Question: This is my Java assignment using NetBeans but it isn't working. Could anyone show me the whole process? Thank you in advance! Given that your
This is my Java assignment using NetBeans but it isn't working. Could anyone show me the whole process? Thank you in advance!

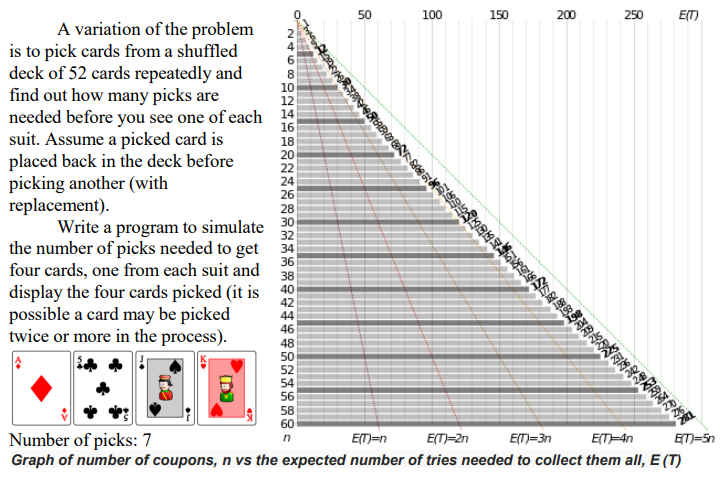
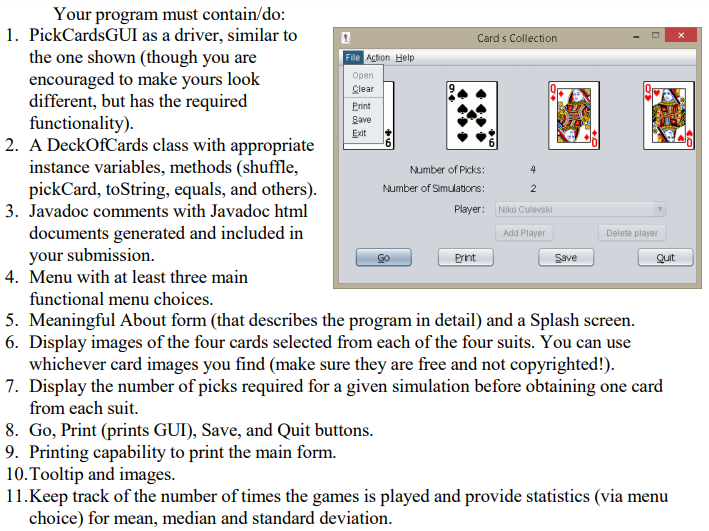


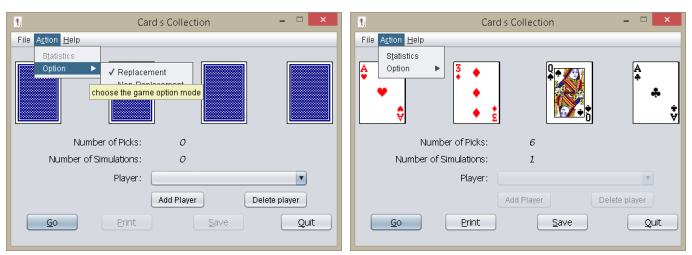
Given that your GUI resembles the given one, follow these guidelines:



From Wiki In probability theory, the coupon collector's problem describes the "collect all coupons and win" contests. It asks the following question: Suppose that there is an urn ofn different coupons, from which coupons are being collected, equally likely, with replacement. What is the probability that more than t sample trials are needed to collect all n coupons? An alternative statement is: Given n coupons, how many coupons do you expect you need to draw with replacement before having drawn each coupon at least once? For example, when n-50 it takes about 225 trials to collect all 50 coupons. The key to solving the problem is understanding that it takes very little time to collect the first few coupons. On the other hand, it takes a long time to collect the last few coupons. In fact, for 50 coupons, it takes on average 50 trials to collect the very last coupon after the other 49 coupons have been collected. This is why the expected time to collect all coupons is much longer than 50. The idea now is to split the total time into 50 intervals where the expected time can be calculated. [https:/len.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coupon collector%27s_problem] From Wiki In probability theory, the coupon collector's problem describes the "collect all coupons and win" contests. It asks the following question: Suppose that there is an urn ofn different coupons, from which coupons are being collected, equally likely, with replacement. What is the probability that more than t sample trials are needed to collect all n coupons? An alternative statement is: Given n coupons, how many coupons do you expect you need to draw with replacement before having drawn each coupon at least once? For example, when n-50 it takes about 225 trials to collect all 50 coupons. The key to solving the problem is understanding that it takes very little time to collect the first few coupons. On the other hand, it takes a long time to collect the last few coupons. In fact, for 50 coupons, it takes on average 50 trials to collect the very last coupon after the other 49 coupons have been collected. This is why the expected time to collect all coupons is much longer than 50. The idea now is to split the total time into 50 intervals where the expected time can be calculated. [https:/len.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coupon collector%27s_problem]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


