Question: This is the slide 2 and 3 above this is slide from 9 to 12 above this is the slide above for questions 4 please


This is the slide 2 and 3 above


this is slide from 9 to 12 above



this is the slide above for questions 4
please take time and answer them correctly promise you like
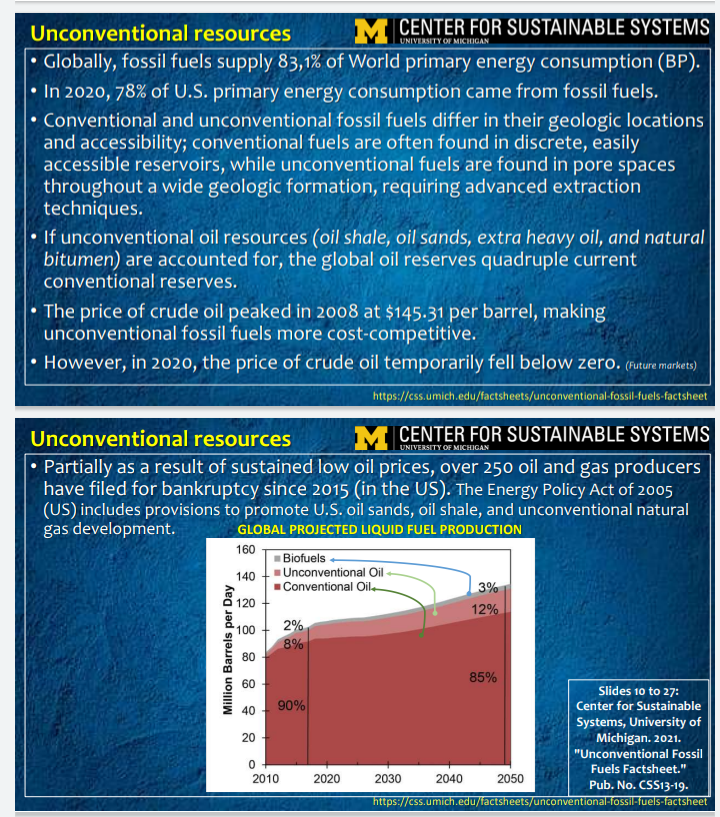
1. a) How are the "Unconventional oil and gas differentiated from conventional hydr ocarbon resources? Based on which factors? Read the information given in slides 2 and 3 and then with your own words, explain the basic differences between conventio nal and unconventional oil and gas (deposits). (10 points) About Unconventional Energy Resources http://www.unconventionalenergyresources.com/ Unconventional oil and gas is differentiated from conventional hydrocarbon resources based on the state of the hydrocarbon, nature of the geologic reservoirs and the types of technologies required to extract the hydrocarbon. Conventional oil and gas deposits have a well-defined areal extent, the reservoirs are porous and permeable, the hydrocarbon is produced easily through a wellbore, and reservoirs generally do not require extensive well stimulation to produce. Unconventional hydrocarbon deposits are very diverse and difficult to characterize overall, but in general are often lower in resource concentration, dispersed over large areas, and require well stimulation or additional extraction or conversion technology. They also are often more expensive to develop per unit of energy and require a higher price to be economic. About Unconventional Energy Resources http://www.unconventionalenergyresources.com/ Research and investment into unconventional resources has increased significantly over the last two decades due to the higher price environment for oil and natural gas. In several cases, the technologies for economic production have already been developed, while in other cases, the resources are still in the research stage. What has qualified as "unconventional" is a complex and changing interplay of resource characteristics, the available exploration and production technologies and the current economic environment. For example through the use of technology, oil resources such as the Bakken have been converted from previously uneconomic unconventional oil into proved reserves and production. The resources of the Bakken Formation are defined by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) as unconventional "continuous-type" oil resources. 2. Explain what "unconventional oil" is in detail using the informaton given in slides # 9 to 12. (10 points) Unconventional resources https://energyeducation.ca/encyclopedia/Unconventional_resource Because of this, new technologies are constantly being introduced that allows for the more economic extraction of non-traditional oil and gas that may have been previously impossible to obtain. Development of these unconventional resources has significant economic potential as a large portion of oil and gas resources is estimated to exist in unconventional deposits. Unconventional Oil Unconventional oil is a very specific type of petroleum obtained by methods that are different from the extraction technique of using a traditional well. This type of oil is seen as being more costly and difficult to extract and refine, as well as being more environmentally harmful. In general, unconventional oil is heavier and requires more processing and upgrading. . . Unconventional resources https://energyeducation.ca/encyclopedia/Unconventional_resource Unconventional oil includes shale oil, oil sands and extra-heavy oil (natural bitumen deposits). Although it is more difficult and costly to extract unconventional oil, it is becoming more common as the demand for oil is increasing and more research is being done to see how unconventional oil can be made more simple and cost-effective to produce. Unconventional OIL Resources Bitumen soaked sandstone Oil shale Unconventional resources M CENTER FOR SUSTAINABLE SYSTEMS Globally, fossil fuels supply 83,1% of World primary energy consumption (BP). In 2020,78% of U.S. primary energy consumption came from fossil fuels. Conventional and unconventional fossil fuels differ in their geologic locations and accessibility; conventional fuels are often found in discrete, easily accessible reservoirs, while unconventional fuels are found in pore spaces throughout a wide