Question: This is the example code: f_x (1/2)*(1/sqrt(2*pi))*exp(-(x-1)^(2)/2) + (1/2)*(1/sqrt(2*pi))*exp(-(x-3)^(2)/2) } n x # proposal distribution # normal distribution with mean at current point (symmetric) #
This is the example code:
f_x
(1/2)*(1/sqrt(2*pi))*exp(-(x-1)^(2)/2) + (1/2)*(1/sqrt(2*pi))*exp(-(x-3)^(2)/2)
}
n
x
# proposal distribution
# normal distribution with mean at current point (symmetric)
# the function sampling new point from the proposal distribution
q
rnorm(1, mean = x, sd = 1)
}
# initial value
x[1]
for(i in 1:(n-1)){
# pick new sample
xp
# acceptance probability
alpha
# accept new point with probability alpha
if (runif(1)
x[i+1]
}
else{
x[i+1]
}
}
and this is what I have written:
n
x
f_x
x/4*exp(-x^2/8)
}
q
rgamma(1, x, rate = 1)
}
Not sure where to go from here, thanks
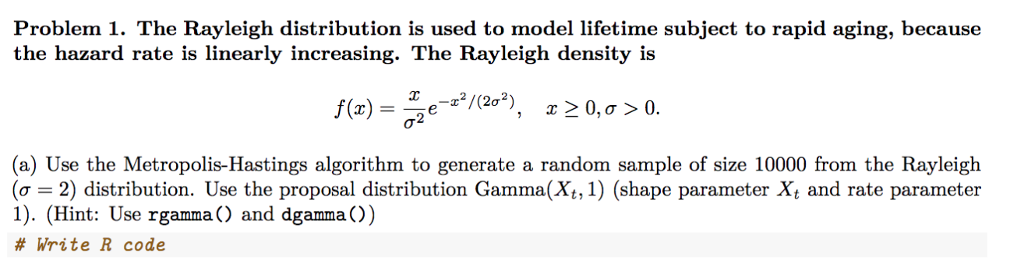
Problem 1. The Rayleigh distribution is used to model lifetime subject to rapid aging, because the hazard rate is linearly increasing. The Rayleigh density is f(x) = 2e 120, > 0 (a) Use the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm to generate a random sample of size 10000 from the Rayleigh ( = 2) distribution. Use the proposal distribution Gamma(, 1) (shape parameter Xt and rate parameter 1). (Hint: Use rgamma () and dgamma () # Write R code Problem 1. The Rayleigh distribution is used to model lifetime subject to rapid aging, because the hazard rate is linearly increasing. The Rayleigh density is f(x) = 2e 120, > 0 (a) Use the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm to generate a random sample of size 10000 from the Rayleigh ( = 2) distribution. Use the proposal distribution Gamma(, 1) (shape parameter Xt and rate parameter 1). (Hint: Use rgamma () and dgamma () # Write R code
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


