Then reserve the memory spaces for the 5-byte BCD result starting from $1020 using assembly directives. HexData: $1010 598 HEX input data $1011 $20 The data definitions are placed after ORG RAMStart. First, delete the prewritten sample code provided by the CodeWarrior in main.asm. Type the below assembly directives. $1012 $1013 $1014 ORG $1010 DC.W. $982D HexData: ;Binary number to be converted BCD output BCDNum: $1020 $1021 $1022 $1023 $1024 ORG $1020 DS.B 5 BCDNum: ; reserve 5-byte for the BCD output To convert the binary number into BCD, procedures are summarized in pseudocode below: Step 1. Use Y register to hold the address of the BCD digits. Initialize Y register with the address of the least significant digit. Use '#' sign to load the address itself rather than the contents in the address: Ex) LDY #BCDNum+4 ; BCDNum=$1020, Y=$1020+4=1024 ;D is the dividend Step 2. Step 3. Load the 16 bit binary number into D register Compare Y with #BCDNum Ex) CPY #BCDNum Step 4. Step 5. Step 6. Exit loop if Y is lower than #BCDNum Use the unsigned branch instruction (ex: BLO) Load #10 into X ;X is the divider Use IDIV instruction: D% - Quotient will be saved in X -Remainder will be saved in D Since the divider is 10, the remainder is less than 10 ( [0 to 9] ). The remainder is in B register. Save the remainder in B register into the memory pointed by Y register. Step 7. D: A B Step 8. XGDX ; Exchange D with X Dregister can hold the Quotient for the next division. Note: you can also use a TFR instruction instead of exchange instruction. Step 9. Decrement Y register by 1 (Repeat steps from step3 to step9 if y register >= #BCDNum ). end Main: BRA end Main ; add this instruction at the end of the your program. To start your assembly instruction at the memory location $4500, you need to add the assembly directive ORG $4500 just before your code line 1. ; export symbols XDEF Entry, _Startup ABSENTRY Entry export 'Entry' symbol ; for absolute assembly: mark this as application entry point ; Include derivative-specific definitions INCLUDE 'derivative.inc ROMStart EQU $4000 absolute address to place my code/constant data ; variable data section ORG RAMStart Insert here your data definition : initialize the stack pointer ORG $1010 HexData: DC. W $982D ORG $1020 BCDNum: DS.B 5 ; code section ORG ROMStart Entry: _Startup: LDS #RAMEnd+1 ORG $4500 LDY #BCDNM+4 LDD HexData CPY #BCDNM BEQ Y=#$BCDN EndLoop endMain: BRA endMain line 51 Col13
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