geologic formation, requiring advanced extraction techniques. If unconventional oil resources (oil shale, oil sands, extra heavy oil, and natural bitumen) are accounted for, the global oil reserves quadruple current conventional reserves. The price of crude oil peaked in 2008 at $145.31 per barrel, making unconventional fossil fuels more cost-competitive. However, in 2020, the price of crude oil temporarily fell below zero. (Future markets) https://css.umich.edu/factsheets/unconventional-fossil fuels-factsheet Unconventional resources M CENTER FOR SUSTAINABLE SYSTEMS Partially as a result of sustained low oil prices, over 250 oil and gas producers have filed for bankruptcy since 2015 (in the US). The Energy Policy Act of 2005 (US) includes provisions to promote U.S. oil sands, oil shale, and unconventional natural gas development. GLOBAL PROJECTED LIQUID FUEL PRODUCTION 160 Biofuels 140 Unconventional Oil Conventional Oil 3% 12% 2% 120 100 Million Barrels per Day 8% 80 60 40 90% 20 85% Slides 10 to 27: Center for Sustainable Systems, University of Michigan. 2021. "Unconventional Fossil Fuels Factsheet." 2030 2040 2050 Pub. No. CSS13-19. https://css.umich.edu/factsheets/unconventional-fossil-fuels-factsheet 0 2010 2020 4. LIFE CYCLE IMPACTS" for Major Unconventional Sources are explained in abovet he referred file. 4. a) Explain in detail the life cycle "Green House Gas impacts from major unconvent ional Sources. (10 points) 4.b) Explain in detail the life cycle "WATER related impacts from major unconventio nal Sources (10 points) MAJOR UNCONVENTIONAL SOURCES M CENTER FOR SUSTAINABLE SYSTEMS LIFE CYCLE IMPACTS GREENHOUSE GASES Fossil fuel combustion accounted for 74% of U.S. greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2019. Equivalent amounts of GHGs are released by conventional and unconventional fuels at the point of use. Life cycle emissions for unconventional oil are higher than conventional oil on average, though some studies suggest they are similar. Studies have found life cycle emissions for oil sands are 17% higher than average refined U.S. crude, and oil shale emissions are 21% to 47% higher than conventional oil. Studies of life cycle emissions for UG have resulted in estimates from 6% lower to 43% higher than conventional natural gas sources. https://css.umich.edu/factsheets/unconventional-fossil-fuels-factsheet . MAJOR UNCONVENTIONAL SOURCES M CENTER FOR SUSTAINABLE SYSTEMS LIFE CYCLE IMPACTS GREENHOUSE GASES ... continues ... Overall, natural gas generates fewer GHG emissions when combusted than other fossil fuels. Natural gas is primarily methane (CH4) and CH4 leakage can significantly decrease any emissions benefit of natural gas over other fossil fuels. CH4 leakage from the U.S. oil and natural gas supply chain is estimated to be 13 million metric tons (MMT) per year, equivalent to 2.3% of U.S. annual gross natural gas production and nearly 42% of U.S. anthropogenic CH4 emissions. https://css.umich.edu/factsheets/unconventional-fossil-fuels-factsheet MAJOR UNCONVENTIONAL SOURCES M CENTER FOR SUSTAINABLE SYSTEMS LIFE CYCLE IMPACTS WATER Producing one barrel of oil from oil shale uses 1 to 12 barrels of water for in situ production and 2 to 4 barrels of water for mining production; one barrel of oil from oil sands uses 0.4 to 3.1 barrels of water. Producing one barrel of oil in Saudi Arabia requires 1.4 barrels of water. A horizontal gas well can require 2 to 4 million gallons of water to drill and fracture. One study found shale gas production consumes up to four times more water than producing conventional natural gas. CBM production requires groundwater extraction; U.S. CBM basins withdraw 32 million to 15 billion gallons of water from aquifers per year. 1 US gallon = 3.78541178 liter https://css.umich.edu/tactsheets/unconventional-fossil-fuels-factsheet MAJOR UNCONVENTIONAL SOURCES M CENTER FOR SUSTAINABLE SYSTEMS LIFE CYCLE IMPACTS WATER.. continues ... Wastewater, produced water, and flowback water from oil and gas extraction can contain excess salts, high levels of trace elements, and naturally occurring radioactive materials. Groundwater can be polluted through above and below.ground activities, including construction, drilling, chemical spills, leaks, and discharge of wastewater. https://css.umich.edu/factsheets/unconventional-fossil-fuels-factsheetStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


