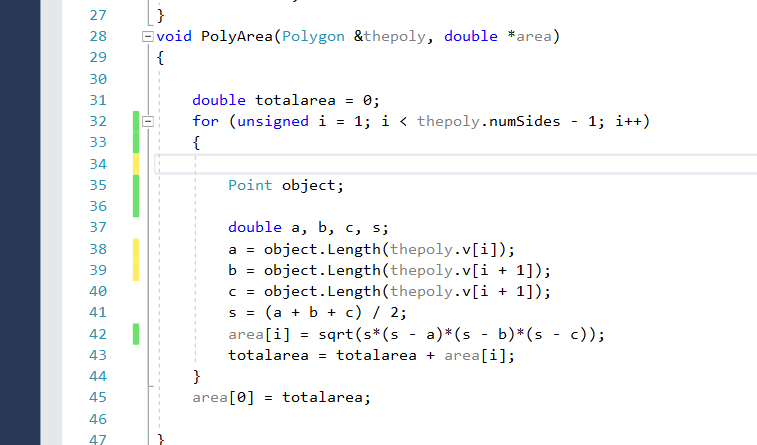
Question: This is the PolyArea function, I don't understand why the values are wrong. I used Point Object to access the 'Length function' of the class
This is the PolyArea function, I don't understand why the values are wrong. I used Point Object to access the 'Length function' of the class 'Point'. But I'm really clueless. I'm attaching the error part of .h and .cpp screenshots which only includes the function definition, function call.
This is the class definition of the class POINT.

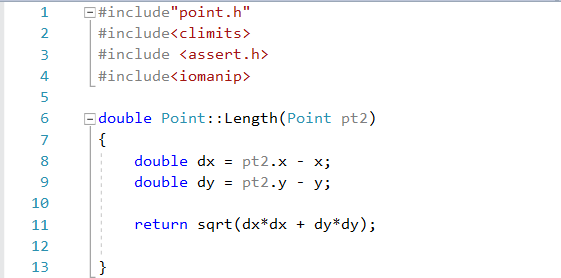
POINT.CPP file which defines the length function.
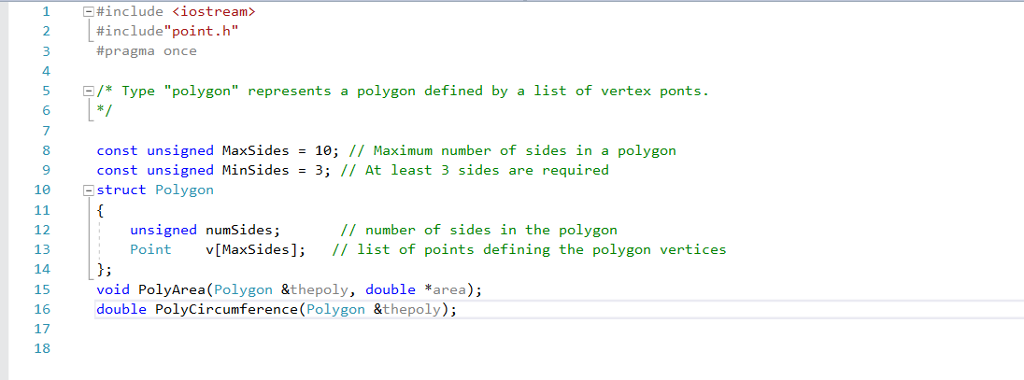
Struct Polygon.
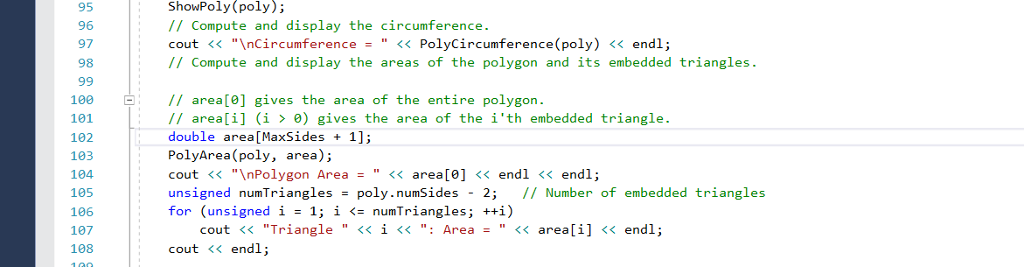
The main program calling the function.
