Question: This is the answer if you can just show your work please and thank you 6.14 Example 6.8 examined the slow, steady release of a


This is the answer if you can just show your work please and thank you
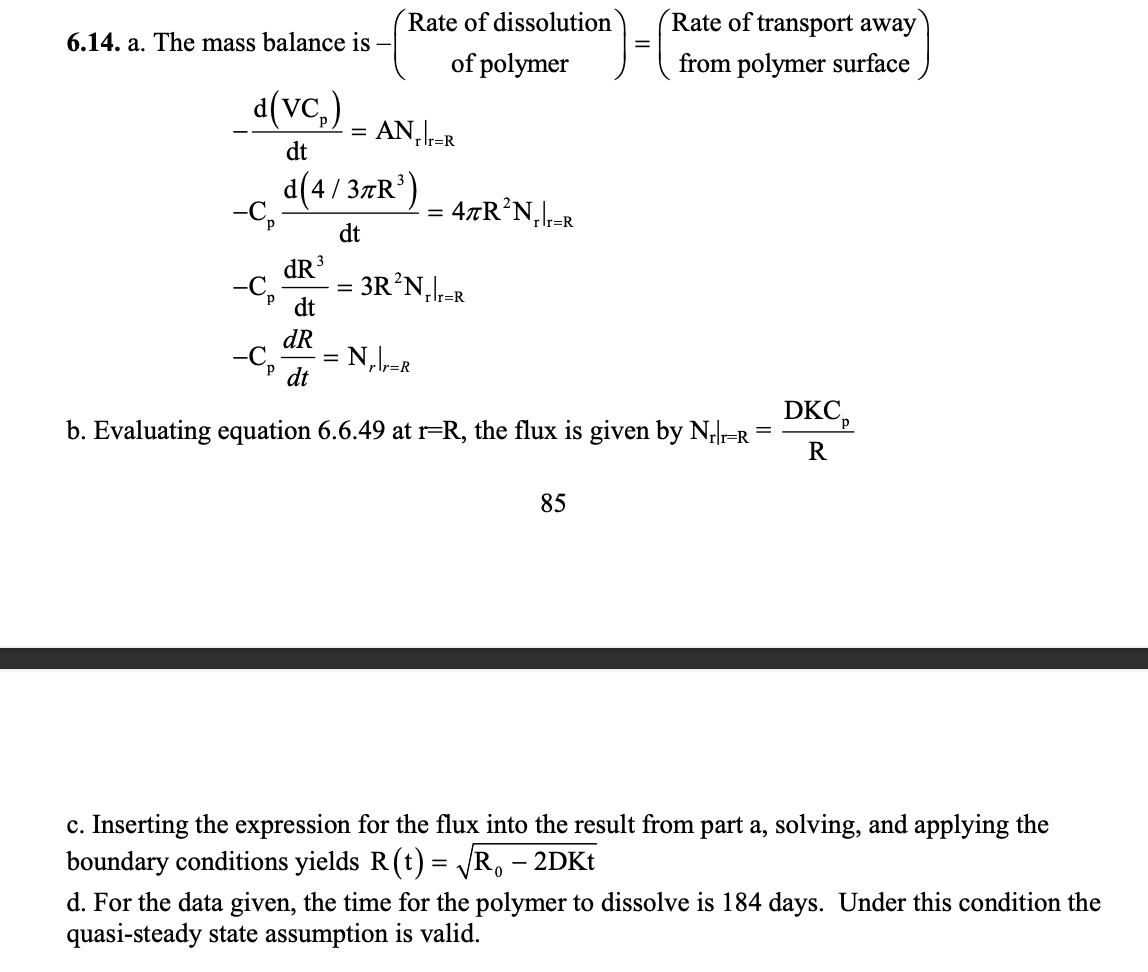
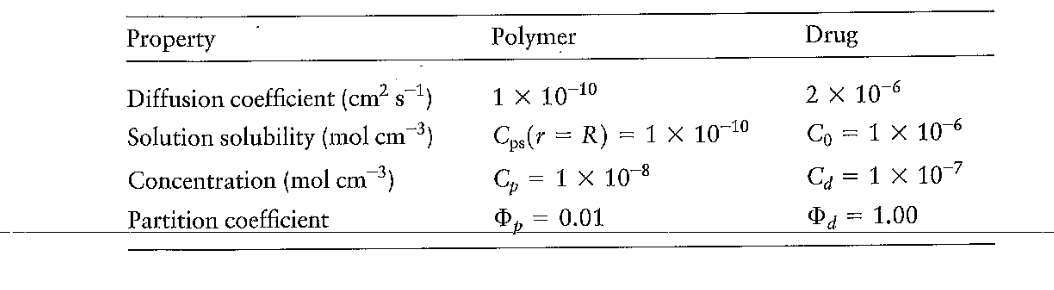
6.14 Example 6.8 examined the slow, steady release of a drug from a polymer. The erosion of the polymer was neglected, on the grounds that polymer erosion is slow relative to the rate of transport of the drug. We can test this assumption quantitatively by using the following model for erosion: Erosion results from the polymer dissolving in the solvent and drug leaves the polymer as a result of erosion. Assume that the rate of polymer erosion at the surface equals the rate of diffusion of the polymer from the surface. (a) Show that a material balance leads to the following relation for the polymer: CpdtdR3=3R2Nprr=R. Cp is the polymer concentration in the undissolved state. (b) Determine the flux, assuming steady-state diffusion of the polymer away from the surface. The concentration of polymer in solution Cps is Cps(r=R)=pCp where p is the polymer partition coefficient. (c) Use the solution from part (b) to solve Equation (6.12.4) and find R(t) for t=0,r=R0. (d) The initial radius of the polymer is 0.25cm. Use the table at the top of next page to determine the validity of the quasi-steady-state assumption, and determine how long it takes for the polymer to dissolve. \begin{tabular}{lll} \hline Property & Polymer & Drug \\ \hline Diffusion coefficient (cm2s1) & 11010 & 2106 \\ Solution solubility (molcm3) & Cps(r=R)=11010 & C0=1106 \\ Concentration (molcm3) & Cp=1108 & Cd=1107 \\ Partition coefficient & p=0.01 & d=1.00 \end{tabular} 6.14. a. The mass balance is (Rateofdissolutionofpolymer)=(Rateoftransportawayfrompolymersurface) dtd(VCp)=ANrr=RCpdtd(4/3R3)=4R2Nrr=RCpdtdR3=3R2Nrr=RCpdtdR=Nrr=R b. Evaluating equation 6.6 .49 at r=R, the flux is given by Nrr=R=RDKCp 85 c. Inserting the expression for the flux into the result from part a, solving, and applying the boundary conditions yields R(t)=R02DKt d. For the data given, the time for the polymer to dissolve is 184 days. Under this condition the quasi-steady state assumption is valid. 