Sample Run

polygon.cpp code:
double PolyCircumference(Polygon &thepoly)
{
double circ = 0;
for (unsigned i = 0; i
{
Point pt1 = thepoly.v[i];
Point pt2 = thepoly.v[(i + 1) % thepoly.numSides];
circ += pt1.Length(pt2);
}
return circ;
}
void PolyArea(Polygon &thepoly, double *area)
{
double totalarea = 0;
for (unsigned i = 1; i
{
Point object;
double a, b, c, s;
a = thepoly.v[0].Length(thepoly.v[i]);
b = thepoly.v[i].Length(thepoly.v[i + 1]);
c = thepoly.v[0].Length(thepoly.v[i + 1]);
s = (a + b + c) / 2;
area[i] = sqrt(s*(s - a)*(s - b)*(s - c));
totalarea = totalarea + area[i];
}
area[0] = totalarea;
}
point.cpp code:
#include"point.h"
#include
#include
#include
double Point::Length(Point pt2)
{
double dx = pt2.x - x;
double dy = pt2.y - y;
return sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy);
}
void Point::Get(istream &is)
{
defined = false;
if (is.peek() != ' ')
{
is >> x >> y;
defined = true;
}
is.ignore(INT_MAX, ' ');
return;
}
void Point::Show(ostream &os)
{
assert(defined);
os
}
double Point::Y()
{
assert(defined);
return y;
}
double Point::X()
{
assert(defined);
return x;
}
bool Point::Defined()
{
return defined;
}
void Point::Set(double xVal, double yVal)
{
cout
}
Point::Point()
{
defined = false;
}
Point::Point(double xVal, double yVal)
{
Set(xVal, yVal);
}
point.h code:
/* Type "point" represents the location of a point in cartesian coordinates.*/
#include
#pragma once
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
// Default constructor: mark point undefined
Point();
// Explicit constructor: Intitalize the x and y corrdinates
Point(double xVal, double yVal);
//Accessor Functions
double X(); // Returns the value of the x coordinate
double Y(); // Returns the value of the y coordinate
bool Defined(); // Returns the Boolean member defined
// Mustor: Assign values to the x and y coordinates of the point.
void Set(double xVa1, double yVa1);
// Returns the legth of the line from the calling point to pt2
double Length(Point pt2);
// Input- Output
void Get(istream &is = cin); // Read the x and y coordinates of the point from the keyboard.
void Show(ostream &os = cout); // Display the x and y coordinates of the point on the screen.
private:
double x; // x coordinate value
double y; // y coordinate value
bool defined; // true if this point has been defiend; otherwise false
};
polygon.h code:
#include
#include"point.h"
#pragma once
/* Type "polygon" represents a polygon defined by a list of vertex ponts.
*/
const unsigned MaxSides = 10; // Maximum number of sides in a polygon
const unsigned MinSides = 3; // At least 3 sides are required
struct Polygon
{
unsigned numSides; // number of sides in the polygon
Point v[MaxSides]; // list of points defining the polygon vertices
};
void PolyArea(Polygon &thepoly, double *area);
double PolyCircumference(Polygon &thepoly);
proram main.cpp code:
#include
using namespace std;
#include "Point.h"
#include "Polygon.h"
/*--------------- S h o w P o l y ( ) ----------
PURPOSE: Display a polygon.
INPUT PARAMETERS:
p -- the polygon to be displayed.
*/
void ShowPoly(Polygon &p)
{
// Show all of the polygon's vertexes.
for (unsigned i = 0; i
{
// Get the next point and display it.
Point nextPt = p.v[i];
nextPt.Show(cout);
cout
}
}
//--------------- m a i n ( ) ---------------
int main()
{
Polygon poly; // The polygon definition
// Start out with zero polygon sides.
poly.numSides = 0;
// Read in a polygon definition. If a valid polygon was entered,
// display its circumference and area; otherwise display an
// error message and terminate execution.
cout
for (;;)
{
// Read in the next point
cout
Point nextPt;
nextPt.Get(cin);
if (!nextPt.Defined())
break;
poly.v[poly.numSides] = nextPt;
// Update the ploygon size.
++poly.numSides;
// If the polygon is full, say so and stop taking input.
if (poly.numSides >= MaxSides - 1)
{
cout
break;
}
}
// Make sure that the polygon is valid.
if (poly.numSides
{
cout
return 0;
}
// The definition is valid, show the definition.
cout
ShowPoly(poly);
// Compute and display the circumference.
cout
// Compute and display the areas of the polygon and its embedded triangles.
// area[0] gives the area of the entire polygon.
// area[i] (i > 0) gives the area of the i'th embedded triangle.
double area[MaxSides + 1];
PolyArea(poly, area);
cout
unsigned numTriangles = poly.numSides - 2; // Number of embedded triangles
for (unsigned i = 1; i
cout
cout
// Add one more point to the polygon.
cout
double x; // x and y coordinates of extra point
double y;
// Read in the x and y coordinates.
cin >> x >> y;
// Use the Point constructor function to combine x and y.
Point newPt(x, y);
// Use the Point accessors to display the x and y coordinates of the added point.
cout
// Append the new point to the polygon.
poly.v[poly.numSides++] = newPt;
// Make sure that the polygon is valid.
if (poly.numSides
{
cout
return 0;
}
// The definition is valid, show the definition.
cout
ShowPoly(poly);
// Compute and display the circumference.
cout
// Compute and display the areas of the polygon and its embedded triangles.
PolyArea(poly, area);
cout
numTriangles = poly.numSides - 2; // Number of embedded triangles
for (unsigned i = 1; i
cout
cout
return 0;
}
27 28 void PolyArea (Polygon &thepoly, double *area) 29 30 31 32 E: for (unsigned 1-1;
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