6.14 Example 6.8 examined the slow, steady release of a drug from a polymer. The erosion of the polymer was neglected, on the grounds that polymer erosion is slow relative to the rate of transport of the drug. We can test this assumption quantitatively by using the following model for erosion: Erosion results from the polymer dissolving in the solvent and drug leaves the polymer as a result of erosion. Assume that the rate of polymer erosion at the surface equals the rate of diffusion of the polymer from the surface. (a) Show that a material balance leads to the following relation for the polymer: CpdtdR3=3R2Nprr=R. Cp is the polymer concentration in the undissolved state. (b) Determine the flux, assuming steady-state diffusion of the polymer away from the surface. The concentration of polymer in solution Cps is Cps(r=R)=pCp where p is the polymer partition coefficient. (c) Use the solution from part (b) to solve Equation (6.12.4) and find R(t) for t=0,r=R0. (d) The initial radius of the polymer is 0.25cm. Use the table at the top of next page to determine the validity of the quasi-steady-state assumption, and determine how long it takes for the polymer to dissolve. \begin{tabular}{lll} \hline Property & Polymer & Drug \\ \hline Diffusion coefficient (cm2s1) & 11010 & 2106 \\ Solution solubility (molcm3) & Cps(r=R)=11010 & C0=1106 \\ Concentration (molcm3) & Cp=1108 & Cd=1107 \\ Partition coefficient & p=0.01 & d=1.00 \end{tabular} 6.14. a. The mass balance is (Rateofdissolutionofpolymer)=(Rateoftransportawayfrompolymersurface) dtd(VCp)=ANrr=RCpdtd(4/3R3)=4R2Nrr=RCpdtdR3=3R2Nrr=RCpdtdR=Nrr=R b. Evaluating equation 6.6 .49 at r=R, the flux is given by Nrr=R=RDKCp 85 c. Inserting the expression for the flux into the result from part a, solving, and applying the boundary conditions yields R(t)=R02DKt d. For the data given, the time for the polymer to dissolve is 184 days. Under this condition the quasi-steady state assumption is valid
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


